Liège–Bastogne–Liège facts for kids
| Liège–Bastogne–Liège logo.svg | |
| Race details | |
|---|---|
| Date | Late April |
| Region | Wallonia, Ardennes, Belgium |
| English name | Liège–Bastogne–Liège |
| Local name(s) | Liège–Bastogne–Liège |
| Nickname(s) | La Doyenne ("The Old Lady") |
| Discipline | Road |
| Competition | UCI World Tour |
| Type | One-day Classic |
| Organiser | Amaury Sport Organisation |
| Race director | Christian Prudhomme |
| History | |
| First edition | 1892 |
| Editions | 111 (as of 2025) |
| First winner | |
| Most wins | |
| Most recent | |
Liège–Bastogne–Liège, often called La Doyenne ("The Old Lady"), is a famous one-day bicycle race in Belgium. It is the oldest of the five "Monuments" in professional road cycling. These Monuments are the most important and respected one-day races. Liège–Bastogne–Liège happens every year in late April. It takes place in the Ardennes region of Belgium, starting in Liège, going to Bastogne, and then returning to Liège.
This race is known as one of the toughest one-day cycling events in the world. This is because it is very long and has many challenging hills. The rider with the most wins is Eddy Merckx from Belgium, who won five times. Other great riders like Moreno Argentin and Alejandro Valverde have won four times each.
Liège–Bastogne–Liège is part of the UCI World Tour, which is a series of top cycling races. It is the final race in a group called the Ardennes classics. This group also includes the Amstel Gold Race and La Flèche Wallonne. The company that organizes Liège–Bastogne–Liège also organizes the famous Tour de France.
Contents
History of the Race
Early Beginnings
Like many old cycling races, Liège–Bastogne–Liège was first organized by a newspaper. The race has always been held in the southern, hilly part of Belgium where people speak French.
The first race was for amateur riders in 1892. It went from Spa to Bastogne and back, covering about 250 kilometers (155 miles). Back then, bicycles were expensive, so cycling was mostly a sport for wealthy people. Thirty-three Belgian riders started the race, and only 17 finished. The halfway point was a train station in Bastogne, which was handy for tired riders who wanted to take the train back! Léon Houa, from Liège, won the first race after riding for almost 11 hours. The second-place rider finished 22 minutes later.
Léon Houa won again the next year. In 1894, the first race for professional riders was held, and Houa won for a third time. After these first three races, the event stopped for 14 years. It then started again in 1908, with the start and finish in Liège for the first time.
The race was paused during World War I but came back in 1919. Belgian riders, especially those from the northern part of Belgium called Flanders, started to win most of the races.
Becoming a Classic Race
Liège–Bastogne–Liège was interrupted during World War II but returned in 1945. It began to attract famous European cyclists. In the 1950s, Swiss rider Ferdinand Kübler won the race twice.
In the late 1950s, Fred De Bruyne won the race three times in a row. In 1957, two riders were declared winners because of a confusing situation with a railway crossing. In 1959, Liège–Bastogne–Liège became part of a major cycling competition, making it one of the most important races of the year.

The era of cycling legend Eddy Merckx began in 1969. He won Liège–Bastogne–Liège five times, including three wins in a row. The 1971 race was very tough, with snow and cold weather. Merckx attacked far from the finish line and won, even though he got very tired near the end. In 1975, he won his fifth and final victory, becoming the record holder for La Doyenne.
French cycling star Bernard Hinault won the race twice, both times in terrible weather. In 1980, he won in a snowstorm and freezing temperatures. Only 21 out of 174 riders finished that race!
In the 1980s, Italian rider Moreno Argentin won the race four times. He was known as the "King of the Ardennes" because he also won the sister race, La Flèche Wallonne, three times.
Changes to the Finish Line
In 1990, the race organization teamed up with the company that runs the Tour de France. This led to big changes in the race course. The finish line moved to Ans, a suburb of Liège. A steep climb called the Côte de Saint-Nicolas was added near the end, followed by a final uphill section to the finish. This made the race exciting for climbers who could sprint uphill.

