Overseas departments and regions of France facts for kids
The overseas departments and regions of France are parts of France that are located outside of Europe. Think of them as regular French departments and regions, but far away! They have the exact same rules and laws as mainland France. This means French laws about daily life, taxes, and government apply there too. However, these laws can be slightly changed to fit the special needs of each overseas region.
Since these places are full parts of France and the European Union, their citizens have the same rights as people in mainland France. They elect representatives to the French Parliament (the National Assembly and Senate). They also vote for members of the European Parliament. And just like in mainland France, they use the euro as their money!
It's important to know that overseas departments and regions are different from "overseas collectivities". Collectivities have a bit more freedom to make their own rules.
Each overseas department is also its own overseas region. This means that each one has the same powers as the larger regions in mainland France. Because of this, people often just say "overseas department" (or DOM in French) instead of "overseas region."
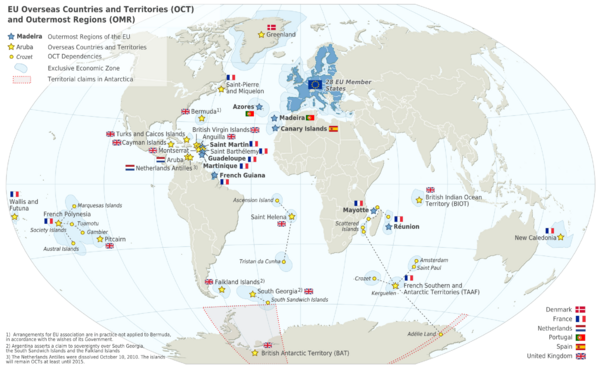
As of March 2011, France has five overseas departments and regions:
- French Guiana: Located in South America.
- Guadeloupe: Found in the Caribbean Sea.
- Martinique: Also in the Caribbean Sea.
- Mayotte: In the Indian Ocean, near East Africa.
- Réunion: Also in the Indian Ocean, near East Africa.
In Guadeloupe and Réunion, there are separate councils for the department and the region. But in Mayotte, French Guiana, and Martinique, these two government levels are combined into one body. This single body handles both sets of powers. These overseas areas gained more powers in 1982. This was part of France's plan to give more control to local governments. The term "overseas region" officially started in 2003.
A Look at History
France has had overseas territories for a long time. The idea of making them "departments" like those in mainland France isn't new. One early attempt was in 1797. After Napoleon took over the Republic of Venice, some Ionian Islands became French departments. But this didn't last long.
After World War II, under the 1947 Constitution, several French colonies officially became overseas departments. These included Guadeloupe, Martinique, French Guiana, and Réunion. Algeria was also an overseas department but became independent in 1962. The others are still French departments today.
Since 1982, the French government has worked to give more power to local areas. This policy is called decentralisation. Because of this, overseas departments now have elected regional councils. These councils have powers similar to those in mainland France. In 2003, the French Constitution was changed. This change officially called these areas "overseas regions." Even so, many people still use the older term "overseas department."
The overseas collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon was an overseas department from 1976 to 1985. However, it only has about 6,000 people. Because it was so small, it made more sense for it to become a "collectivity" instead.
Mayotte held a special vote in 2009. About 95% of the people voted to become an overseas department. So, Mayotte officially became an overseas department on March 31, 2011.
Population of Overseas Regions
The overseas departments and regions are home to many people. Their populations have grown a lot over the years. For example, in 1950, there were about 720,000 people living in these areas combined. By 2020, this number had grown to over 2.1 million people! This shows that these regions are active and growing parts of France.
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1950 | 720,000 | — |
| 1960 | 949,000 | +31.8% |
| 1970 | 1,194,000 | +25.8% |
| 1980 | 1,286,000 | +7.7% |
| 1990 | 1,566,000 | +21.8% |
| 2000 | 1,865,000 | +19.1% |
| 2010 | 2,148,000 | +15.2% |
| 2020 | 2,165,749 | +0.8% |
| Sources: | ||
See also
 In Spanish: Departamento y región de ultramar para niños
In Spanish: Departamento y región de ultramar para niños
- Administrative divisions of France
- Overseas France
- Overseas territory
 | John T. Biggers |
 | Thomas Blackshear |
 | Mark Bradford |
 | Beverly Buchanan |