Qinhuangdao facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Qinhuangdao
秦皇岛市
|
||
|---|---|---|
|
Prefecture-level city
|
||
|
Clockwise from the top: City view, Shanhai Pass, Longtan Falls, Yan Mountains, Old Dragon Head, Habitat Apartments
|
||
|
||
| Nickname(s):
Back Garden of Beijing and Tianjin (京津后花园)
|
||
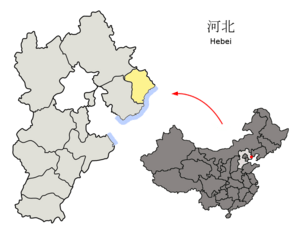
Location of Qinhuangdao City in Hebei Province
|
||
| Country | People's Republic of China | |
| Province | Hebei | |
| Settled | 1737 | |
| Established | March 3, 1983 | |
| Municipal seat | Haigang District | |
| Area | ||
| • Prefecture-level city | 7,791.57 km2 (3,008.34 sq mi) | |
| • Urban | 2,122.9 km2 (819.7 sq mi) | |
| • Metro | 2,122.9 km2 (819.7 sq mi) | |
| Population
(2020 census)
|
||
| • Prefecture-level city | 3,136,879 | |
| • Density | 402.5991/km2 (1,042.7269/sq mi) | |
| • Urban | 1,881,047 | |
| • Urban density | 886.074/km2 (2,294.92/sq mi) | |
| • Metro | 1,881,047 | |
| • Metro density | 886.074/km2 (2,294.92/sq mi) | |
| GDP | ||
| • Prefecture-level city | CN¥ 184 billion US$ 22.2 billion |
|
| • Per capita | CN¥ 48,230 US$7,143 |
|
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) | |
| Postal code |
066000
|
|
| Area code(s) | (0)335 | |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-HE-03 | |
| Licence Plate Prefix | 冀C | |
| Website | www.qhd.gov.cn | |
| Qinhuangdao | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

"Qinhuangdao", as written in Simplified Chinese (top) and Traditional Chinese (bottom)
|
|||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 秦皇岛 | ||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 秦皇島 | ||||||||
| Literal meaning | Qin Shi Huang Island | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
Qinhuangdao (/ˈtʃɪnˈhwɑːŋˈdaʊ/; Chinese: 秦皇岛) is a port city located on the coast of northern Hebei province in China. It is a large city that manages several smaller areas, known as a prefecture-level city. Qinhuangdao is about 300 kilometers (186 miles) east of Beijing, right on the Bohai Sea, which is part of the Yellow Sea.
In 2020, about 3.1 million people lived in Qinhuangdao. More than 1.8 million of these people lived in the main city area, which includes four urban districts.
Contents
History of Qinhuangdao
The name "Qinhuangdao" means "Qin Emperor island." It comes from a story about the first emperor of China, Qin Shi Huang. He is said to have visited a mountain area near here in 210 BC, looking for a way to live forever.
The "island" part of the name refers to an area that used to be a small island offshore. This island later became connected to the mainland. This happened in the late 1800s when the port was built. Dirt and sand from digging out the harbor were used to connect the island to the land.
In the 19th century, Qinhuangdao was made up of two separate towns. These towns were important stops on the Peking–Mukden Railway. Engineers from Britain helped design and build the new harbor and port around 1900.
During the start of the Chinese Civil War, soldiers landed in Qinhuangdao. They used this city because other ports were not available.
Qinhuangdao was also a special place for the 2008 Summer Olympics. The Qinhuangdao Olympic Sports Center Stadium hosted some of the soccer games.
Geography and Climate
Qinhuangdao is located on the northwest coast of the Bohai Sea. It shares borders with Tangshan to the southwest, Chengde to the northwest, and Liaoning province to the northeast. The city covers a total area of about 7,812 square kilometers (3,016 square miles).
Since the city of Tianjin became a special province-level city, Qinhuangdao has become the main port for Hebei province.
Qinhuangdao has three main developed areas:
- Beidaihe: This is a popular summer resort by the sea. Important government officials often come here for vacations.
- Haigang: This is the main harbor city and the heart of Qinhuangdao. It is home to Yan Shan University, a leading university in the area.
