Respiratory tract facts for kids
The respiratory tract is a super important part of your body! It's like a special pathway that helps you breathe. Its main job is to bring oxygen into your body and get rid of carbon dioxide, which is a waste gas. Think of it as your body's air delivery and waste removal system.
Contents
What are the Parts of Your Breathing Pathway?
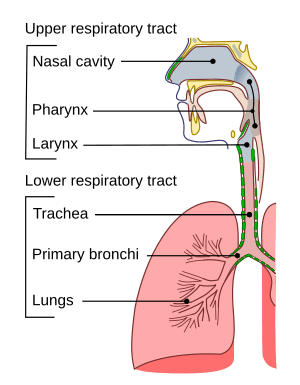
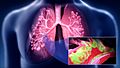
Your breathing pathway, or respiratory tract, is split into two main sections: the upper airways and the lower airways. These two parts are separated by your vocal cords, which are also known as your voice box!
Your Upper Airways
The upper airways are the first part of the journey for the air you breathe.
Your Nose and Nasal Cavity
The adventure begins when you breathe in through your nose. The air first enters your nasal cavity. This area is lined with a sticky substance called mucus and tiny hairs called cilia. These helpers work together like a filter, catching dust and other tiny particles before they can get deep into your body. The nasal cavity also warms the air, making it more comfortable for your lungs.
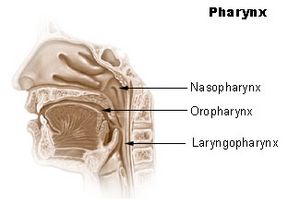
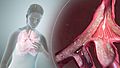
Your Pharynx (Throat)
Next, the air travels to your pharynx, which you might know better as your throat. This part is special because it's a common pathway for both air and food! When you breathe, air goes through the pharynx on its way to your lungs. When you eat, food passes through the pharynx on its way to your digestive system.
Your pharynx has three main sections:
- The nasopharynx: This is the upper part, behind your nose.
- The oropharynx: This is the middle part, behind your mouth.
- The laryngopharynx: This is the lower part. It splits into two tubes:
Your Larynx (Voice Box)
The last part of your upper airways is the larynx. This is often called your "voice box" because it holds your vocal cords, which allow you to speak and sing! The larynx also acts like a guard, protecting your trachea.
Important parts of your larynx include:
- The epiglottis: This is a small, leaf-shaped piece of cartilage. When you swallow food, the epiglottis drops down to cover the opening of your trachea. This stops food from going down the wrong pipe and into your lungs.
- The thyroid cartilage: This is the largest cartilage in your larynx, often called the Adam's apple in boys.
- The vocal cords: These are folds of tissue that vibrate to make sounds when air passes over them.
Your vocal cords are the boundary between your upper and lower airways.
Your Lower Airways
After the vocal cords, the air continues its journey into your lower airways.
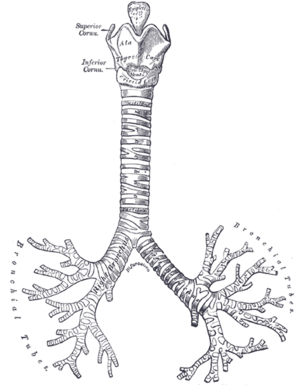
The Trachea (Windpipe)
The trachea, or windpipe, is a strong tube made of smooth muscle. It's about 10-12 centimeters long in adults. To keep it from collapsing, the trachea has many C-shaped rings of cartilage around it. These rings act like strong supports, making sure the air pathway stays open. The trachea's job is to bring air all the way down to your lungs.
The Bronchi (Air Tubes to Lungs)
At the bottom, your trachea splits into two main tubes called bronchi. One bronchus goes into your left lung, and the other goes into your right lung.
Once inside the lungs, these main bronchi split into smaller and smaller tubes, like the branches of a tree. These smaller tubes are also called bronchi. The very smallest branches are called bronchioles. Finally, these tiny bronchioles end in tiny air sacs called alveoli.
How Your Breathing Pathway Works
The main job of your airways is to guide air all the way to the alveoli deep inside your lungs. This is where a super important process called "gas exchange" happens.
During gas exchange:
- Oxygen from the air you breathe in moves from the alveoli into your blood.
- Your bloodstream then carries this oxygen to every single part of your body, giving your cells the energy they need.
- At the same time, carbon dioxide (a waste gas from your body) moves from your blood into the alveoli.
- You then breathe out this carbon dioxide.
If this exchange of gases didn't happen, your body wouldn't get enough oxygen to stay alive, and it would also get poisoned by too much carbon dioxide. So, your respiratory tract is truly a lifesaver!
Related pages
Images for kids
-
A cross-section of tracheal tissue.
See also
 In Spanish: Vía aérea (anatomía) para niños
In Spanish: Vía aérea (anatomía) para niños