Sparta facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Lacedaemon
Λακεδαίμων (Ancient Greek)
|
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 900s–192 BC | |||||||||||
|
The letter lambda was used by the Spartan army as a symbol of Lacedaemon
|
|||||||||||
Territory of ancient Sparta
|
|||||||||||
| Capital | Sparta | ||||||||||
| Common languages | Doric Greek | ||||||||||
| Religion | Greek polytheism | ||||||||||
| Government | Diarchy | ||||||||||
| King | |||||||||||
|
• 1104–1066 BC
|
Eurysthenes | ||||||||||
|
• 1104–1062 BC
|
Procles | ||||||||||
|
• 489–480 BC
|
Leonidas I | ||||||||||
| Legislature |
|
||||||||||
| Historical era | Classical antiquity | ||||||||||
| 900s BC | |||||||||||
|
• Messenian War
|
685–668 BC | ||||||||||
| 480 BC | |||||||||||
| 431–404 BC | |||||||||||
|
• Battle of Mantinea
|
362 BC | ||||||||||
| 192 BC | |||||||||||
|
|||||||||||


Sparta is a famous city in Greece. It is the capital of the Laconia area. You can find it in the south of the Peloponnese peninsula. Long ago, Sparta was incredibly powerful. Today, it is a smaller city. In 2001, about 16,726 people lived there.
The word Spartan is often used to describe someone who lives a very simple life. It can also mean someone who is tough and doesn't show pain or sadness easily. It suggests a life without anything fancy or expensive.
Contents
Geography of Sparta
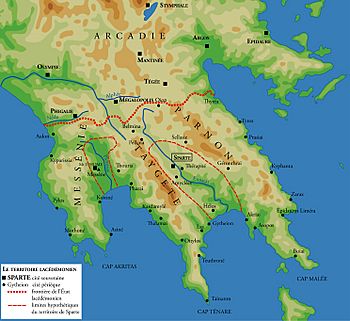
Sparta is located in the mountainous area of Laconia. This region is in the south-east of the Peloponnese. Ancient Sparta was built next to the Evrotas River. The river flows through a valley with mountains on both sides.
To the west, you'll find the Taygetus Range, which has peaks as high as 2407 meters. To the east is the Parnon Range, with its highest point at 1935 meters. Because of these strong natural defenses, the ancient Spartans did not need to build city walls. Sparta was well known for its strong military. They were one of the greatest military forces of their time.
Spartan Society
Sparta was a city-state known for its very strong army and well-organized government. It was considered one of the most powerful city-states in ancient Greece. Spartans believed that only the strongest should survive, whether male or female.
If a baby was thought to be too weak, they were left on a slope of Mount Taygetus. This place was called the Apothetae, meaning 'the place of rejection'. At its peak around 500 BC, Sparta had about 20,000 to 35,000 citizens. There were also many helots and perioikoi. This made Sparta one of the larger Greek city-states.
Spartan Customs
Young Spartan boys were taken from their homes at age seven. They began a military life, training to become strong warriors. Spartans became soldiers at age 20 and full citizens at age 30. They would retire from military life at age 60.
Spartan women were encouraged to stay healthy and fit. This was so they could have strong, healthy babies. These children would then grow up to be strong Spartans.
Spartan Government
Sparta had a government with a system of checks and balances. This means different parts of the government kept each other in check. Two kings led the executive branch. The citizens were in charge of the legislative branch. The judicial branch was controlled by a group of elders.
There was also a committee of five men called the ephors. They were in charge of the education system for young boys and girls. Boys and girls were taken from their parents at age seven. Boys lived in barracks with other boys their age. Girls went to school to learn gymnastics, wrestling, and other physical activities.
Liking Sparta: Laconophilia
Laconophilia means a love or liking for Sparta and its culture. Sparta was often admired when it was powerful. Many people, including some important Athenians, thought Sparta was an almost perfect state.
Many Greek philosophers, especially those who followed Plato, described Sparta as a good state. They saw it as strong, brave, and free. Sparta was also seen as a model of social purity by people in Revolutionary and Napoleonic France.
Marriage Customs
Spartan men usually married when they were 30 years old. They had some very unusual customs for their wedding night. The husband would visit his wife in secret for some time after the marriage. These customs were unique to Spartans. Some people believe that certain parts of the ceremony showed the wife was entering a new life.
History of Sparta
Sparta took control of the people of Messenia and Laconia (the land around them) between 680 and 560 BC. These people became known as the helots. They were not slaves, but more like serfs. Serfs had a lower position in society, similar to those in medieval Europe.
Helots spent their lives farming the land given to Spartan citizens. A Spartan poet named Tyrtaios said helots could marry and keep half of what they produced. Most of the time, there were ten helots for every one Spartan master. They often rebelled, but they were never able to defeat their rulers.
Once a Spartan reached the age of 20, they became a homoios. This meant they were a member of the ruling class and a full citizen. Both men and women could be citizens. Sparta was unusual for its time because women had more rights and were considered more equal than in many other Greek city-states. The Spartan army used a special formation called the phalanx. This helped them win many battles.
Images for kids
-
Lycurgus, a legendary lawgiver of Sparta.
See also
 In Spanish: Esparta para niños
In Spanish: Esparta para niños