Liang dynasty facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Liang
梁
|
|||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 502–557 | |||||||||||||||
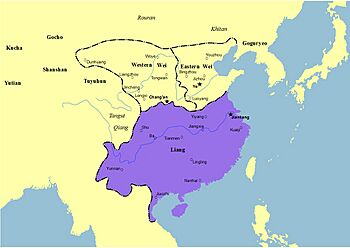
Liang alongside Western Wei and Eastern Wei after 534.
|
|||||||||||||||
| Capital | Jiankang (502–552, 555–557) Jiangling (552–555) |
||||||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||||||
| Emperor | |||||||||||||||
|
• 502–549
|
Emperor Wu of Liang | ||||||||||||||
|
• 549–551
|
Emperor Jianwen of Liang | ||||||||||||||
|
• 552–555
|
Emperor Yuan of Liang | ||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||
|
• Established
|
30 April 502 | ||||||||||||||
|
• Jiankang's fall to Hou Jing
|
24 April 549 | ||||||||||||||
|
• Jiangling's fall to Western Wei
|
7 January 555 | ||||||||||||||
|
• Emperor Jing's yielding the throne to Chen Baxian
|
16 November 557 | ||||||||||||||
|
• Disestablished
|
16 November 557 | ||||||||||||||
| Currency | Chinese cash coins (Taiqing Fengle cash coins) |
||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| Today part of | China Vietnam |
||||||||||||||
The Liang dynasty (Chinese: 梁朝; pinyin: Liáng Cháo) was an important period in Chinese history. It was also known as the Southern Liang or Xiao Liang. This dynasty was the third of four "Southern dynasties" during a time called the Northern and Southern dynasties period. It started after the Southern Qi dynasty and was followed by the Chen dynasty. A smaller part of the Liang dynasty, called Western Liang, lasted until the year 587.
Contents
The Liang Dynasty: A Time of Change
The Liang dynasty ruled parts of China from 502 to 557 CE. It was a time of both cultural growth and political challenges. Many important events shaped the future of China during this period.
Key Events and Rulers
The Liang dynasty saw several emperors and many power struggles. Let's look at some of the main events.
The Hou Jing Rebellion
In 548, a prince named Hou Jing started a big rebellion. He joined forces with Xiao Zhengde, who was a nephew of the ruling Emperor Wu of Liang. Hou Jing managed to take control of the capital city, Jiankang, in 549. He put Emperor Wu under house arrest, meaning the emperor was held captive in his own home.
Emperor Wu died in 550. Hou Jing then made Emperor Wu's son, Crown Prince Gang, the new emperor. However, Emperor Jianwen was also kept under house arrest. Hou Jing tried to control everyone who didn't agree with him.
Struggles Among Princes
While Hou Jing was in power, the Liang princes fought among themselves. They should have worked together to defeat Hou Jing. Instead, they weakened each other. For example, Xiao Yi, one of Emperor Wu's sons, fought against his own relatives. These fights sometimes led to princes asking for help from other kingdoms, like Western Wei or Northern Qi.
The End of Hou Jing's Rule
In 551, Hou Jing forced Emperor Jianwen to give up his throne. Then, Hou Jing killed Emperor Jianwen. Hou Jing tried to start his own new dynasty called Han. But in 552, another Liang prince, Xiao Yi, defeated Hou Jing. Xiao Yi then became the new emperor, known as Emperor Yuan of Liang. He moved the capital to Jiangling.
The Fall of Liang
The relationship between Emperor Yuan and the Western Wei kingdom became very bad. In 555, the Western Wei army attacked Jiangling. They captured Emperor Yuan and killed him and his sons. Western Wei then put Xiao Cha on the throne as the emperor of a smaller "Western Liang" state.
Meanwhile, in Jiankang, Liang generals tried to crown Xiao Fangzhi, the only living son of Emperor Yuan, as the new emperor. But the Northern Qi army interfered. Eventually, a general named Chen Baxian took control. He made Xiao Fangzhi the emperor, known as Emperor Jing of Liang.
In 557, Chen Baxian started his own powerful dynasty, the Chen dynasty. This marked the official end of the main Liang dynasty. The small Western Liang state continued until 587, when it was conquered by the Sui dynasty. Later, in 617, another member of the Liang royal family, Xiao Xian, tried to bring back the Liang dynasty, but his kingdom was also defeated.
Art and Culture
The Liang dynasty was a rich period for Chinese art and literature. Many important works were created during this time.
Famous Paintings
One very special artwork from this period is the Portraits of Periodical Offering of Liang. This painting was made by Emperor Yuan of Liang himself in the 6th century. It shows foreign ambassadors who visited China to pay tribute. The original painting is lost, but a copy from the Song dynasty (11th century) still exists. It is kept at the National Museum of China.
The painting shows ambassadors from many different places. These include people from Persia, Korea, Japan, and other regions. It helps us understand how China connected with other parts of the world back then.
Ancient Tombs and Statues
Many tombs of the Liang dynasty's royal family can still be found near Nanjing. These tombs often have amazing stone statues. The best example is the tomb of Xiao Xiu, who was a brother of Emperor Wu. His tomb has large, impressive statues that show the art style of the Liang dynasty. These statues often include mythical creatures like the bixie, which looks like a winged lion.
- Tombs of the Liang Dynasty
Important Writings
The Liang dynasty is known for having many written works that still exist today. These include official histories of earlier dynasties, like the Book of Song. There was also a famous poetry collection called Wenxuan. Another important work was Wenxin diaolong, which discussed how literature should be written. These texts help us understand the thoughts and ideas of people from that time.
Emperors of Liang
The Liang dynasty had several emperors during its rule. Here is a list of the main emperors:
| Posthumous Name | Personal Name | Period of Reigns |
|---|---|---|
| Emperor Wu of Liang | Xiao Yan | 502–549 |
| Emperor Jianwen of Liang | Xiao Gang | 549–551 |
| – | Xiao Dong | 551–552 |
| Emperor Yuan of Liang | Xiao Yi | 552–555 |
| – | Xiao Yuanming | 555 |
| Emperor Jing of Liang | Xiao Fangzhi | 555–557 |
Rulers' family tree
| Liang dynasty and Western Liang | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
- Liang emperors - Western Liang emperors - Liang throne pretenders
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
- King of Liang
- Chen dynasty
- Book of Liang
- History of Northern Dynasties
- History of Southern Dynasties
- Zizhi Tongjian