Lion facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Lion |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Male | |
 |
|
| Female (Lioness) | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Binomial name | |
| Panthera leo (Linnaeus, 1758)
|
|
 |
|
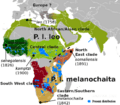
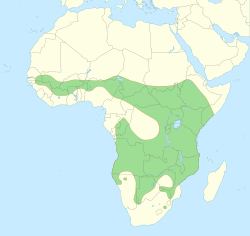
| Distribution of lions in Africa | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Linnaeus, 1758 |
|
The lion (Panthera leo) is a very large mammal that belongs to the Felidae (cat) family. Some big male lions can weigh more than 250 kilograms (about 550 pounds). Today, wild lions live in parts of Africa (south of the Sahara desert) and in Asia. Lions are good at living in grasslands and areas with a mix of trees and grass. Female lions, called lionesses, are smaller and very fast over short distances. They work together to hunt herd animals.
Long ago, lions lived on almost every continent. But over time, they disappeared from North Africa and southwest Asia. About 10,000 years ago, the lion was the most common large land mammal after humans.
Sadly, the lion is now a vulnerable species. This means their numbers are dropping. In Africa, their population went down by 30–50% in just 20 years during the late 1900s. Losing their habitat (their natural home) and conflicts with humans are the biggest problems. There are only about a quarter as many lions in Africa today as there were 40 years ago.
Lions are often called the "king of the beasts." They are used as symbols of courage. You can see them in heraldry (symbols on shields or flags) more than any other animal. They represent bravery and royalty.
In the wild, lions usually live for 10 to 14 years. If they live in zoos, they can live longer than 20 years. Male lions in the wild often don't live past 10 years because of injuries from fighting with other males.
Even though they are sometimes called the "King of the Jungle," lions don't actually live in jungles. They usually live in savannas and grasslands. These areas have some bushes and trees, but lions are mostly adapted to hunt their prey in open grasslands.
Contents
Appearance of Lions
A male lion's mane is the easiest way to tell it apart. The mane starts growing when a lion is about one year old. The color of the mane can change, and it gets darker as the lion gets older. Scientists have found that things like the average temperature where a lion lives can affect its mane's color and size. A longer mane seems to show how good a male lion is at fighting. Lions with darker manes might live longer and have more cubs that survive, even though they can get very hot in the warmest months.
How much mane a lion has, its color, and its size depend on its genes, age, climate, and how much testosterone it produces. Generally, a darker and fuller mane means a healthier lion. In the Serengeti National Park, female lions prefer to mate with males that have thick, dark manes. Some lions even have manes that go along their belly. When a male lion gets old, its mane might start to fall out. The main reason for the mane is probably to protect the lion's neck and throat during fights with other males over their territory. No other big cat looks so different between males and females.
Lions have tawny, or yellowish-brown, fur. They can grow to be about 3 meters (10 feet) long and stand about 1.2 meters (4 feet) tall. Male lions are bigger than lionesses (females). Males can weigh as much as 250 kilograms (550 pounds), which is like the weight of five average men! The more slender lioness usually weighs around 180 kilograms (400 pounds).
Both male and female lions have tufts of fur on the end of their tails. This is something no other cat has. If you could touch a male lion's tail, you would feel a sharp bone hidden inside that tail tuft.
The white lion is a rare type of lion with a genetic condition called leucism. This condition is caused by a special gene. White lions are not albinos; they have normal color in their eyes and skin. White lions have only been seen in and around Kruger National Park and the nearby Timbavati Private Game Reserve in South Africa. They were taken from the wild in the 1970s, which reduced their numbers. However, 17 white lion cubs have been born in five different prides between 2007 and 2015.
The largest lion ever recorded was almost 3.6 meters (11.8 feet) long and weighed nearly 400 kilograms (900 pounds).
- Size Comparison
* Female lions are usually 140–175 cm (4.6–5.7 ft) long from head to body, with tails 70–100 cm (2.3–3.3 ft) long. They weigh between 120–182 kg (265–401 lb). * Male lions are typically 170–298 cm (5.6–9.8 ft) long from head to body, with tails 90–105 cm (3.0–3.4 ft) long. They weigh between 150–250 kg (331–551 lb).
Lion Behavior
Compared to other cats, lions are very social animals. A group of lions is called a pride. A pride usually includes related female lions, their young cubs, and one or two adult male lions. Female lions often hunt together. Lions are the only big cats that live in such large groups. A pride can have anywhere from 10 to 40 lions. Each pride has its own home area, called its territory. Lions don't let other meat-eating animals hunt in their territory. A territory can be as big as 260 square kilometers (100 square miles).
Each lion's roar is unique, like a fingerprint. Lions use their roars to mark their territory and warn off other lions from different prides or lone lions. Male lions usually do this roaring to compete with each other. Lions also have the loudest roar of any cat, which can be heard from up to eight kilometers (five miles) away!
