Treaty of Karlowitz facts for kids

The official document of the treaty
|
|
| Context | Great Turkish War of 1683–1697 |
|---|---|
| Drafted | From 16 November 1698 |
| Signed | 26 January 1699 |
| Location | Karlowitz, Military Frontier, Habsburg monarchy (now Sremski Karlovci, Serbia) |
| Signatories | |
| Parties |
|
| Languages | |
The Treaty of Karlowitz was a very important peace agreement. It ended a big war called the Great Turkish War, which lasted from 1683 to 1697. In this war, the Ottoman Empire was defeated by a group of European countries called the Holy League.
The treaty was signed on January 26, 1699, in a place called Karlowitz. This area was part of the Habsburg Monarchy at the time. Today, it is known as Sremski Karlovci in Serbia. This treaty was a huge deal because it marked the end of the Ottoman Empire's control over a large part of Central Europe. It was their first major loss of land in Europe. This event started to reverse nearly 400 years of Ottoman expansion. The treaty also made the Habsburg monarchy the most powerful group in that region.
Contents
What Happened and Why
This peace treaty was signed after two months of talks. The talks were between the Ottoman Empire and the Holy League of 1684. The Holy League was a team of powerful European states. It included the Holy Roman Empire, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, the Republic of Venice, and Peter the Great, who was the Tsar of Russia.
Land Changes After the Treaty
The treaty used a rule called uti possidetis. This rule meant that each country kept the land it controlled when the treaty was signed.
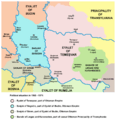
- The Habsburgs gained a lot of land from the Ottomans. This included large parts of what is now Hungary, Croatia, and Slavonia. A region called Transylvania remained somewhat independent. But it was still controlled by Austrian governors.
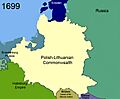
- The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth got back a region called Podolia. This included the strong fortress at Kamianets-Podilskyi. This meant they got back lands they had lost 27 years earlier in the Treaty of Buchach in 1672. In return, the Commonwealth gave back fortresses they had captured in Moldova. The treaty also said that prisoners should be freed. It stopped Tatar raids and ended tribute payments from the Commonwealth. After this treaty, the Commonwealth never fought the Ottomans again.
- Venice gained most of Dalmatia and the Morea. The Morea is a peninsula in southern Greece. However, Venice gave the Morea back to the Turks within 20 years. This happened with the Treaty of Passarowitz.
- The Ottomans kept control of Belgrade and a region called Banat of Temesvár. They also kept control over Wallachia and Moldavia.
Russia's Part in the Peace
Russia had a separate agreement. They signed a truce at Karlowitz. Their full peace treaty, the Treaty of Constantinople, was signed a year later in 1700. In this treaty, the Sultan gave the Azov region to Peter the Great. However, Russia had to give these lands back 11 years later. This happened after a failed war and the Treaty of the Pruth in 1711.
Drawing New Borders
Groups were formed to draw the new borders between the Austrians and the Turks. Some parts of the border were argued about until 1703. Thanks to the efforts of a Habsburg official named Luigi Ferdinando Marsili, the borders in Croatia and Bihać were agreed upon by mid-1700. The border at Temesvár was set by early 1701. This led to a border that was marked by physical landmarks for the first time.
A Turning Point for Empires
The Treaty of Karlowitz was a huge turning point for the Ottoman Empire. For the first time in over 350 years, they lost a lot of land. Before this, they had always been expanding in Europe. After this treaty, the Ottoman Empire's borders in the region would change a bit. But they would never again gain land on the same scale as before.
The Habsburg Monarchy grew much larger because of this treaty. They gained about 60,000 square miles of Hungarian land. This made the Archduchy of Austria a very powerful force in the region. They later grew even more by gaining Polish lands and other territories.
Images for kids
-
Political situation in 1568–71, before the treaty. All territories shown are Ottoman eyalets or vassals.
-
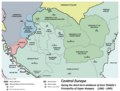
Central Europe in 1683, before the treaty:
Habsburg Empire
Ottoman Empire -
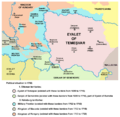
Political situation in 1699, after the treaty:
Habsburg Empire
Ottoman Empire -
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1686, before the treaty
See also
- Great Migrations of the Serbs
 | Audre Lorde |
 | John Berry Meachum |
 | Ferdinand Lee Barnett |