In 2005, Alexander Vinokourov and Jens Voigt made a surprising breakaway very early in the race and managed to stay ahead to the finish.
In 2009, Andy Schleck won the race with a solo attack. In 2010, Alexander Vinokourov won again, but his victory was controversial because of a suggestion that he had paid another rider not to challenge him.
In the 2010s, Spanish rider Alejandro Valverde won four times, usually by winning a sprint among a small group of riders at the finish.
In 2019, the finish line moved back to the center of Liège. This meant the Côte de Saint-Nicolas and the final climb to Ans were removed. Now, the race finishes on a flat road. Slovenian rider Tadej Pogačar has won the race three times, including in 2025, often with solo attacks.
Race Route and Challenges
The Course
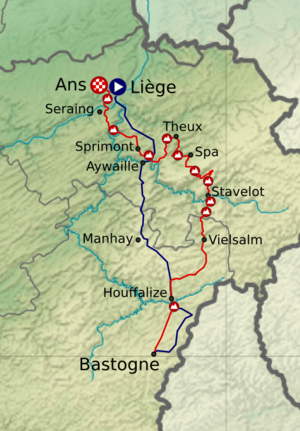
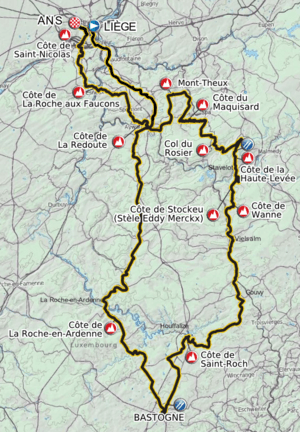
The Liège–Bastogne–Liège route goes through two eastern provinces of Belgium: Liège and Luxembourg. The race is usually about 250 to 260 kilometers (155 to 160 miles) long. It starts in the city of Liège, goes south for about 95 kilometers (59 miles) to Bastogne, and then winds back to Liège for about 163 kilometers (101 miles).
The second half of the race has many climbs, like the Stockeu, Haute-Levée, La Redoute, and the Côte de la Roche-aux-Faucons. The last 15 kilometers (9 miles) of the race change from quiet countryside to the city of Liège.
Demanding Climbs
Liège–Bastogne–Liège is known as one of the hardest one-day races because of its length and many steep climbs. In every race, there are about a dozen climbs that vary in length and steepness. These climbs offer chances for riders to attack and try to get ahead.
A cycling magazine once said that this race is "probably the toughest classic" because the climbs are long, steep, and happen very often near the end. Four-time winner Moreno Argentin explained that riders who win Liège need great stamina. He said the climb of La Redoute is very tough because it comes after more than 220 kilometers (136 miles) of riding. He also mentioned that Liège is a race where riders are slowly eliminated, and only the strongest and smartest riders can win.
Key Climbs
The most famous climb is the Côte de La Redoute. It is 2 kilometers (1.2 miles) long with an average steepness of 8.9%, and some parts are over 20% steep! For many years, La Redoute, which is about 40 kilometers (25 miles) from the finish, was where the race was often decided. However, in recent years, many riders can keep up, and favorites often wait until closer to the end to make their move.
Since the finish moved back to Liège in 2019, the important climbs are now the Côte de la Redoute, Côte des Forges, and Côte de la Roche-aux-Faucons. The race route often changes slightly each year, with some climbs being added or removed.
