Aromatic hydrocarbon facts for kids
An aromatic hydrocarbon, also called an arene, is a special type of hydrocarbon. These are chemical compounds made of carbon and hydrogen atoms. They form rings with alternating single and double bonds. Many of them have a sweet smell, which is why they are called 'aromatic'. The most common ring has six carbon atoms and is called a benzene ring. Benzene is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon. Aromatic hydrocarbons can have one ring (monocyclic) or many rings (polycyclic).
Sometimes, other atoms like oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur can replace a carbon atom in the ring. These are called heteroarenes. They are also aromatic if they follow a special rule called Hückel's rule.
Contents
Understanding the Benzene Ring
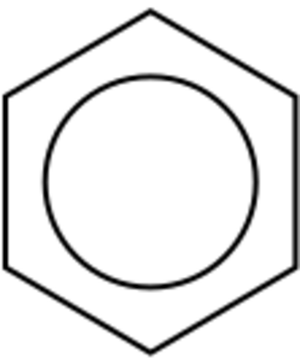
Benzene, with the formula C6H6, is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon. A scientist named Kekulé first figured out its unique bonding in the 1800s.
Imagine a hexagon made of six carbon atoms. Each carbon atom has four electrons it can share. One electron connects to a hydrogen atom. Two more electrons connect to its two carbon neighbors in the ring. This leaves one electron for each carbon. These last six electrons are special. They are not fixed in one place. Instead, they float around the entire ring. This makes the bonds between the carbon atoms all equally strong. It's like a mix of single and double bonds.
Scientists often draw a circle inside the benzene ring. This circle shows these six electrons moving freely. They float above and below the ring. This special movement helps keep the ring flat and stable.
Aromatic compounds have some general features:
- They show aromaticity, which means they are very stable.
- They have a high number of carbon atoms compared to hydrogen atoms.
- They burn with a sooty yellow flame because of all the carbon.
- They usually react by replacing one atom with another (substitution reactions).
The circle symbol for aromaticity was first used by Sir Robert Robinson in 1925. It became popular later in textbooks.
How Arenes Are Made
Making an arene compound from other ring-shaped molecules is called aromatization. Scientists have many ways to create arenes in a lab. They start with molecules that are not yet aromatic.
Why Aromatic Compounds Are Important
Aromatic compounds are super important for all living things.
- Four of the 20 basic building blocks of proteins are aromatic. These are histidine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, and tyrosine.
- All five nucleotides that make up DNA and RNA are aromatic. These include adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine, and uracil.
- The molecule heme, found in blood, has an aromatic system. Chlorophyll, which plants use for photosynthesis, also has a similar system.
Aromatic compounds are also very important in industry.
- Key ones include benzene, toluene, and xylene.
- About 35 million tons of these are made every year around the world.
- They are taken from oil refining or distillation of coal tar.
- They are used to make many important chemicals and polymers. These include styrene, phenol, aniline, polyester, and nylon.
Different Kinds of Aromatic Compounds
Most aromatic compounds are made of carbon. But some can have other elements too.
Heterocyclic Aromatics
In these compounds, one or more atoms in the aromatic ring are not carbon. Instead, they might be oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur. Examples include pyridine, pyrazine, and thiophene.
Polycyclic Aromatics
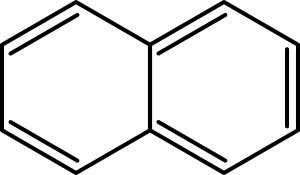
These molecules have two or more simple aromatic rings joined together. They share two carbon atoms. Examples are naphthalene, anthracene, and phenanthrene.
Substituted Aromatics
Many chemical compounds are aromatic rings with other groups attached to them. Examples include trinitrotoluene (TNT), acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin), paracetamol, and the nucleotides in DNA.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Compuesto aromático para niños
In Spanish: Compuesto aromático para niños