Sugar maple facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Sugar maple |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Sugar maple foliage | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Sapindales |
| Family: | Sapindaceae |
| Genus: | Acer |
| Section: | Acer sect. Acer |
| Series: | Acer ser. Saccharodendron |
| Species: |
A. saccharum
|
| Binomial name | |
| Acer saccharum Marshall
|
|
 |
|
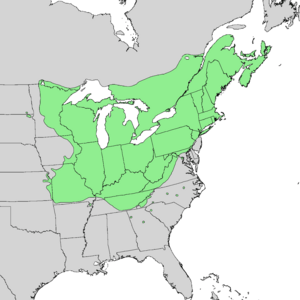
| Native range of Acer saccharum | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The sugar maple (Acer saccharum) is a type of flowering plant. It belongs to the soapberry and lychee family. This tree grows naturally in the hardwood forests of eastern Canada and the northeastern United States. You can find it from Nova Scotia to Manitoba in Canada. In the U.S., it grows from Minnesota east to Maine and south to Virginia, Tennessee, and Missouri.
Sugar maples are famous for two main things. First, they are the main source of maple syrup. Second, their leaves turn bright, beautiful colors in the fall. People also call this tree "rock maple" or "hard maple" when talking about its wood. Other names include "sugar tree," "birds-eye maple," "sweet maple," or "curly maple."
Contents
What Does a Sugar Maple Look Like?
The sugar maple is a deciduous tree. This means it loses its leaves every year. These trees usually grow to be about 25 to 35 meters (80 to 115 feet) tall. Some can even reach 45 meters (150 feet). A young sugar maple, about 10 years old, is usually around 5 meters (16 feet) tall. Trees growing in a forest tend to have taller trunks and narrower tops. Trees growing in open areas are usually shorter and wider.
Sugar Maple Leaves and Buds
The leaves are large, up to 20 centimeters (8 inches) long and wide. They have five main points, or lobes. The two bottom lobes are small, while the top ones are larger. The edges of the leaves have rounded notches. This is different from the silver maple, which has pointed notches.
In autumn, the leaves change color in an amazing way. They can turn bright yellow, orange, or even a glowing red-orange. Sometimes, one tree can show all these colors at once. Different parts of a mature tree might change color at different times. Some parts might change weeks before or after the rest of the tree. The leaf buds are pointy and brown. New branches are green at first, then turn dark brown.
Flowers and Seeds
The sugar maple's flowers grow in clusters of five to ten. They are yellow-green and do not have petals. These flowers appear in early spring. A sugar maple usually starts flowering when it is between 10 and 200 years old.
The fruit of the sugar maple is a pair of samaras. These are winged seeds that look like tiny helicopters. The seeds are round, about 7 to 10 millimeters (0.3 to 0.4 inches) across. Their wings are 2 to 3 centimeters (0.8 to 1.2 inches) long. The seeds fall from the tree in autumn. To grow, they need to be cold for about 45 days, below 4 degrees Celsius (39 degrees Fahrenheit). They will not sprout until the next spring, after the soil warms up and there is no more frost.
How to Tell Sugar Maple Apart
The sugar maple is closely related to the black maple. Some scientists consider them the same species, while others see them as separate. The bigtooth maple from western America is also sometimes seen as a type of sugar maple.
It is easy to confuse the sugar maple with the Norway maple. Norway maples are not native to America but are often planted in cities. They are not closely related to sugar maples. You can tell them apart by checking the sap in the leaf stem. Sugar maples have clear sap, while Norway maples have white sap. Sugar maples have brown, pointy buds. Norway maples have blunt, green or reddish-purple buds. Older sugar maples have shaggy bark, but Norway maples have small grooves in their bark. Also, sugar maple leaves have more triangular lobes, while Norway maple leaves have squarer lobes.
Many people think the red maple leaf on the flag of Canada is a sugar maple leaf. However, the leaf on the flag does not belong to any specific maple species. It was designed to be easily seen on a waving flag.
Where Sugar Maples Grow (Ecology)
The sugar maple is very important to the forests of the northern United States and Canada. It often grows in pure groups. It is a major part of the hardwood forests in the northern and Midwestern U.S.
Sugar maples need cold winters to grow well. They are mostly found in areas where January temperatures average around -18 degrees Celsius (0 degrees Fahrenheit). In the southern parts of their range, where summers are hot, sugar maples are less common. There, they usually grow in cool, moist areas like ravines.
A sugar maple tree must be about 30 years old before it can produce seeds. These trees live a long time, usually 200 years, and sometimes up to 300 years.
Growing Conditions
Sugar maples are very good at growing in the shade. Only the striped maple, a smaller tree, can tolerate more shade. Sugar maples can sprout and grow under a thick forest canopy. When a gap appears in the canopy, they grow quickly towards the light.
Sugar maples can grow in almost any type of soil except pure sand. However, they do not like very dry or swampy places. They have deeper roots than most maples. They can pull water from lower soil layers and release it into drier upper layers. This helps the sugar maple and other plants around it.