| Distance from start | Name | Length | Steepness |
|---|---|---|---|
| 75.0 km | Côte de la Roche-en-Ardenne | 2.8 km | 6.2% |
| 121.0 km | Côte de Saint-Roch | 1.0 km | 11.2% |
| 161.0 km | Côte de Mont-le-Soie | 1.7 km | 7.9% |
| 169.5 km | Côte de Wanne | 3.6 km | 5.1% |
| 176.0 km | Côte de Stockeu | 1.0 km | 12.5% |
| 181.5 km | Côte de la Haute-Levée | 3.6 km | 5.6% |
| 194.5 km | Côte du Rosier | 4.4 km | 5.9% |
| 207.0 km | Col du Maquisard | 2.5 km | 5.0% |
| 219.0 km | Côte de la Redoute | 2.0 km | 8.9% |
| 231.0 km | Côte des Forges | 1.3 km | 7.8% |
| 241.0 km | Côte de la Roche-aux-Faucons | 1.3 km | 11.0% |
Weather Challenges
The weather in April can be very unpredictable. The race has often been affected by harsh conditions, including heavy snowfall in some years like 1919, 1957, 1980, and 2016. The 1980 race was especially difficult. Snow fell from the start, and temperatures were freezing. This led people to call it 'Neige-Bastogne-Neige' (Snow-Bastogne-Snow). Bernard Hinault attacked with 80 kilometers (50 miles) to go and finished almost 10 minutes ahead of everyone else. Only 21 riders finished that race. Hinault himself said it took three weeks for two of his fingers to feel normal again after the extreme cold.
Ardennes Classics
Liège–Bastogne–Liège is the last race in the Ardennes classics series, which also includes La Flèche Wallonne. Both races are organized by the same company.
For a long time, La Flèche Wallonne was considered more important than Liège–Bastogne–Liège. At one point, these two races were held on back-to-back days, known as Le Weekend Ardennais.
Only eight riders have won both races in the same year:
- Ferdinand Kübler (Switzerland) - twice (1951, 1952)
- Stan Ockers (Belgium) - 1955
- Eddy Merckx (Belgium) - 1972
- Davide Rebellin (Italy) - 2004
- Alejandro Valverde (Spain) - three times (2006, 2015, 2017)
- Philippe Gilbert (Belgium) - 2011
- Moreno Argentin (Italy) - 1991
- Tadej Pogačar (Slovenia) - 2025
In 2011, Belgian rider Philippe Gilbert won Liège–Bastogne–Liège. He also won three other hilly races in April, achieving a special "quadruple" of victories.
Winners of Liège–Bastogne–Liège
| Rider | Team | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1892 | Léon Houa | – | ||
| 1893 | Léon Houa | – | ||
| 1894 | Léon Houa | – | ||
| 1895–1907 | No race | |||
| 1908 | André Trousselier | – | ||
| 1909 | Victor Fastre | – | ||
| 1910 | No race | |||
| 1911 | Joseph Van Daele | – | ||
| 1912 | Omer Verschoore | – | ||
| 1913 | Maurits Moritz | – | ||
| 1914–1918 | No race | |||
| 1919 | Léon Devos | – | ||
| 1920 | Léon Scieur | La Sportive | ||
| 1921 | Louis Mottiat | La Sportive | ||
| 1922 | Louis Mottiat | Alcyon–Dunlop | ||
| 1923 | René Vermandel | Alcyon–Dunlop | ||
| 1924 | René Vermandel | Alcyon–Dunlop | ||
| 1925 | Georges Ronsse | – | ||
| 1926 | Dieudonné Smets | – | ||
| 1927 | Maurice Raes | – | ||
| 1928 | Ernest Mottard | – | ||
| 1929 | Alfons Schepers | – | ||
