Proso millet facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Proso millet |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Proso millet panicles | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Monocots |
| Clade: | Commelinids |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Genus: | Panicum |
| Species: |
P. miliaceum
|
| Binomial name | |
| Panicum miliaceum |
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
Panicum miliaceum is a type of grain plant. It has many common names, like proso millet, broomcorn millet, common millet, hog millet, red millet, and white millet.
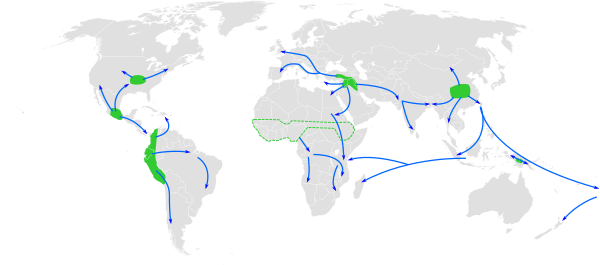
Scientists who study ancient plants believe proso millet was first grown by people about 10,000 years ago. This happened in Northern China. Today, it is grown in many countries. These include China, India, Russia, Ukraine, and the United States.
Proso millet is special because it grows very quickly. Some types can produce grain in just 60 days after being planted. It also does not need much water. This makes it a very efficient crop for dry areas. Proso millet is related to other grains like foxtail millet and maize (corn).
Contents
How Proso Millet Developed
Proso millet is a special plant because it has twice the usual number of chromosomes. Scientists think it formed from two different types of Panicum plants joining together.
One of its original plant parts might have come from a plant like Panicum capillare. The other part is still a mystery. It does not look like any known Panicum plant today.
Scientists believe these two original plants separated about 5.6 million years ago. In 2019, scientists mapped out the entire genetic code of proso millet. This helps us understand how it grows and develops.
History of Growing Proso Millet
Wild versions of proso millet grow across central Asia. This area stretches from the Caspian Sea to Mongolia. These wild plants might be the ancestors of today's proso millet. They could also be plants that escaped from farms and became wild again.
The oldest proof of farmed proso millet comes from China. It was found at a place called Cishan. This evidence dates back to about 8,000 BCE. Early proso millet grew very fast, sometimes in just 45 days. This quick growth may have helped early people start farming. It was a bridge between hunting and gathering and settled farm life.
Evidence of proso millet farming in Europe dates back to at least 5,000 BCE. This was found in places like Georgia and Germany. It might have spread from Asia along old trade routes. Or, it could have been grown independently in Europe.
How to Grow Proso Millet
Proso millet is a tough plant that does not need much care. It is not often affected by diseases. Because of this, it is often used in organic farming in Europe. In the United States, farmers sometimes plant it between other crops.
This helps keep the soil covered and healthy. Proso millet has shallow roots. This means the soil can store water for the next crop. Its leftover stalks can also help collect snow, which adds more water to the soil.
Climate and Soil Needs
Proso millet loves warm weather, like corn. It grows best in sunny spots. It does not like temperatures below 10 to 13°C. This plant is very good at handling dry conditions. This makes it a great crop for places that do not get much rain.
The soil should be light or medium-heavy. Proso millet has flat roots, so the soil should not be too packed down. It also does not like very wet soil.
Preparing the Ground and Planting Seeds
The ground for planting should be finely broken up, like for sugar beets. In Europe, farmers plant proso millet from mid-April to the end of May. They use about 500 grams of seeds per acre. This is about 500 seeds per square meter.
Farmers can use regular planting machines, similar to those used for wheat. It is good to leave 16 to 25 cm between rows. This allows for machines to work between the rows later. Seeds should be planted 1.5 to 2 cm deep in good soil. In dry soil, they can be planted 3 to 4 cm deep. Rolling the ground after planting can help.
Some farmers in the United States use "no-till farming." This means they plant seeds without turning over the soil first. This is also possible with proso millet.
Taking Care of the Field
Proso millet usually does not have many problems with diseases or pests. Weeds are a bigger issue. It is very important to control weeds when the plant is young. This is when the grains start to form. After this, the millet needs all the nutrients.
In regular farming, farmers might use herbicides to kill weeds. In organic farming, they can use a harrow weeder or a machine that works between rows.
To help the crop grow well, farmers often add nitrogen to the soil. It is best not to plant proso millet after corn. This is because they can have the same weed problems. Since proso millet is an easy crop, it can be planted at the end of a crop rotation cycle.
Harvesting and After-Harvest Care
Proso millet is usually harvested from late August to mid-September. It can be tricky to know the exact best time to harvest. This is because not all the grains ripen at the same time. The grains at the top of the plant ripen first. Grains at the bottom need more time. Farmers try to harvest at the best time to get the most grain.
