Basin and Range facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Great Basin Ranges |
|
|---|---|

|
|
| Highest point | |
| Peak | White Mountain Peak |
| Elevation | 14,252 ft (4,344 m) |
| Geography | |
| Country | United States |
| Parent range | North American Cordillera |
| Basin and Range | |
| physiographic region | |
|
NASA satellite photo of typical Basin and Range topography across central Nevada
|
|
| Countries | United States, Mexico |
|---|---|
| Location | western United States |
| - coordinates | 33°N 112°W / 33°N 112°W |
| Area | 170,000 sq mi (440,298 km²) |
| Biome | North American Desert ecoregion |
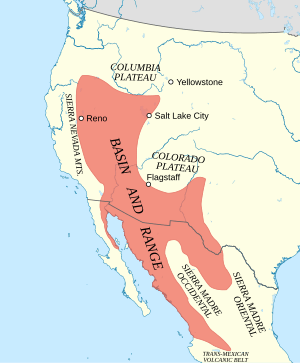
The Basin and Range Province is a huge area of land in the western United States and northwest Mexico. It's known for its unique look. Imagine many long, narrow mountain ranges standing next to wide, flat valleys. These valleys are often dry and desert-like.
This special landscape was formed over millions of years. It happened because the Earth's outer layer, called the lithosphere, stretched and became thinner. Scientists are still studying exactly why this stretching began about 17 million years ago.
Contents
What Does It Look Like?
The Basin and Range Province has a very distinct appearance. It's like a giant "washboard" on the Earth's surface. You'll see many mountain ranges that run mostly north to south. Between these ranges are flat, wide valleys.
Mountains and Valleys
The mountains here are often steep and rocky. The valleys are usually flat and can be very dry. Many of these valleys are basins, meaning water doesn't flow out to the ocean. Instead, it collects in the lowest parts, sometimes forming temporary lakes.
A famous scientist named Clarence Dutton once described the many narrow mountain ranges. He said they looked like an "army of caterpillars marching toward Mexico." This helps you picture how they stretch across the land.
Where Is It Located?
The Basin and Range Province covers a large part of the western United States. It includes most of Nevada, a lot of Utah, and parts of California, Arizona, New Mexico, Idaho, Oregon, and Texas. It also extends into northwest Mexico.
Highs and Lows
This region has some amazing differences in elevation. The highest point completely within the province is White Mountain Peak in California. It stands at 14,252 feet (4,344 meters) tall.
On the other hand, the lowest point in North America is also found here. This is Badwater Basin in Death Valley, California. It's 282 feet (86 meters) below sea level!
Basin and Range vs. Great Basin
It's easy to get the Basin and Range Province confused with the Great Basin. They are related but different.
Understanding the Differences
The Basin and Range Province is a large area defined by its unique landscape. This landscape has many parallel mountains and valleys.
The Great Basin is a smaller part of the Basin and Range Province. It's defined by its watershed. This means all the rain and snow that falls in the Great Basin stays there. It doesn't flow out to any ocean. Instead, it either sinks into the ground or evaporates.
So, while all of the Great Basin is part of the Basin and Range Province, not all of the Basin and Range Province is part of the Great Basin.
Volcanic Activity
The Basin and Range Province has also seen a lot of volcanic activity over millions of years. This is because of the stretching and thinning of the Earth's crust.
Past and Present Volcanoes
Many areas within the province show signs of past eruptions. You can find old lava flows, volcanic cones, and calderas (large bowl-shaped hollows formed when a volcano collapses). Some of these volcanic areas are still active today, like the famous Yellowstone hotspot.