Chengde facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Chengde
承德市
Chengte, Jehol
|
|
|---|---|
|
Prefecture-level city
|
|
|
Clockwise from top: Jinshanling, Mountain Resort, Skyline of Chengde, Putuo Zongcheng Temple, Sledgehammer Peak
|
|
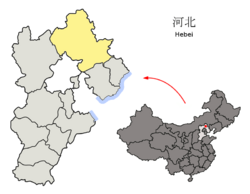
Location of Chengde City jurisdiction in Hebei
|
|
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Hebei |
| Settled | 1681 |
| Established | November 15, 1983 |
| Municipal seat | Shuangqiao District |
| Area | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 39,519 km2 (15,258 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 724.03 km2 (279.55 sq mi) |
| • Districts | 1,252.7 km2 (483.7 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 327 m (1,073 ft) |
| Population | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 3,473,200 |
| • Density | 91/km2 (240/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 920,395 |
| • Urban density | 1,271.211/km2 (3,292.422/sq mi) |
| • Districts | 642,000 |
| GDP | |
| • Prefecture-level city | CN¥ 135.9 billion US$ 21.8 billion |
| • Per capita | CN¥ 38,506 US$6,182 |
| Area code(s) | 314 |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-HE-08 |
| License Plate Prefix | 冀H |
| Website | http://www.chengde.gov.cn |
|
Pagoda Tree Rugosa Rose |
|
| Chengde | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese name | |||||||||
| Chinese | 承德 | ||||||||
| Postal | Chengte | ||||||||
| Literal meaning | Upholding Virtue Receiving Virtue |
||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Rehe | |||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 熱河(兒) | ||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 热河(儿) | ||||||||
| Postal | Jehol | ||||||||
| Literal meaning | Hot River | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Mongolian name | |||||||||
| Mongolian Cyrillic | Халуун гол | ||||||||
| Mongolian script | ᠬᠠᠯᠠᠭᠤᠨ ᠭᠣᠣᠯ | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Manchu name | |||||||||
| Manchu script | ᠊ᡵᡩᡝᠮᡠ ᠪᡝ ᠠᠯᡳᡥᠠ | ||||||||
| Abkai | Erdemu Be Aliha | ||||||||
Chengde, once known as Jehol and Rehe, is a large city in Hebei province, China. It is located about 225 kilometers northeast of Beijing. Chengde is famous for its Mountain Resort. This huge imperial garden and palace was once used by the Qing emperors as their summer home.
About 3.47 million people live in Chengde. It's a city with a rich past and beautiful natural sights.
Contents
History of Chengde

In 1703, the Kangxi Emperor chose Chengde as his summer home. The Mountain Resort was built over many years in the 1700s. Both the Yongzheng and Qianlong emperors used it. Today, it is a special UNESCO World Heritage Site. This means it's a place of great importance to the world.
Because the emperor stayed there, Chengde became a very important political center for China during those times. The city, also called Jehol, was at its busiest under the Qianlong Emperor (1735-1796).
One amazing building is the Putuo Zongcheng Temple. It was finished in just four years in 1771. This temple looks a bit like the Potala Palace in Lhasa, Tibet. It was decorated with lots of gold, and the emperor would worship there.
During the time of the Republic of China, Chengde was the capital of Rehe province. From 1933 to 1945, Japan controlled the city. It was part of a state called Manchukuo. After World War II, the Chinese government took control again. In 1948, the People's Liberation Army took over Chengde. The city stayed part of Rehe until 1955. Then, Rehe province was removed, and Chengde became part of Hebei province.
Chengde is home to many different ethnic groups. The Mongol and Manchu people are especially common here.
Geography and Climate
Chengde is in the northeastern part of Hebei province. It borders Inner Mongolia, Liaoning, Beijing, and Tianjin. It's the largest city area in Hebei province. Most of its land is mountainous.
The city used to be named after the Jehol or Rehe River. "Rehe" means "Hot River" because it didn't freeze in winter. Now, most of the river's path is dry because of modern dams.
Chengde's Weather
Chengde has four seasons, like many places. Winters are long, cold, and windy, but they are also dry. Summers are hot and humid. Because Chengde is higher up than Beijing, its temperatures are cooler.
