Popigai impact structure facts for kids

Landsat image of Popigai crater
|
|
| Impact crater/structure | |
|---|---|
| Confidence | Confirmed |
| Diameter | 90 km (56 mi) |
| Age | 35.7 ± 0.2 Ma Late Eocene |
| Exposed | Yes |
| Drilled | Yes |
| Bolide type | H chondrite |
| Location | |
| Coordinates | 71°39′N 111°11′E / 71.650°N 111.183°E |
| Country | Russia |
| State | Krasnoyarsk |
The Popigai impact structure is what's left of a giant impact crater in northern Siberia, Russia. An impact crater is a big hole made when a space rock hits Earth. This crater is one of the four largest confirmed impact structures on our planet. It is tied with the Manicouagan structure in Canada.
A very large space rock, called a bolide, crashed here about 35 million years ago. This happened during a time period known as the late Eocene epoch. The crash created a huge crater about 100-kilometre (62 mi) wide. Some scientists think this event might be connected to a big extinction event that happened around the same time.
The Popigai structure is located about 300 km (190 mi) east of a village called Khatanga. It's also about 880 km (550 mi) northeast of the city of Norilsk. UNESCO has named it a Geopark, which means it's a special place because of its unique geology. It's possible that the Popigai crater formed at the same time as the Chesapeake Bay and Toms Canyon craters. These are also about 35 million years old.
For many years, scientists called paleontologists (who study ancient life) and geologists (who study Earth's rocks) were very interested in Popigai. However, the area was closed off because of the valuable diamonds found there. In 1997, a major scientific trip was finally allowed. This trip helped scientists learn much more about the crater. They believe the space rock that hit Earth was an H chondrite asteroid. It was likely several kilometers wide.
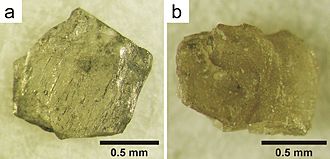
The extreme pressure from the impact instantly changed graphite in the ground into diamonds. This happened within about 13.6 km (8.5 mi) of where the space rock hit. These diamonds are usually very small, about 0.5 to 2 mm (0.020 to 0.079 in) across. However, some special ones can be as large as 10 mm (0.39 in). The diamonds kept the flat shape of the original graphite grains. They also have the same delicate lines, called striations, that the graphite crystals had.
Popigai's Unique Diamonds
Most diamonds used in industries today are made by humans in factories. These are called synthetic diamonds. The diamonds at Popigai have not been mined because the location is very remote. There are no roads or buildings nearby to help with mining. Also, these diamonds are not likely to be cheaper than synthetic ones.
Many of the diamonds found at Popigai contain a special type of carbon called lonsdaleite. Lonsdaleite is an allotrope of carbon, which means it's a different form of carbon, just like graphite and regular diamond are. Lonsdaleite has a hexagonal crystal structure. When made purely in a lab, lonsdaleite can be up to 58% harder than regular diamonds.
These special diamonds are known as "impact diamonds." This is because they are created when a meteorite crashes into a deposit of graphite at very high speed. They might be useful for industrial purposes, like cutting tools. However, they are not suitable to be used as gems for jewelry.
Scientists have also found even harder forms of carbon in the crater. These are called carbon polymorphs. They are a mix of diamond and lonsdaleite, and they are even harder than pure lonsdaleite.
See also
 In Spanish: Cráter Popigai para niños
In Spanish: Cráter Popigai para niños
- List of impact craters on Earth
- List of possible impact structures on Earth
- Logancha crater
 | Aaron Henry |
 | T. R. M. Howard |
 | Jesse Jackson |