Threats to Sugar Maples
Human activities have caused sugar maples to decline in some areas. When forests are cut down, faster-growing species often replace them. Climate change is also affecting sugar maples. Warmer temperatures are pushing their suitable habitat further north.
Sugar maples are also sensitive to pollution. Acid rain and changes in soil acidity are big problems. Also, the salt used on roads in winter can harm sugar maples planted along streets. The mushroom Pholiota squarrosoides can cause decay in sugar maple logs.
In some parts of New England, the Norway maple is taking over from the sugar maple. Norway maples can handle city pollution much better. They also produce many more seeds, which helps them outcompete native trees.
How We Use Sugar Maples
Maple Syrup and Food
The sugar maple is one of the most important Canadian trees. It is the main source of sap for making maple syrup, along with the black maple. Other maple trees can be used, but their sap might have less sugar or make cloudy syrup.
To make maple syrup, sap is collected from the trees. A small hole is drilled into the tree, and a tap is inserted. The collected sap is then boiled. As the water evaporates, the sap thickens into syrup. It takes about 40 gallons of sap to make just 1 gallon of pure maple syrup! Sugar maples in warmer southern areas do not produce much sap because they need cold winters for good syrup production.
The seeds of the sugar maple can also be eaten. After removing their wings, they can be boiled, seasoned, and roasted.
Sugar Maple Wood (Timber)
The inner wood of the sugar maple, called sapwood, can be white. Smaller logs often have more of this valuable white wood. Sugar maple wood is very strong and is used for many things. Bowling alleys and bowling pins are often made from it.
Trees with wavy woodgrain are very special. This wavy grain can appear as "curly," "quilted," or "birdseye maple." These types of wood are highly valued. Maple wood is also used for basketball courts, including those used by the NBA. It is a popular wood for baseball bats, along with white ash. Because white ash trees are now threatened by a beetle, sugar maple wood is being used more for bats.
Sugar maple wood is also used to make musical instruments. This includes parts of violins, guitar necks, grand piano rims, and drum shells. It is also common in sporting goods.
Canadian maple, sometimes called "Canadian hardrock maple," is prized for pool cues, especially the shafts. The best wood for cue shafts has a very even grain with no marks. Sugar maple wood is also used for gunstocks and flooring because of its strength. It is also used for electric guitar necks. This is because it is very stable and produces a bright, clear sound. If the wood has curly patterns, it is often saved for more expensive instruments.
Planting in Cities
In the 1800s, sugar maples were popular trees for streets and parks. They were easy to grow and move, grew fairly fast, and had beautiful fall colors. However, they are sensitive to pollution from cars. Because of this, they were replaced by Norway maples and other tougher trees in cities.
The shade from sugar maples and their shallow roots can make it hard for grass to grow underneath them. They grow best in deep, well-drained soil. They can also grow well in sandy soil with lots of rich plant matter. They do not do well in poorly drained areas or places that flood often. They are also sensitive to salt and boron. Caterpillars of moths like the rosy maple moth (Dryocampa rubicunda) can sometimes eat their leaves.
Cultivars (Special Varieties)
There are many special types of sugar maples, called cultivars, that people have grown for certain features:
- 'Apollo' – grows in a tall, narrow shape.
- 'Arrowhead' – has a pyramid-shaped top.
- 'Astis' ('Steeple') – can handle heat well, good for the southeastern USA.
- 'Caddo' – a natural type from Oklahoma, very good at handling drought and heat.
- 'Columnare' ('Newton Sentry') – very narrow shape.
- 'Fall Fiesta' – has tough leaves and bright fall colors.
- 'Green Mountain' – leaves resist heat and drought, has an oval top.
- 'Inferno' – possibly the toughest type, with more red fall color.
- 'Legacy' – strong, popular, and grows well.
- 'Lord Selkirk' – very tough, grows more upright than other northern types.
- 'September Flare' - very tough, turns orange-red early in fall.
- 'Sweet Shadow' – has delicate, lacy leaves.
- 'Unity' – very tough, from Manitoba, grows slowly but steadily.
How Native Americans Used Sugar Maples
The Mohegan people used the inner bark of the sugar maple as a cough medicine. They also used the sap to sweeten food and make maple syrup.
Famous Sugar Maple Trees
The largest known Acer saccharum in the United States is in Charlemont, Massachusetts. In 2007, this tree was measured. It had a trunk that was 5.92 meters (19.4 feet) around. It was 34.1 meters (112 feet) tall. Its branches spread out about 27.7 meters (91 feet).
Another very large sugar maple is in Lyme, Connecticut. In 2012, its trunk was 5.56 meters (18.25 feet) around. This tree was 37.5 meters (123 feet) tall, with a crown spread of 26.2 meters (86 feet).
Sugar Maples in Pop Culture
The sugar maple is the official state tree for several U.S. states. These include New York, Vermont, West Virginia, and Wisconsin.
It is also shown on the state quarter for Vermont, which was made in 2001.
|
See also
 In Spanish: Arce azucarero para niños
In Spanish: Arce azucarero para niños













