Gene expression facts for kids
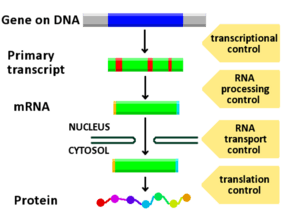
Gene expression is how your body uses the instructions in your DNA to make things it needs, like proteins or RNA. Think of DNA as a giant recipe book inside your cells. Gene expression is like actually baking the cake or cooking the meal from those recipes!
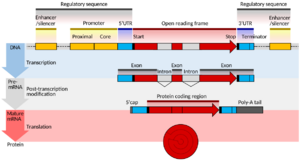
First, the DNA recipe is copied into a message called RNA. Then, this RNA message is used to build proteins. Proteins do most of the work in your cells and make up many parts of your body. For example, some proteins are like tiny machines (called enzymes) that help your body do important jobs.
Your body can control how much of a gene is expressed. It can turn genes on or off, or change how much protein is made. This control is super important for how your body grows and develops. This control helps cells become different types, like nerve cells or muscle cells. It also guides how a living thing forms its shape. How genes are turned on and off can even lead to changes in living things over many generations, helping them evolve.
Sometimes, one gene can affect many different traits or parts of your body. This is a common idea in genetics.
Contents
Epigenetics: Beyond the DNA Code
In biology, epigenetics is about changes in how your genes work, but without changing the actual DNA sequence itself. Imagine you have a cookbook (your DNA). Epigenetics is like adding sticky notes or bookmarks to the recipes. The words in the recipe don't change, but the notes tell you which recipes to use more often, less often, or not at all.
These changes can stay with a cell as it divides and can even be passed down for a few generations. But remember, the DNA letters (A, T, C, G) themselves don't change. Instead, other things make your genes behave differently.
A great example of epigenetics is how stem cells become different types of cells. When you were a tiny embryo, you started as one single cell. This cell divided many times. All those new cells had the exact same DNA. But then, some cells became nerve cells, some became muscle cells, and others became blood vessels. This happens because certain genes are turned on in some cells and turned off in others.
Epigenetic changes are long-lasting. They often involve how your DNA is packaged inside your cells. Your DNA is wrapped around special proteins called histones, forming structures called chromatin. How tightly or loosely this DNA is wrapped can affect whether a gene can be read or not.
Gene Regulation: Turning Genes On and Off
Gene regulation is all about controlling which genes are active and how much protein they make. It's like having a dimmer switch for each gene.
Up-regulation and Down-regulation
- Up-regulation means increasing how much a gene is expressed. This leads to more of its protein being made.
- Down-regulation means decreasing how much a gene is expressed. This leads to less of its protein being made.
Induction vs. Repression
Gene regulation can also be thought of as:
- Inducible systems: These genes are normally "off." They only turn "on" when a specific molecule (called an inducer) is present.
- Repressible systems: These genes are normally "on." They turn "off" only when a specific molecule (called a corepressor) is present.
Regulatory RNAs
Some types of RNA molecules don't make proteins. Instead, they help control other genes. Here are two important examples:
miRNA
Micro RNAs (miRNA) are tiny RNA molecules. They work by teaming up with an enzyme to either block other RNA messages (called messenger RNA or mRNA) or speed up their breakdown. This process is known as RNA interference. It's like a tiny censor that stops unwanted messages.
siRNA
Small interfering RNAs (siRNA) are also very small, double-stranded RNA molecules. They interfere with the expression of specific genes, often by silencing them. The discovery of siRNAs has opened up new ways to study diseases and develop new medicines.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
The extended central dogma of molecular biology includes all the cellular processes involved in the flow of genetic information
-
The patchy colours of a tortoiseshell cat are the result of different levels of expression of pigmentation genes in different areas of the skin.
-
The lambda repressor transcription factor (green) binds as a dimer to major groove of DNA target (red and blue) and disables initiation of transcription. From PDB 1LMB.
-
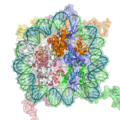
In eukaryotes, DNA is organized in form of nucleosomes. Note how the DNA (blue and green) is tightly wrapped around the protein core made of histone octamer (ribbon coils), restricting access to the DNA. From PDB 1KX5.
-
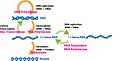
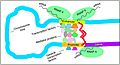
Regulation of transcription in mammals. An active enhancer regulatory region is enabled to interact with the promoter region of its target gene by formation of a chromosome loop. This can initiate messenger RNA (mRNA) synthesis by RNA polymerase II (RNAP II) bound to the promoter at the transcription start site of the gene. The loop is stabilized by one architectural protein anchored to the enhancer and one anchored to the promoter and these proteins are joined to form a dimer (red zigzags). Specific regulatory transcription factors bind to DNA sequence motifs on the enhancer. General transcription factors bind to the promoter. When a transcription factor is activated by a signal (here indicated as phosphorylation shown by a small red star on a transcription factor on the enhancer) the enhancer is activated and can now activate its target promoter. The active enhancer is transcribed on each strand of DNA in opposite directions by bound RNAP IIs. Mediator (a complex consisting of about 26 proteins in an interacting structure) communicates regulatory signals from the enhancer DNA-bound transcription factors to the promoter.
-
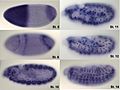
In situ-hybridization of Drosophila embryos at different developmental stages for the mRNA responsible for the expression of hunchback. High intensity of blue color marks places with high hunchback mRNA quantity.
-
The three-dimensional structure of green fluorescent protein. The residues in the centre of the "barrel" are responsible for production of green light after exposing to higher energetic blue light. From PDB 1EMA.
See also
 In Spanish: Expresión génica para niños
In Spanish: Expresión génica para niños
 | Bessie Coleman |
 | Spann Watson |
 | Jill E. Brown |
 | Sherman W. White |