Olancho Department facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Olancho Department
Departamento de Olancho
|
||
|---|---|---|
|
department
|
||
|
||
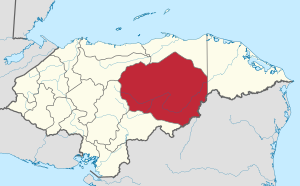
Location of Olancho in Honduras
|
||
| Country | ||
| Municipalities | 23 | |
| Villages | 287 | |
| Founded | 1825 | |
| Capital city | Juticalpa | |
| Government | ||
| • Type | Departmental | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 24,038 km2 (9,281 sq mi) | |
| Population
(2015)
|
||
| • Total | 537,306 | |
| • Density | 22.3524/km2 (57.8923/sq mi) | |
| Time zone | UTC-6 (CDT) | |
| Postal code |
16101, 16201
|
|
| ISO 3166 code | HN-OL | |
| HDI (2017) | 0.586 medium · 8th |
|
| Statistics derived from Consult INE online database: Population and Housing Census 2013 | ||
Olancho is the largest of the 18 departments in Honduras. It covers a huge area of about 24,057 square kilometers. In 2015, around 537,306 people lived there.
The main city and capital of Olancho is Juticalpa. This city is also home to the Roman Catholic Diocese of Juticalpa, which serves the department.
Contents
Exploring Olancho's Landscape
Olancho has a very interesting and varied landscape. It ranges from tall mountains to wide, flat plains and thick rainforests.
Mountains and Forests
In the western and northern parts of Olancho, you'll find rugged mountain ranges. Some of these include the Sierra de Agalta, the Montaña de Tembladeros, and the Montaña de Botaderos. These mountains are covered with huge pine and hardwood forests.
Central Plains and Rivers
The central part of Olancho has rolling plains. These plains are watered by the Guayape River and its smaller streams. They are sometimes called "pampas" because they look a bit like the large plains in Argentina. These areas are well-known for their many cattle herds and large farms. The main cities, Juticalpa and Catacamas, are both located in these plains.
The Guayape River is also famous for its gold deposits. People have been finding gold here since the time of the Spanish colonists. Even today, you might see local people looking for gold in the riverbanks during the dry season.
Rainforests and Wildlife
The eastern part of the department is covered in thick rainforests. However, some of these forests are being cut down for farming and timber. A part of the Rio Platano Biosphere Reserve is located here. This reserve is a tropical rainforest with many different kinds of plants and animals. UNESCO has named it a World Heritage site. It stretches across the borders of Olancho and the nearby departments of Gracias a Dios and Colón.
A Look at Olancho's Past
Olancho has a rich history, including ancient discoveries and times of local resistance.
Ancient Discoveries: The Talgua Caves
Near Catacamas, you can find the Cave of Talgua, also known as "The Cave of the Glowing Skulls." This cave was used long ago as a burial site by native peoples. Over many years, minerals dripping from the cave ceiling covered the bones. This made them sparkle in a unique way.
Scientists used radiocarbon dating to find out that these burials happened around 900 B.C. This was even before the famous Mayans and other big civilizations. The main burial chamber was found in 1994 by a Peace Corps volunteer named Timothy Berg, along with two local men, Desiderio Reyes and Jorge Yáñez. Research is still ongoing in this amazing place.
Times of Local Resistance
In the 18th and 19th centuries, people in Olancho sometimes disagreed with the government in Tegucigalpa. This led to some conflicts.
One notable event happened in 1864. A local leader was arrested, which caused a rebellion. More than a thousand people marched towards Tegucigalpa. The president of Honduras, General José María Medina, led soldiers to stop them. After fighting, the rebels were defeated, and their leaders were captured. Many towns and villages in Olancho were affected, and many people moved away. The capital of the department was also moved from Manto to Juticalpa.
A few years later, in 1868, a young man known as Cinchonero led another challenge to the government. He honored the past rebel leaders. The government again sent soldiers, and this rebellion was also put down. These events caused the population of Olancho to decrease significantly.
Olancho Today
Even today, people from Olancho, called Olanchanos, have a strong sense of local pride. The department is very important to Honduras because it produces a lot of food and agricultural goods.
Two former presidents of Honduras come from Olancho: Porfirio Lobo from Juticalpa, and Manuel Zelaya Rosales from Catacamas. This shows the department's important role in the country's leadership.
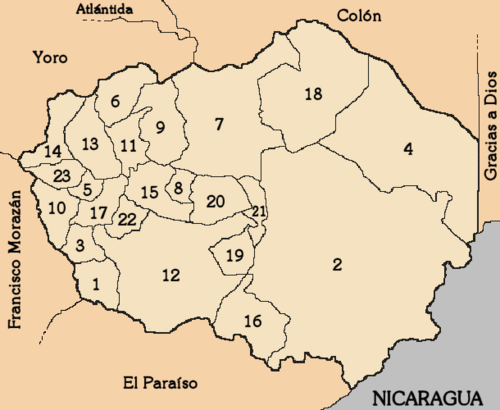
Cities and Towns: Municipalities
Olancho is divided into 23 main areas called municipalities. Each municipality has its own local government and communities.
- Campamento
- Catacamas
- Concordia
- Dulce Nombre de Culmí
- El Rosario
- Esquipulas del Norte
- Gualaco
- Guarizama
- Guata
- Guayape
- Jano
- Juticalpa
- La Unión
- Mangulile
- Manto
- Patuca
- Salamá
- San Esteban
- San Francisco de Becerra
- San Francisco de la Paz
- Santa María del Real
- Silca
- Yocón
Who Lives in Olancho? Demographics
According to the 2013 census in Honduras, Olancho Department had 520,761 people. Most of the people living there, about 94.54%, are Mestizo. This means they have mixed European and Indigenous heritage.
About 3.39% of the population is White. Around 1.23% are Indigenous, including groups like the Pech, Lenca, and Nahua. A smaller group, 0.60%, are Black or Afro-Honduran. The remaining 0.24% belong to other groups.
Places to Visit: Tourism
Olancho offers many interesting places to explore, especially for those who love nature and history.
- The old colonial church in the town of Catacamas.
- The amazing Talgua Caves, with their sparkling ancient bones.
- Part of the Río Plátano Biosphere Reserve, a beautiful rainforest with diverse wildlife.
- The National Parks of Patuca, great for nature lovers.
- The Agalta mountain range, offering stunning views and forests.
- Other natural attractions like The Wall and The Boquerón.
See also
 In Spanish: Departamento de Olancho para niños
In Spanish: Departamento de Olancho para niños