In January, the average temperature is about -9.3°C (15.3°F). In July, it's about 24.2°C (75.6°F). Spring brings quick warming, but sometimes dust storms can blow in. Autumn also cools down quickly. Most of the rain falls during the three summer months. Chengde gets a lot of sunshine throughout the year.
| Climate data for Chengde, elevation 422 m (1,385 ft), (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1951–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 8.8 (47.8) |
18.9 (66.0) |
28.4 (83.1) |
31.6 (88.9) |
39.3 (102.7) |
38.8 (101.8) |
43.3 (109.9) |
38.9 (102.0) |
35.4 (95.7) |
30.1 (86.2) |
20.1 (68.2) |
12.2 (54.0) |
43.3 (109.9) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | −1.4 (29.5) |
3.4 (38.1) |
11.1 (52.0) |
19.6 (67.3) |
26.0 (78.8) |
29.4 (84.9) |
30.7 (87.3) |
29.5 (85.1) |
24.9 (76.8) |
17.3 (63.1) |
7.2 (45.0) |
−0.5 (31.1) |
16.4 (61.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −8.8 (16.2) |
−4.4 (24.1) |
3.3 (37.9) |
11.8 (53.2) |
18.2 (64.8) |
22.1 (71.8) |
24.3 (75.7) |
22.9 (73.2) |
17.1 (62.8) |
9.3 (48.7) |
0.0 (32.0) |
−7.5 (18.5) |
9.0 (48.2) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −14.4 (6.1) |
−10.6 (12.9) |
−3.5 (25.7) |
4.3 (39.7) |
10.7 (51.3) |
15.9 (60.6) |
19.3 (66.7) |
17.7 (63.9) |
11.1 (52.0) |
3.1 (37.6) |
−5.4 (22.3) |
−12.6 (9.3) |
3.0 (37.3) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −27.0 (−16.6) |
−23.7 (−10.7) |
−19.5 (−3.1) |
−8.3 (17.1) |
1.0 (33.8) |
7.4 (45.3) |
12.5 (54.5) |
7.9 (46.2) |
−0.1 (31.8) |
−10.6 (12.9) |
−18.8 (−1.8) |
−23.2 (−9.8) |
−27.0 (−16.6) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 1.5 (0.06) |
3.9 (0.15) |
7.9 (0.31) |
22.7 (0.89) |
49.5 (1.95) |
95.7 (3.77) |
141.1 (5.56) |
101.5 (4.00) |
49.4 (1.94) |
30.9 (1.22) |
10.4 (0.41) |
2.0 (0.08) |
516.5 (20.34) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 1.4 | 1.9 | 3.1 | 4.8 | 7.5 | 12.0 | 13.3 | 10.7 | 7.7 | 5.1 | 3.1 | 1.6 | 72.2 |
| Average snowy days | 2.7 | 2.7 | 2.7 | 0.8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.4 | 2.6 | 2.5 | 14.4 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 52 | 46 | 41 | 40 | 47 | 62 | 73 | 74 | 70 | 61 | 58 | 55 | 57 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 196.2 | 198.6 | 234.9 | 243.2 | 265.2 | 221.3 | 197.0 | 212.3 | 217.2 | 215.2 | 182.1 | 182.0 | 2,565.2 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 66 | 66 | 63 | 61 | 59 | 49 | 43 | 50 | 59 | 63 | 62 | 64 | 59 |
| Source: China Meteorological Administration | |||||||||||||
Chengde's Divisions
Chengde is divided into several smaller areas. These include districts and counties.
