Erasmus Darwin facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Erasmus Darwin
|
|
|---|---|

Erasmus Darwin c. 1792–1793, oil painting by Joseph Wright of Derby, Derby Museum and Art Gallery
|
|
| Born |
Erasmus Robert Darwin
12 December 1731 |
| Died | 18 April 1802 (aged 70) Breadsall, Derby, England
|
| Resting place | All Saints Church, Breadsall |
| Alma mater | |
| Children | 14 |
| Parent(s) |
|
| Relatives | See Darwin–Wedgwood family |
Erasmus Robert Darwin (born December 12, 1731 – died April 18, 1802) was an amazing English doctor and thinker. He was a very important person during a time called the Midlands Enlightenment. This was a period when many smart people in the Midlands of England shared new ideas.
Erasmus Darwin was not just a doctor. He was also a natural philosopher (someone who studied nature and science), a physiologist (who studied how living things work), and an abolitionist. This means he worked to end the slave trade.
He was also an inventor and a poet. His poems often talked about natural history and even hinted at the idea of evolution. This is the idea that all living things are connected and change over time.
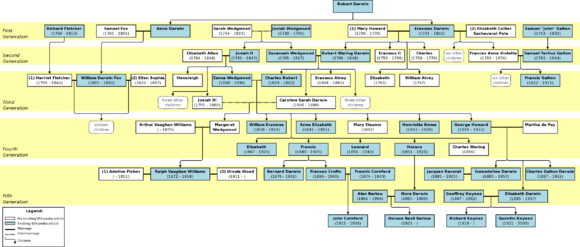
Erasmus Darwin was part of the famous Darwin–Wedgwood family. His grandsons include Charles Darwin, who developed the theory of evolution, and Francis Galton, another important scientist.
He helped start the Lunar Society of Birmingham. This was a group of leading thinkers, inventors, and business people who met to discuss new ideas. He even turned down an offer from King George III to be the Royal Doctor!
Contents
Early Life and Learning
Erasmus Darwin was born in 1731 at Elston Hall in Nottinghamshire, England. He was the youngest of seven children. His father, Robert Darwin of Elston, was a lawyer and doctor.
He went to Chesterfield Grammar School. Later, he studied at St John's College at Cambridge University. He then studied medicine at the University of Edinburgh Medical School.
In 1756, Darwin started working as a doctor in Nottingham. He didn't have much success there at first. So, the next year, he moved to Lichfield to try again.
Soon after arriving in Lichfield, he helped a young fisherman who was very sick. Darwin used a new treatment, and the fisherman got better. This made Darwin famous in the area, and he became a very successful doctor for over 50 years.
While in Lichfield, Darwin wrote poems and worked on his ideas about evolution. He also invented many things. These included a steering system for carriages and a machine that could copy documents.
Family Life
Erasmus Darwin married twice and had a large family with 14 children.
In 1757, he married Mary Howard. They had five children together. Sadly, two of them died when they were very young.
- Charles Darwin (1758–1778)
- Erasmus Darwin Jr (1759–1799)
- Robert Waring Darwin (1766–1848), who was the father of the famous naturalist Charles Darwin.
Mary Darwin passed away in 1770. Later, in 1775, Darwin met Elizabeth Pole. She was married at the time, but after her husband died, Darwin married her. They moved to her home, Radbourne Hall, near Derby.
In 1782, they moved to Derby. They had seven children together, though one died as a baby.
- Frances Ann Violetta Darwin (1783–1874), who became the mother of Francis Galton.
- Sir Francis Sacheverel Darwin (1786–1859).
- Revd. John Darwin (1787–1818).
People described Darwin as being of average height and a bit heavy. He was known for being a bit messy in his clothes and how he walked.
Later Years and Passing
Erasmus Darwin passed away suddenly on April 18, 1802. He had just moved to Breadsall Priory, north of Derby. He had been sick with chest and lung problems in the years before.
His body is buried at All Saints' Church, Breadsall. Today, a special monument in Birmingham called a "Moonstone" remembers him and his work with the Lunar Society.
Important Writings
Botanical Works
Darwin helped create 'A Botanical Society, at Lichfield'. This small group of three men worked to translate the writings of a famous Swedish botanist named Carl Linnaeus from Latin into English. This project took seven years!
Their work resulted in two books: A System of Vegetables (1783–1785) and The Families of Plants (1787). In these books, Darwin created many of the English names for plants that we still use today.
