End–Triassic extinction event facts for kids
The End–Triassic extinction event was a huge event that happened about 200 million years ago. It marks the end of the Triassic period and the start of the Jurassic period. Many living things on Earth disappeared during this time.
This event was one of the biggest extinction events in Earth's history. It changed life a lot, both on land and in the oceans. Scientists believe that at least half of all the species living then went extinct.
For example, a whole group of sea creatures called conodonts disappeared. Also, 20% of all marine families were wiped out. Many large crurotarsans (which were like crocodiles but not dinosaurs) and some large amphibians also vanished.
This event cleared out many ecological niches, which are like "jobs" or "roles" in nature. This allowed the dinosaurs to become the main animals on Earth during the Jurassic period. The extinction happened very quickly, in less than 10,000 years. It took place just before the supercontinent Pangaea started to break apart.
Contents
What Caused the Extinction?
Scientists have different ideas about what caused this massive extinction. Each idea has its own challenges and questions that are still being researched.
Asteroid Impact Idea
One idea is that a large asteroid hit Earth. However, scientists have not found any impact crater that matches the exact time of the Triassic–Jurassic boundary. This makes the asteroid impact theory less likely for this specific event.
Climate Change Idea
Another idea suggests that gradual climate change or changes in sea levels caused the extinctions. At the end of the Triassic period, Sea level was low. The climate on Pangaea was very dry, or arid. But this idea doesn't fully explain why so many species disappeared so suddenly. Gradual changes usually lead to slower extinctions.
Massive Volcanic Eruptions
A strong idea is that huge volcanic eruptions caused the event. These eruptions would have released a lot of carbon dioxide into the air. This would lead to intense global warming. Or, they could have released sulfur dioxide and tiny particles called aerosols. These would have blocked the sun, causing severe cooling.
Scientists have found evidence of massive lava flows from the Central Atlantic Magmatic Province (CAMP). These eruptions happened right around the Triassic-Jurassic boundary. This makes volcanic activity a strong candidate for causing the extinction.
Images for kids
-
Reptile extinction at the end of the Triassic is poorly understood, but phytosaurs (such as this Redondasaurus) went from abundant to extinct by the end of the Rhaetian.
-
The Manicouagan reservoir in Quebec, a massive crater formed by a Late Triassic impact. Radiometric dating has determined that it is about 13 million years older than the Triassic–Jurassic boundary, and thus an unlikely candidate for a mass extinction.
-
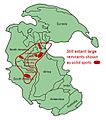
Maximum extent of CAMP volcanism at the Triassic-Jurassic boundary
See also
 In Spanish: Extinción masiva del Triásico-Jurásico para niños
In Spanish: Extinción masiva del Triásico-Jurásico para niños
 | Selma Burke |
 | Pauline Powell Burns |
 | Frederick J. Brown |
 | Robert Blackburn |