- Shanhaiguan: This is a famous place for tourists. You can see the eastern end of the Great Wall here.
Weather in Qinhuangdao
Qinhuangdao has a climate with four clear seasons. Winters are cold and dry, with winds often blowing from the northwest. The average temperature in January is about -5.6°C (21.9°F). Summers are hot and humid, with warm air coming from the sea. The average high temperature in July is about 28.3°C (82.9°F). Most of the rain falls from June to August.
| Climate data for Qinhuangdao (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1971–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 12.7 (54.9) |
18.3 (64.9) |
25.6 (78.1) |
28.6 (83.5) |
37.1 (98.8) |
39.2 (102.6) |
39.2 (102.6) |
35.2 (95.4) |
34.2 (93.6) |
29.5 (85.1) |
21.6 (70.9) |
14.0 (57.2) |
39.2 (102.6) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 0.1 (32.2) |
2.9 (37.2) |
9.2 (48.6) |
16.4 (61.5) |
22.4 (72.3) |
25.5 (77.9) |
28.3 (82.9) |
28.5 (83.3) |
25.3 (77.5) |
18.6 (65.5) |
9.7 (49.5) |
2.3 (36.1) |
15.8 (60.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −5.6 (21.9) |
−2.7 (27.1) |
3.7 (38.7) |
11.0 (51.8) |
17.3 (63.1) |
21.3 (70.3) |
24.7 (76.5) |
24.4 (75.9) |
19.8 (67.6) |
12.4 (54.3) |
3.9 (39.0) |
−3.1 (26.4) |
10.6 (51.0) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −10.6 (12.9) |
−7.5 (18.5) |
−1.3 (29.7) |
6.1 (43.0) |
12.3 (54.1) |
17.5 (63.5) |
21.5 (70.7) |
20.6 (69.1) |
14.8 (58.6) |
6.9 (44.4) |
−1.0 (30.2) |
−7.7 (18.1) |
6.0 (42.7) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −26.0 (−14.8) |
−18.6 (−1.5) |
−13.1 (8.4) |
−5.0 (23.0) |
3.0 (37.4) |
9.9 (49.8) |
14.2 (57.6) |
11.4 (52.5) |
4.4 (39.9) |
−6.4 (20.5) |
−11.8 (10.8) |
−17.7 (0.1) |
−26.0 (−14.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 2.6 (0.10) |
4.3 (0.17) |
7.9 (0.31) |
24.4 (0.96) |
47.6 (1.87) |
86.3 (3.40) |
171.2 (6.74) |
163.9 (6.45) |
47.0 (1.85) |
28.1 (1.11) |
15.0 (0.59) |
3.6 (0.14) |
601.9 (23.69) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 1.6 | 2.1 | 2.9 | 5.4 | 6.9 | 10.1 | 11.3 | 9.3 | 6.6 | 4.6 | 3.9 | 2.0 | 66.7 |
| Average snowy days | 2.8 | 2.4 | 1.6 | 0.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 1.6 | 2.6 | 11.4 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 54 | 56 | 56 | 58 | 64 | 77 | 83 | 81 | 73 | 65 | 58 | 54 | 65 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 189.3 | 187.4 | 235.4 | 243.5 | 262.0 | 218.2 | 188.4 | 209.9 | 221.6 | 204.7 | 174.7 | 178.5 | 2,513.6 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 63 | 62 | 63 | 61 | 59 | 49 | 42 | 50 | 60 | 60 | 59 | 62 | 58 |
| Source 1: China Meteorological Administration | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Weather China | |||||||||||||
City Districts and Areas
Qinhuangdao is divided into several smaller areas. These include urban districts, suburban districts, and rural counties.