| 1930 | Hermann Buse | Duerkopp | ||
| 1931 | Alfons Schepers | La Française | ||
| 1932 | Marcel Houyoux | – | ||
| 1933 | François Gardier | Cycles De Pas | ||
| 1934 | Theo Herckenrath | La Française | ||
| 1935 | Alfons Schepers | Dilecta | ||
| 1936 | Albert Beckaert | Alcyon–Dunlop | ||
| 1937 | Éloi Meulenberg | Alcyon–Dunlop | ||
| 1938 | Alfons Deloor | Helyett–Hutchinson | ||
| 1939 | Albert Ritserveldt | Dilecta–De Dion | ||
| 1940–1942 | No race | |||
| 1943 | Richard Depoorter | Helyett–Hutchinson | ||
| 1944 | No race | |||
| 1945 | Jean Engels | Alcyon–Dunlop | ||
| 1946 | Prosper Depredomme | Dilecta–Wolber–Garin | ||
| 1947 | Richard Depoorter | Garin–Wolber | ||
| 1948 | Maurice Mollin | Mercier–Hutchinson | ||
| 1949 | Camille Danguillaume | Peugeot–Dunlop | ||
| 1950 | Prosper Depredomme | Girardengo | ||
| 1951 | Ferdinand Kübler | Fréjus–Ursus | ||
| 1952 | Ferdinand Kübler | Fréjus | ||
| 1953 | Alois De Hertog | Alcyon–Dunlop | ||
| 1954 | Marcel Ernzer | Terrot–Hutchinson | ||
| 1955 | Stan Ockers | Elvé–Peugeot | ||
| 1956 | Fred De Bruyne | Mercier–BP–Hutchinson | ||
| 1957 | Frans Schoubben (BEL) (victory shared with Germain Derycke) | Elvé–Peugeot | ||
| 1957 | Germain Derycke (BEL) (victory shared with Frans Schoubben) | Faema–Guerra | ||
| 1958 | Fred De Bruyne | Carpano | ||
| 1959 | Fred De Bruyne | Carpano | ||
| 1960 | Albertus Geldermans | Saint-Raphaël–R. Geminiani–Dunlop | ||
| 1961 | Rik Van Looy | Faema | ||
| 1962 | Jef Planckaert | Flandria–Faema–Clément | ||
| 1963 | Frans Melckenbeeck | Mercier–BP–Hutchinson | ||
| 1964 | Willy Blocklandt | Flandria–Romeo | ||
| 1965 | Carmine Preziosi | Pelforth–Sauvage–Lejeune | ||
| 1966 | Jacques Anquetil | Ford France–Hutchinson | ||
| 1967 | Walter Godefroot | Flandria–De Clerck | ||
| 1968 | Valere Van Sweevelt | Smith's | ||
| 1969 | Eddy Merckx | Faema | ||
| 1970 | Roger De Vlaeminck | Flandria–Mars | ||
| 1971 | Eddy Merckx | Molteni | ||
| 1972 | Eddy Merckx | Molteni | ||
| 1973 | Eddy Merckx | Molteni | ||
| 1974 | Georges Pintens | MIC–Ludo–de Gribaldy | ||
| 1975 | Eddy Merckx | Molteni–RYC | ||
| 1976 | Joseph Bruyère | Molteni–Campagnolo | ||
| 1977 | Bernard Hinault | Gitane–Campagnolo | ||
| 1978 | Joseph Bruyère | C&A | ||
| 1979 | Dietrich Thurau | IJsboerke–Warncke Eis | ||
| 1980 | Bernard Hinault | Renault–Gitane | ||
| 1981 | Josef Fuchs | Cilo–Aufina | ||
| 1982 | Silvano Contini | Bianchi–Piaggio | ||
| 1983 | Steven Rooks | Sem–France Loire–Reydel–Mavic | ||
| 1984 | Sean Kelly | Skil–Reydel–Sem–Mavic | ||
| 1985 | Moreno Argentin | Sammontana–Bianchi | ||
| 1986 | Moreno Argentin | Sammontana–Bianchi | ||
| 1987 | Moreno Argentin | Gewiss–Bianchi | ||
| 1988 | Adri van der Poel | PDM–Ultima–Concorde | ||
| 1989 | Sean Kelly | PDM–Ultima–Concorde | ||
| 1990 | Eric Van Lancker | Panasonic–Sportlife | ||
| 1991 | Moreno Argentin | Ariostea | ||
| 1992 | Dirk De Wolf | Gatorade–Chateau d'Ax | ||
| 1993 | Rolf Sørensen | Carrera Jeans–Tassoni | ||