Lions are not built for speed like cheetahs. Instead, they are good at hunting together in a group. This is quite unusual for cats. The female lions usually do most of the hunting for the pride. However, the males can sometimes help, especially when they need to take down very large animals. Lions have long claws that can be pulled back into their paws. These claws act like hooks to hold onto prey. Even though a lion is a skilled hunter, they are not usually considered the most dangerous animals to humans.
Lion Diet
Lions are carnivores, meaning they eat meat. They are also scavengers, which means they eat animals that are already dead. More than half of what they eat is meat from dead animals. Lions will scavenge animals that died from natural causes (like disease) or animals killed by other predators. They constantly watch for circling vultures, because vultures flying in circles often mean there's a dead or injured animal nearby.
Lions eat large prey like gazelles, antelopes, zebras, wildebeests, giraffes, and buffalo. They have even been known to hunt elephants, but only when all the adult lions in the pride work together. Even elephants are afraid of hungry lions. When food is hard to find, lions will hunt smaller animals or sometimes steal the kills of other animals. A lion can eat up to 69 kilograms (152 pounds) of meat in one day!
A lion can run as fast as 80 kilometers per hour (50 mph) for short distances. They can also leap more than 9 meters (30 feet). However, most prey animals can run much faster than an average lion. Because of this, lions hunt in well-organized groups. They will stalk, or sneak up on, their prey. They might try to surround the animals first, then make a quick, sudden charge from the tall grass. A lion's eyesight is five times better than a human's, and they can hear prey that is more than a mile away.
The grass where lions live is not short and green. Most of the time, it grows very tall and is a light brownish color. The lions' fur is the same color as this grass. This makes it hard for other animals to see them. This kind of coloring that helps an animal hide is called "camouflage."
Lions might spend hours stalking their prey, but the actual kill happens in just minutes. After a kill is made, the female lions let out low roars. This tells the rest of the pride to come and eat. Adult males eat first, then the females, and then the cubs. It can take up to four hours for a pride of lions to finish eating. Lions rarely eat an entire animal; hyenas and vultures usually finish the rest. After eating, a thirsty lion might drink water for as long as 20 minutes.
To avoid the dangerous heat of the midday sun, lions usually hunt at night. The dim light helps them stay hidden from their prey. Lions have very good night vision, so the darkness is not a problem for them. Animals that are active at night, like lions, are called nocturnal creatures.
Lion Reproduction and Life Cycle
A lioness is ready to have young when she is 2-3 years old. Baby lions are called cubs. Cubs are born after about 3 and a half months. When cubs are born, they are blind. Their eyes don't open until they are about a week old, and they can't see well until they are about two weeks old. Lions don't have a permanent den (home) where they live for a long time. The lioness hides her cubs in thick bushes, gullies, or rocky areas. If other predators have seen the hiding place, the lioness will move her cubs to a new, safer spot. The cubs are usually introduced to the rest of the pride when they are about 6 weeks old.
Cubs are very vulnerable when the lioness goes out to hunt and has to leave them behind. Also, when a new male lion takes over a pride from another male, he usually kills all the existing cubs. This makes the cub's mothers ready to mate with the new pride male, so the next cubs born will be his offspring. A lioness usually gives birth to 2-6 cubs, but most often 2-3. Sadly, only 1-2 cubs usually survive until they are old enough to be introduced to the pride, where the whole pride helps protect them.
In zoos, lions have been known to breed with tigers. If the parents are a male lion and a female tiger, the offspring is called a liger. A tigon is born from a male tiger and a female lion.
Lions in Heraldry
Lions appear in heraldry (symbols on shields, flags, or coats of arms) more often than any other animal. They traditionally symbolize courage, bravery, and royalty. They can be shown in many different ways on a shield or as a crest. One reason lions are shown in so many different ways is that when heraldry first started, many people wanted a lion on their coat of arms, but no two coats of arms can be exactly the same.
Images for kids
-
Skull of an American lion on display at the National Museum of Natural History.
-
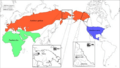
red Panthera spelaea
blue Panthera atrox
green Panthera leo
The largest areas where modern lions
and their ancient relatives lived
in the late Pleistocene. -
A stone carving of a wounded lioness from Nineveh, around 645–635 BC.
-
The famous Tsavo maneaters of East Africa on display in the Field Museum of Natural History in Chicago.
-
A granite statue of the Egyptian goddess Sekhmet from the Luxor Temple, made around 1403–1365 BC.
-
A roaring lion from the Throne Room of Nebuchadnezzar II, 6th century BC, from Babylon, Iraq.
-
Dorothy Gale meets the Cowardly Lion in The Wonderful Wizard of Oz. Art by W. W. Denslow, 1900.
See also
 In Spanish: León para niños
In Spanish: León para niños
 | Tommie Smith |
 | Simone Manuel |
 | Shani Davis |
 | Simone Biles |
 | Alice Coachman |