| Map | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
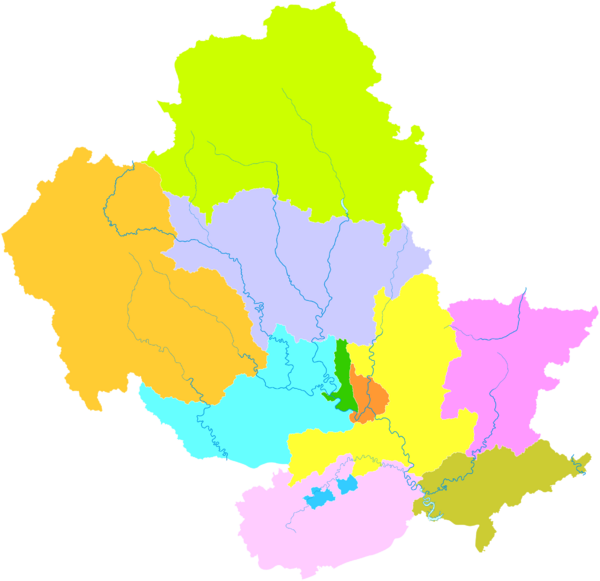
Shuangqiao
Shuangluan
Yingshouyingzi
Chengde
County Xinglong
County Luanping
County Longhua
County Kuancheng
County Weichang
County Pingquan
(city) |
||||||
| Name | Hanzi | Hanyu Pinyin | Population (2004 est.) |
Area (km2) | Density (/km2) | |
| Shuangqiao District | 双桥区 | Shuāngqiáo Qū | 290,000 | 311 | 932 | |
| Shuangluan District | 双滦区 | Shuāngluán Qū | 100,000 | 250 | 400 | |
| Yingshouyingzi Mining District | 鹰手营子 矿区 |
Yīngshǒuyíngzi Kuàngqū |
70,000 | 148 | 473 | |
| Pingquan City | 平泉市 | Píngquán Shì | 470,000 | 3,297 | 143 | |
| Chengde County | 承德县 | Chéngdé Xiàn | 470,000 | 3,990 | 118 | |
| Xinglong County | 兴隆县 | Xīnglóng Xiàn | 320,000 | 3,116 | 103 | |
| Luanping County | 滦平县 | Luánpíng Xiàn | 320,000 | 3,195 | 100 | |
| Longhua County | 隆化县 | Lónghuà Xiàn | 420,000 | 5,474 | 77 | |
| Fengning Manchu Autonomous County |
丰宁满族 自治县 |
Fēngníng Mǎnzú Zìzhìxiàn |
380,000 | 8,747 | 43 | |
| Kuancheng Manchu Autonomous County |
宽城满族 自治县 |
Kuānchéng Mǎnzú Zìzhìxiàn |
230,000 | 1,933 | 119 | |
| Weichang Manchu and Mongol Autonomous County |
围场满族 蒙古族自治县 |
Wéichǎng Mǎnzú Měnggǔzú Zìzhìxiàn |
520,000 | 9,058 | 57 | |
Sports and Transport
Bandy in Chengde
Chengde is important for the sport of bandy in China. The very first bandy match in China took place here in January 2015. It was played between top teams from Russia and Sweden. Chengde also helped start the China Bandy Federation in December 2014. The city hosted the 2018 Women's Bandy World Championship. Eight teams from around the world competed in this event.
Getting Around Chengde
Chengde is a growing city with good transportation links. Roads and railroads connect it to Beijing. The new Jingcheng Expressway links Chengde directly to central Beijing. More highways are being planned.
The city's new airport opened on May 31, 2017. It is located about 19.5 kilometers northeast of the city center. The Beijing–Harbin high-speed railway, finished in January 2021, has five stations within Chengde. This makes travel even faster.
Main Sights to See
The Chengde Mountain Resort is a must-see. Its construction began in 1703 and finished in 1790. This huge royal garden covers an area of 5.64 million square meters. It is the largest royal garden in all of China. The wall around the resort is over 10,000 meters long! In the summer, Qing dynasty emperors came here to relax and escape Beijing's heat.
The Resort has three main parts: the lakes area, the plains area, and the hills area. The lakes area has eight lakes and covers 496,000 square meters. The plains area is where emperors held horse races and hunted. It covers 607,000 square meters. The largest part is the hills area, covering 4.435 million square meters. Many palaces and temples were built on these hills.
Outside the main wall are the Eight Outer Temples (Chinese: 外八庙). These temples were built in different styles from all over China. One of the most famous is the Putuo Zongcheng Temple. It looks like the Potala Palace in Lhasa, Tibet. The resort and these temples became a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1994. The nearby Puning Temple, built in 1755, has the world's tallest wooden statue of the Bodhisattva Avalokiteśvara.
Another popular sight is Sledgehammer Peak (Chinese: 磬锤峰). This is a huge rock that looks like an upside-down sledgehammer. Chengde also has many other mountains, valleys, and grasslands to explore.
Sister Cities
Chengde has special partnerships with cities in other countries. These are called sister cities:
- Santo André, São Paulo, Brazil
- Takasaki, Gunma, Japan
- Dakota County, Minnesota, United States
- Kashiwa, Chiba, Japan
Images for kids