A regular combine harvester can be used. The grains should have about 15-20% moisture. Often, proso millet is first cut into rows called windrows. This helps the plants dry out. Then, a combine harvester with a special attachment picks up the dried plants.
Farmers can get between 2.5 and 4.5 tons of grain per hectare. Studies in Germany have shown that even higher amounts are possible.
Proso Millet in the United States
About half of the proso millet grown in the United States is in eastern Colorado. It covers about 340,000 acres. For a long time, it was mostly used as food for animals and birds. But since 2020, it has become popular as an organic, gluten-free grain for people.
Uses of Proso Millet

| Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) | |
|---|---|
| Energy | 1,597 kJ (382 kcal) |
|
75.1 g
|
|
| Dietary fiber | 3.5 g |
|
4.2 g
|
|
|
Protein
|
10.8 g
|
| Vitamins | Quantity
%DV†
|
| Thiamine (B1) |
35%
0.4 mg |
| Riboflavin (B2) |
6%
0.07 mg |
| Niacin (B3) |
38%
6 mg |
| Pantothenic acid (B5) |
26%
1.3 mg |
| Vitamin B6 |
28%
0.37 mg |
| Folate (B9) |
11%
42 μg |
| Vitamin E |
1%
0.11 mg |
| Vitamin K |
1%
0.8 μg |
| Minerals | Quantity
%DV†
|
| Calcium |
1%
14 mg |
| Iron |
30%
3.9 mg |
| Magnesium |
34%
119 mg |
| Manganese |
48%
1 mg |
| Phosphorus |
41%
285 mg |
| Potassium |
7%
224 mg |
| Sodium |
0%
4 mg |
| Zinc |
27%
2.6 mg |
| Other constituents | Quantity |
| Water | 8.7 g |
|
Full Report of USDA Database entry
|
|
| †Percentages estimated using US recommendations for adults. | |
Proso millet is not grown in Africa, unlike some other types of millet. In the United States, Russia, and parts of South America, it is mainly used as food for farm animals. As animal feed, it is missing some important nutrients like lysine. So, other foods need to be added.
Proso millet is also not the best animal feed on its own. This is because it has fewer leaves compared to its stems. Its stems can also be a bit prickly. Foxtail millet is often preferred for animal feed.
Recently, people have been looking for new ways to use proso millet. For example, the starch from millet can be used to make ethanol. This is a type of alcohol that can be used as fuel. Scientists are working to make proso millet even better for producing ethanol.
Since proso millet grows well with little care, it could be grown on less fertile land. This could create a new market for farmers.
People in richer countries are also looking for more varied and healthy foods. This could open up new markets for proso millet in human diets. Proso millet grains have a similar amount of protein as wheat. But they have more of some important amino acids. These include leucine, isoleucine, and methionine.
Proso millet also has healthy plant compounds. Its high calcium content is good for strong bones and teeth. Some popular foods made from proso millet include breakfast cereals. It is also used in noodles and baked goods. These are often mixed with wheat flour to make them taste better.
Pests of Proso Millet
A few insect pests can attack proso millet. However, they usually do not cause major economic damage.
- Pests that attack young plants
- shoot fly (Atherigona pulla)
- wheat stem maggot (Meromyza americana)
- thrip (Haplothrips aculeatus)
- armyworms (like Mythimna separata and Spodoptera frugiperda)
- field cricket (Brachytrupes sp.)
- Pests that attack stems
- stem borers (like Chilo partellus and Sesamia inferens)
- Pests that eat leaves
- leaf folders (Cnaphalocrocis medinalis)
- hairy caterpillar (Spilosoma obliqua)
- rice butterfly (Melanitis leda)
- Moroccan locust (Dociostaurus maroccanus)
- migratory locust (Locusta migratoria)
- grasshoppers (like Hieroglyphus banian)
- Pests that attack the grain heads
- cotton boll worm (Helicoverpa zea)
- Other pests
- aphid (Sipha flava)
- earhead bug (Leptocorisa acuta) and green bug (Nezara viridula) suck the milky grains in India.
- termites (Odontotermes spp. and Microtermes spp.) are common in dry seasons in India.
Names in Other Languages
Here are some names for proso millet in other languages:
- Bengali: cheena (Bengali)
- Odia: china bachari bagmu (Odia)
- Kannada: baragu (Kannada)
- Telugu: variga (Telugu)
- Hindi: chena or barri (Hindi)
- Punjabi: cheena (Punjabi)
- Gujarati: cheno (Gujarati)
- Marathi: varaī (Marathi)
- Tamil: pani varagu (Tamil)
- Nepali: dudhe (Nepali)
Images for kids
id:Juwawut
See also
 In Spanish: Mijo común para niños
In Spanish: Mijo común para niños