| Map | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
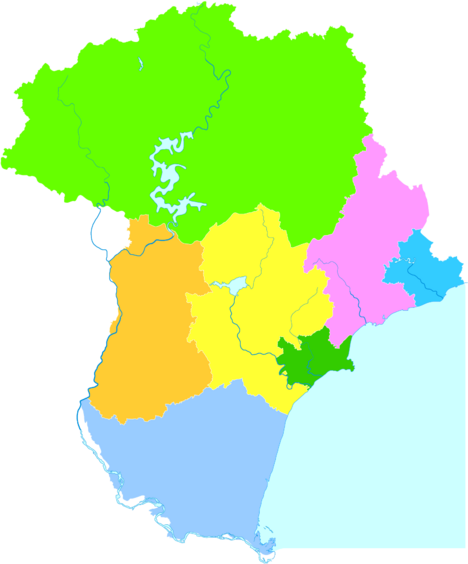
Haigang
Shanhaiguan
Beidaihe
Funing
Qinglong
County Changli
County Lulong
County |
|||||
| Name | Chinese | Pinyin | Population
(2020) |
Area
(km2) |
Density (/km2) |
| Urban Areas | |||||
| Haigang District | 海港区 | Hǎigǎng Qū | 1,024,876 | 754.3 | 4,166 |
| Suburban Areas | |||||
| Shanhaiguan District | 山海关区 | Shānhǎiguān Qū | 164,989 | 205.8 | 855 |
| Beidaihe District | 北戴河区 | Běidàihé Qū | 130,104 | 158.1 | 822.9 |
| Funing District | 抚宁区 | Fǔníng Qū | 291,211 | 1,039 | 352.2 |
| Rural Areas | |||||
| Changli County | 昌黎县 | Chānglí Xiàn | 487,989 | 1,228 | 397.4 |
| Lulong County | 卢龙县 | Lúlóng Xiàn | 333,942 | 959.0 | 348.2 |
| Qinglong Manchu Autonomous County | 青龙满族自治县 | Qīnglóng Mǎnzú Zìzhìxiàn | 431,138 | 3,508 | 122.9 |
Economy and Development
Qinhuangdao has a special area called the Qinhuangdao Economic & Technology Development Zone. This zone was created in 1984 to help the city grow economically. It is close to Beijing (280 km or 174 miles) and Tianjin (245 km or 152 miles). Many businesses, including foreign ones, have invested here.
The city also has an Export Processing Zone. This zone helps companies that make products for export. Industries like electronics, building materials, and computer software are encouraged here.
Qinhuangdao Port
The Qinhuangdao Port is very important for China. It is the largest port in the country for shipping coal. A lot of this coal goes to power plants in other parts of China. The port has been growing and can now handle over 200 million metric tons of goods. It is adding more berths to increase its capacity even further.
China is one of the world's largest coal exporters. Qinhuangdao is expected to handle a lot of these exports. The railway lines that bring coal from Shanxi (China's biggest coal producer) to Qinhuangdao Port are being improved. This will allow the port to handle even more coal in the future.
Many Chinese and foreign companies are moving to Qinhuangdao to support the port's growth. Shipping companies are investing billions of dollars to improve ports across China.
Qinhuangdao is connected by the Beijing−Shenyang Expressway, which links Beijing with Shenyang. The city also has an airport, Qinhuangdao Beidaihe Airport.
Tourism and Attractions
Qinhuangdao offers several attractions for visitors.
- The Qinhuangdao Wildlife Park opened in 1995. It is one of the largest wildlife parks in China.
- The Tanghe River Park is famous for its "Red Ribbon." This is a unique steel sculpture that runs through the park. It provides seating, lighting, and highlights native plants. This project has won awards for its design.
Education in Qinhuangdao
Qinhuangdao is home to several universities and colleges:
- Yanshan University
- Northeastern University at Qinhuangdao
- Hebei Institute of International Business and Economics
- Hebei Normal University of Science and Technology
- Northeastern Petroleum University at Qinhuangdao
Sister Cities
Qinhuangdao has friendly relationships with several cities around the world. These are called "sister cities":
 Lugo, Spain
Lugo, Spain Pesaro, Italy
Pesaro, Italy Toledo, Ohio, United States (since 1985)
Toledo, Ohio, United States (since 1985) Honolulu, Hawaii, United States (since 2010)
Honolulu, Hawaii, United States (since 2010) Terrace, British Columbia, Canada (since 2015)
Terrace, British Columbia, Canada (since 2015)
See also
 In Spanish: Qinhuangdao para niños
In Spanish: Qinhuangdao para niños