Aerosol facts for kids
An aerosol is a mix of tiny solid bits or liquid drops floating in a gas. Think of it like a very fine mist or dust cloud. Common examples are smoke, fog, air pollution, and smog. When most people say "aerosol," they are usually talking about an aerosol spray can, like a can of hairspray or paint.
The word "aerosol" comes from the idea of matter "floating" in the air. It's a type of mixture where small particles are spread throughout a gas. These particles can be liquid drops, solid pieces, or a combination of both. Aerosols can come from many places, like a volcano erupting or a spray can.
Aerosols are used in many ways, including in medicine (like inhalers for asthma) and in different technologies. Scientists study how aerosols are made, how they can be removed, and how they affect our environment and our health.
Aerosols in the Air
The Earth's atmosphere naturally contains many kinds of aerosols. These include:
- Natural non-living materials like dust, smoke from wildfires, sea salt, and tiny water droplets (which form clouds and mist).
- Natural living materials such as pollen, spores, and bacteria.
- Human-made products from burning things, like smoke, ashes, or dust.
You can also find aerosols in cities, such as:
- Dust from roads and construction.
- Smoke from cigarettes.
- Mist from aerosol spray cans.
- Soot or fumes from vehicle exhausts.
The aerosols in Earth's atmosphere have a big impact on our climate and on people's health.
Aerosols at Work
Sometimes, workers are exposed to high amounts of tiny particles in the air. These can be from things like silica (found in sand and rock), asbestos (a mineral once used in building), or diesel engine fumes. Breathing in these particles can cause serious lung diseases, like silicosis or "black lung."
To protect workers, special masks called respirators are used. In the United States, an organization called the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) checks and approves these respirators. This makes sure they can properly protect people from harmful particles in the air.
How Aerosols Affect Climate
Aerosols made by humans, especially tiny sulfate particles from burning fossil fuels, can actually have a cooling effect on the climate. This is because they can reflect sunlight back into space. However, this cooling effect doesn't completely cancel out the warming caused by greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane. Scientists include the effects of aerosols in their climate models.
Recent studies have shown that aerosols can also change rainfall patterns. For example, some scientists believe that the aerosol haze over South and East Asia has been shifting tropical rainfall southward. This might be linked to droughts in places like the Sahel region of Africa and changes in rainfall in parts of Australia.
Images for kids
-
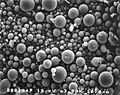
Photomicrograph made with a Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM): Fly ash particles at 2,000× magnification. Most of the particles in this aerosol are nearly spherical.
-
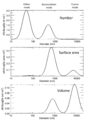
The same hypothetical log-normal aerosol distribution plotted, from top to bottom, as a number vs. diameter distribution, a surface area vs. diameter distribution, and a volume vs. diameter distribution. Typical mode names are shown at the top. Each distribution is normalized so that the total area is 1000.
See also
 In Spanish: Aerosol para niños
In Spanish: Aerosol para niños