Hurricane Hazel facts for kids
| Category 4 major hurricane (SSHWS/NWS) | |
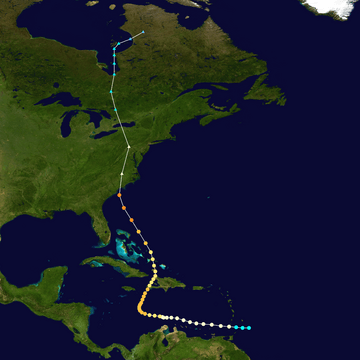
Track map of Hurricane Hazel
|
|
| Formed | October 5, 1954 |
|---|---|
| Dissipated | October 17, 1954 |
| Highest winds | 1-minute sustained: 150 mph (240 km/h) |
| Lowest pressure | ≤ 937 mbar (hPa); 27.67 inHg |
| Fatalities | 600 - 1,200 direct |
| Damage | $381 million (1954 USD) |
| Areas affected | Grenada, Haiti, Bahamas, South Carolina, North Carolina, Virginia, West Virginia, Maryland, Pennsylvania, New York, Toronto and southern and eastern Ontario |
| Part of the 1954 Atlantic hurricane season | |
Hurricane Hazel was an incredibly powerful and destructive storm. It was the worst hurricane of the 1954 Atlantic hurricane season. It was also one of the strongest hurricanes of the 20th century. Hazel caused a lot of damage and sadly, many deaths.
Hurricane Hazel first hit Haiti, where it killed as many as 1,000 people. Then, it moved towards the United States. It struck just south of Wilmington, North Carolina. At that time, it was a very strong Category 4 hurricane. In North Carolina, 19 people lost their lives. The storm then traveled far inland, reaching Toronto, Ontario, Canada. There, it caused the deaths of 81 people. Hazel is known as the strongest hurricane ever to travel so far inland and still be so powerful.
Contents
What is a Hurricane?
A hurricane is a huge, spinning storm that forms over warm ocean waters. It has very strong winds and brings heavy rain. Hurricanes are also called tropical cyclones. They get their energy from warm, moist air above the ocean. As they move, they can cause a lot of damage to land. This includes strong winds, heavy flooding, and storm surges.
Hazel's Powerful Journey
Hurricane Hazel started forming on October 5, 1954. It quickly grew stronger as it moved across the Atlantic Ocean. By October 13, it had become a major hurricane. It reached its peak strength with winds of about 150 miles per hour. This made it a Category 4 storm.
Impact in the Caribbean
Hazel first brought its fury to the Caribbean islands. It caused terrible damage in Grenada and Haiti. In Haiti, the storm caused massive floods and mudslides. Many homes were destroyed, and crops were ruined. The number of people who died in Haiti was very high, possibly up to 1,000. This made it one of the deadliest hurricanes in Haiti's history.
Striking the United States
After leaving the Caribbean, Hurricane Hazel headed for the United States. It made landfall on October 15, 1954. It hit near the border of North Carolina and South Carolina. When it hit, it was still a Category 4 hurricane. This meant it had winds of about 130 miles per hour.
The storm caused a lot of damage along the coast. It created a huge storm surge. This is when the ocean water rises above its normal level. The storm surge flooded many coastal towns. It washed away homes and buildings. In North Carolina, 19 people died because of the storm.
Hazel's Path Inland
What made Hurricane Hazel so unusual was how far inland it traveled. Most hurricanes lose strength quickly after hitting land. But Hazel kept its power as it moved north. It traveled through Virginia, Maryland, Pennsylvania, and New York. Even far from the coast, it still caused strong winds and heavy rain. This led to widespread power outages and flooding.
Devastation in Canada
Hurricane Hazel continued its path into Canada. It hit Ontario, especially the city of Toronto, on October 15, 1954. By this time, it was no longer a hurricane. But it was still a very strong extratropical cyclone. It brought record-breaking rainfall to the area.
The rain caused rivers, like the Humber River, to overflow their banks. This led to severe flash floods. Many bridges and roads were washed away. Homes were swept off their foundations. The flooding was so bad that 81 people died in Canada. This made Hurricane Hazel one of the worst natural disasters in Canadian history.
Remembering Hurricane Hazel
Hurricane Hazel was a truly historic storm. It showed how much damage a powerful hurricane can cause. It also taught people important lessons about preparing for natural disasters. The storm led to better warning systems and flood control measures. This helps keep people safer today.
Images for kids
-
The Weston Golf Club in Toronto was left submerged after the Humber River overflowed its banks.
-
A weir was built on the Humber River near Raymore Drive to lessen the risk of a similar catastrophic flood.




