Music of Africa facts for kids
Africa is a huge continent with many different countries and cultures. Because of this, the music across Africa is incredibly diverse! The music in North Africa has a different history compared to the music in sub-Saharan Africa.
African music has also traveled around the world. For example, many music styles in the African diaspora (people of African descent living outside Africa) are based on African traditions. This includes African-American music and many Caribbean styles like soca and calypso. Even Latin American music like samba and salsa were influenced by the music of enslaved Africans. These styles then influenced popular music back in Africa!
Contents
Music in North Africa and the Horn of Africa
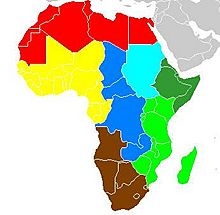
North Africa (the red part on the map) is where ancient civilizations like ancient Egypt and Carthage grew. These places had strong connections to the Middle East and influenced ancient Greek and Roman cultures. Later, Arabs conquered North Africa, making it part of the Arab world.
The music from North Africa, the Nile area, and the Horn of Africa (the sky-blue and dark green parts on the map) is closely related to Middle Eastern music. They use similar musical scales and patterns. North African music includes everything from ancient Egyptian sounds to the music of desert nomads like the Berbers and Tuareg. A popular modern style from Algeria is Raï.
The music of Sudan and countries in the Horn of Africa like Eritrea, Ethiopia, Djibouti, and Somalia also share these connections.
Music in Sub-Saharan Africa
Experts who study music, like Arthur Morris Jones, have noticed that the music in Sub-Saharan African music traditions (the part of Africa south of the Sahara Desert) shares many similar rhythmic ideas. It's like they all come from one main system.
Traditional African music often has a purpose. It's not just for listening! Performances can be long and usually involve the audience. For example, there are work songs, songs for childbirth or marriage, and music for hunting. There's also music to connect with spirits or honor ancestors. This music is usually performed in its special social setting and often goes with a particular dance. Some music is played by professional musicians for religious ceremonies or at royal courts.
For studying music, Sub-Saharan Africa can be divided into four main areas:
- The eastern region (light green on the map) includes countries like Uganda, Kenya, Tanzania, and Zimbabwe. It also includes islands like Madagascar. This region has been influenced by Arabic, Indian, and Indonesian music. However, its main musical traditions come from the Niger–Congo-speaking peoples.
- The southern region (brown on the map) includes countries like South Africa, Lesotho, and Angola.
- The central region (dark blue on the map) includes countries like Chad, the Central African Republic, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. This area is also home to Pygmy music.
- West African music (yellow on the map) covers countries like Senegal, Mali, Ghana, and Nigeria.
Music in Southern, Central, and West Africa also gets influences from Western Europe and North America.
African Musical Instruments
African music uses many different instruments, along with singing. Singers use special techniques like melisma (singing many notes on one syllable) and yodeling.
Some common African instruments include:
- Drums: There are many types, like talking drums, bougarabou, and djembe in West Africa. Water drums are found in Central and West Africa. Ngoma drums are popular in Central and Southern Africa.
- Percussion: Besides drums, there are many rattles, shakers (like the kosika), rain sticks, bells, and wood sticks.
- String Instruments: These include different types of harps, like the Kora, and fiddles.
- Xylophones and Lamellophones: Many kinds of xylophones are used. Lamellophones are instruments with thin metal or wooden strips that are plucked, like the mbira (also called a thumb piano).
- Wind Instruments: These include flutes and trumpets.
One very common feature of music in Sub-Saharan Africa is polyrhythms. This means playing several different rhythms at the same time. This is different from Western music, which often focuses on polyphony (multiple independent melodies). Some unique instruments, like the mbira and Kora, were designed to make it easier to play these complex rhythms.
Music and Language
Many languages in Africa are tonal languages. This means the meaning of a word can change depending on the pitch of your voice. This creates a strong link between music and language in some cultures. When people sing, the tones of the words can affect the melody. Also, in instrumental music, a native speaker can often understand a "text" or message in the music. This is how drum languages (like with talking drums) work!
What Influenced African Music?
Many things have shaped the traditional music of Africa over time. Language, the environment, different cultures, politics, and how people moved around all played a part. Each African tribe lived in a different area, so they experienced different weather, ate different foods, and met different people. This led to unique music styles for each group.
How African Music Influenced North American Music
African music has been very important in shaping styles like Dixieland, the blues, and jazz. These styles borrowed rhythms and sounds that were brought across the Atlantic Ocean by enslaved Africans. While traditional African music is often upbeat and full of polyrhythms, the blues developed in the new world from the difficult conditions of slavery.
In modern times, African music continues to inspire. For example, on his album Graceland, American musician Paul Simon used African bands and rhythms. In the 1970s, drummer Remi Kabaka helped create "Afro-rock" sounds for bands like The Rolling Stones.
Many people believe that rock and roll music started with American blues in the 1940s. Since so many popular music styles today, like heavy metal and pop music, came from rock, you could say that African music is at the root of a huge part of all popular music today!
African musical traditions also had a big impact on Disney's The Lion King. Songs like "Circle of Life" mix Zulu and English words, combining traditional African music with modern Western styles. The movie also uses many words from the Bantu Swahili language. For instance, "hakuna matata" is a real Swahili phrase meaning "no worries." Characters like Simba (lion), Kovu (scar), and Zira (hate) also have Swahili names.
Popular African Music
Just like traditional African music, popular African music is very diverse. Most modern African popular music styles mix with Western popular music. Many popular music styles around the world, including blues, jazz, and rumba, originally came from African musical traditions brought to the Americas by enslaved Africans. These rhythms and sounds were then used in newer styles like rock and rhythm and blues. In return, African popular music has adopted things like Western musical instruments and recording techniques.
The Cuban style called son (a mix of African and European music) has also influenced popular music in Africa. Some of the first guitar bands in the Congo played covers of Cuban songs. This Congolese style eventually became known as soukous.
Images for kids
-
Steve Winwood's band Traffic often used West African rhythms.
-
Miriam Makeba during a performance.
See also
 In Spanish: Música africana para niños
In Spanish: Música africana para niños