| 1994 | Eugeni Berzin | Gewiss–Ballan | ||
| 1995 | Mauro Gianetti | Polti–Granarolo–Santini | ||
| 1996 | Pascal Richard | MG Maglificio–Technogym | ||
| 1997 | Michele Bartoli | MG Maglificio–Technogym | ||
| 1998 | Michele Bartoli | Asics–CGA | ||
| 1999 | Frank Vandenbroucke | Cofidis | ||
| 2000 | Paolo Bettini | Mapei–Quick-Step | ||
| 2001 | Oscar Camenzind | Lampre–Daikin | ||
| 2002 | Paolo Bettini | Mapei–Quick-Step | ||
| 2003 | Tyler Hamilton | Team CSC | ||
| 2004 | Davide Rebellin | Gerolsteiner | ||
| 2005 | Alexandre Vinokourov | T-Mobile Team | ||
| 2006 | Alejandro Valverde | Caisse d'Epargne–Illes Balears | ||
| 2007 | Danilo Di Luca | Liquigas | ||
| 2008 | Alejandro Valverde | Caisse d'Epargne | ||
| 2009 | Andy Schleck | Team Saxo Bank | ||
| 2010 | Alexandre Vinokourov | Astana | ||
| 2011 | Philippe Gilbert | Omega Pharma–Lotto | ||
| 2012 | Maxim Iglinsky | Astana | ||
| 2013 | Dan Martin | Garmin–Sharp | ||
| 2014 | Simon Gerrans | Orica–GreenEDGE | ||
| 2015 | Alejandro Valverde | Movistar Team | ||
| 2016 | Wout Poels | Team Sky | ||
| 2017 | Alejandro Valverde | Movistar Team | ||
| 2018 | Bob Jungels | Quick-Step Floors | ||
| 2019 | Jakob Fuglsang | Astana | ||
| 2020 | Primož Roglič | Team Jumbo–Visma | ||
| 2021 | Tadej Pogačar | UAE Team Emirates | ||
| 2022 | Remco Evenepoel | Quick-Step Alpha Vinyl Team | ||
| 2023 | Remco Evenepoel | Soudal–Quick-Step | ||
| 2024 | Tadej Pogačar | UAE Team Emirates | ||
| 2025 | Tadej Pogačar | {{{team name-2025}}} | ||
Riders with Multiple Wins
Active riders are in italic.
| Wins | Rider | Years |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | 1969, 1971, 1972, 1973, 1975 | |
| 4 | 1985, 1986, 1987, 1991 | |
| 2006, 2008, 2015, 2017 | ||
| 3 | 1892, 1893, 1894 | |
| 1929, 1931, 1935 | ||
| 1956, 1958, 1959 | ||
| 2021, 2024, 2025 | ||
| 2 | 1921, 1922 | |
| 1923, 1924 | ||
| 1943, 1947 | ||
| 1946, 1950 | ||
| 1951, 1952 | ||
| 1976, 1978 | ||
| 1977, 1980 | ||
| 1984, 1989 | ||
| 1997, 1998 | ||
| 2000, 2002 | ||
| 2005, 2010 | ||
| 2022, 2023 |
Wins by Country
| Wins | Country |
|---|---|
| 61 | |
| 12 | |
| 6 | |
| 5 | |
| 4 | |
| 3 | |
| 2 | |
| 1 |
Liège–Bastogne–Liège for Women
In 2017, a women's version of the race, called Liège–Bastogne–Liège Femmes, was started. This followed other women's races like La Flèche Wallonne Féminine. The first women's race was won by Olympic champion Anna van der Breggen from the Netherlands.
The women's race is about half the length of the men's race, at 135.5 kilometers (84 miles). It starts in Bastogne and heads north to finish in Ans, just like the men's race used to. The route includes four main climbs: the Côte de la Vecquée, Côte de La Redoute, Côte de la Roche aux faucons, and Côte de Saint-Nicolas. The top of the last climb, Saint-Nicolas, is about 5.5 kilometers (3.4 miles) from the finish line.
See also
 In Spanish: Lieja-Bastoña-Lieja para niños
In Spanish: Lieja-Bastoña-Lieja para niños