Darwin then wrote a long poem called The Loves of the Plants. This poem made Linnaeus's scientific ideas popular and easy to understand. He also wrote Economy of Vegetation. Both poems were published together as The Botanic Garden.
Zoonomia and Evolution
Darwin's most important scientific book was Zoonomia (1794–1796). It talked about diseases and how living things are created. In this book, he shared ideas that were similar to later theories of evolution.
He believed that all living things came from one original "living filament." He also wrote about the idea of "survival of the fittest." This means that the strongest and most active animals are more likely to have offspring, which helps the species improve.
His grandson, Charles Darwin, later developed a more complete theory called natural selection. This theory explains how living things change over time to better suit their environment.
Poems on Nature and Life
Erasmus Darwin first shared his ideas about evolution in a subtle way in a footnote of his poem The Loves of the Plants (1789). This poem was very popular and was reprinted many times.
His last long poem, The Temple of Nature, was published after he died in 1803. It's considered his best poem. It explores his ideas about evolution, tracing life from tiny organisms to human society. The poem also describes the "struggle for existence" among living things.
His poetry was admired by some famous writers like William Wordsworth. It often included details about his scientific interests, such as botany and steam engines.
Education for Girls
Darwin also wrote a book called A plan for the conduct of female education in boarding schools (1797). In this book, he shared his thoughts on how girls should be educated.
He felt that girls in Britain at the time didn't get a good enough education. He suggested that middle-class girls should learn subjects like botany, chemistry, and even how to handle money. He also thought they should visit places like factories to learn about arts and manufacturing.
While his ideas might seem a bit old-fashioned today (he thought men and women should have different roles), he wanted women to learn about the "man's world." This was a modern idea for his time.
The Lunar Society
Erasmus Darwin was a founding member of the Lunar Society of Birmingham. This was a famous group of friends who were inventors, scientists, and thinkers. They met once a month around the time of the full moon, which made it easier to travel home in the dark.
Some important members of the Lunar Society included:
- Matthew Boulton, a buckle maker.
- John Whitehurst, who made clocks and studied geology.
- Josiah Wedgwood, a famous potter.
- James Watt, who greatly improved the steam engine.
- Joseph Priestley, a chemist who discovered many substances.
Darwin was also good friends with Benjamin Franklin, an important American inventor and statesman. The Lunar Society played a big role in England's Industrial Revolution, a time of great change and new inventions.
The members of the Lunar Society, especially Darwin, were strongly against the slave trade. Darwin wrote about his opposition to slavery in his poems.
Other Interests and Inventions
In 1761, Darwin became a member of the Royal Society, a very old and respected scientific group.
He also belonged to the Derby Philosophical Society. He studied how air and gases could help treat infections and cancers. He even researched how clouds form.
In 1792, he was chosen as a member of the American Philosophical Society in Philadelphia.
Erasmus Darwin's ideas even inspired famous writers! Mary Shelley, who wrote the novel Frankenstein, mentioned that her husband talked about Darwin's experiments. This gave her the idea for her famous story about creating life.
Amazing Inventions
Darwin was a clever inventor, but he never patented any of his inventions. He thought it might hurt his reputation as a doctor. He often encouraged his friends to patent their own versions of his designs.
Some of his inventions included:
- A special windmill he designed for Josiah Wedgwood.
- A carriage that was designed not to tip over (1766).
- A clever steering mechanism for his carriage (1759). This design was later used in cars over 100 years later!
- A speaking machine. This was a mechanical voice box made of wood, silk, and leather. It could make sounds so well that people thought it was a real voice!
- A canal lift to move barges between different water levels.
- A tiny artificial bird.
- A copying machine (1778).
- Different machines to monitor the weather.
He even sketched a design for a simple rocket engine in 1779. This idea, using hydrogen and oxygen gas tanks, was far ahead of its time!
Commemoration
Erasmus Darwin House, his old home in Lichfield, Staffordshire, is now a museum. It teaches visitors all about his life and work. A school near Lichfield was also named Erasmus Darwin Academy in his honor.
A science building at Nottingham Trent University is named after him too.
Images for kids
Family tree
In fiction
- Author Charles Sheffield wrote stories where Darwin acts like a detective, similar to Sherlock Holmes. These stories are in a book called The Amazing Dr. Darwin.
- Darwin's rocket designs are an important part of the plot in Stephen Baxter's book Manifold: Origin.
- Darwin appears as a character in Sergey Lukyanenko's novel New Watch.
See also
 In Spanish: Erasmus Darwin para niños
In Spanish: Erasmus Darwin para niños