Bubonic plague facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Bubonic plague |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
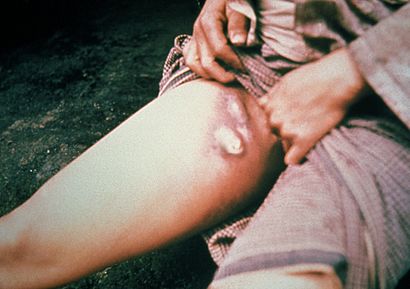
| A bubo on the upper thigh of a person infected with bubonic plague | |
| Symptoms | Fever, headaches, vomiting, swollen lymph nodes |
| Complications | Gangrene, meningitis |
| Usual onset | 1–7 days after exposure |
| Causes | Yersinia pestis spread by fleas |
| Diagnostic method | Finding the bacterium in the blood, sputum, or lymph nodes |
| Treatment | Antibiotics such as streptomycin, gentamicin, or doxycycline |
| Frequency | 650 cases reported a year |
| Deaths | 10% mortality with treatment 30–90% if untreated |
Bubonic plague is a serious illness caused by a tiny germ called Yersinia pestis. It is one of three main types of plague. This disease is mostly known for causing the terrible Black Death in the Middle Ages.
Contents
What is Bubonic Plague?
The word bubonic comes from a Greek word meaning "groin." This is because the disease often causes painful swelling in the lymph nodes, especially in the groin area. These swollen nodes are called "buboes."
What are the Symptoms of Bubonic Plague?
If someone gets infected, they usually start feeling sick within one to seven days. The first signs are often like the flu, including a fever, headaches, and vomiting.
The most noticeable symptom is swollen and painful lymph nodes. These swellings, or "buboes," appear close to where the bacteria entered the body, often from a flea bite. Sometimes, these buboes can even break open. Another symptom can be dark patches on the skin.
How Does Someone Get Bubonic Plague?

Bubonic plague is mainly spread by infected fleas. These fleas usually live on small animals like rats. When an infected flea bites a person, the bacteria enter the skin. The germs then travel through the body's lymphatic vessels to a nearby lymph node, making it swell up.
People can also get the plague if they touch the body fluids of a dead animal that was infected. Animals like rabbits, hares, and some cats can get bubonic plague and often die from it.
Doctors can find out if someone has the plague by looking for the bacteria in their blood, spit (sputum), or fluid from the swollen lymph nodes.
How Can We Prevent and Treat Bubonic Plague?
To prevent bubonic plague, it's important not to touch dead animals in areas where the disease is common. There are vaccines against the plague, but they are usually only recommended for people who are at high risk, like some lab workers or healthcare staff.
If someone does get bubonic plague, it can be treated with antibiotics. Medicines like streptomycin, gentamicin, and doxycycline are very effective.
How Deadly is Bubonic Plague?
Without treatment, bubonic plague is very dangerous. Between 30% and 90% of infected people might die, usually within 10 days. However, with proper treatment, the risk of death drops significantly to about 10%.
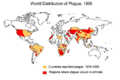
Globally, between 2010 and 2015, there were 3,248 reported cases of plague, and 584 people died. The countries with the most cases were the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Madagascar, and Peru.
The Black Death: A Historical Outbreak
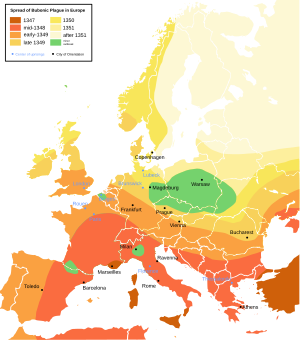
The plague is believed to be the cause of the terrible Black Death. This massive outbreak swept across Asia, Europe, and Africa in the 14th century. It killed an estimated 50 million people. In Europe, about 25% to 60% of the population died.
Because so many workers died, there was a huge demand for labor, and wages went up. Some historians believe this was a major turning point in Europe's economic history.
Where Did the Black Death Start?

The Black Death, also known as the Great Dying, was the deadliest disease outbreak in Europe's history during the Late Middle Ages. It lasted for about six years, from 1346 to 1352.
Many historians believe the Black Death started in Central Asia or Mongolia. Chinese records show a big outbreak in Mongolia in the early 1330s. In 2022, researchers found evidence that the plague might have started near Lake Issyk-Kul in Kyrgyzstan.
The disease then spread to Europe. One way it may have arrived was during the siege of Caffa. This was an attack by Mongol forces on an Italian trading city called Caffa in the Crimea.
How Did the Black Death Spread?
During the siege of Caffa in 1346, plague broke out among the Mongol soldiers. They reportedly threw plague-infected bodies over the city walls as a form of attack. This is one of the earliest known examples of using disease in warfare.
When spring came, Italian merchants fled Caffa on their ships. Without knowing it, they carried the Black Death with them. The disease was carried by fleas living on rats. These rats traveled with people on ships, in grain bags, and in wagons. This helped the plague spread from the Black Sea to the rest of Europe.
Later Plague Outbreaks
The Third Pandemic (Modern Plague)
The plague returned for a third major time in the mid-1800s. This is sometimes called "the modern pandemic." Like the earlier outbreaks, this one also began in Eastern Asia, most likely in Yunnan, a province in China.
The disease stayed in Southwest China for several years before spreading. In the city of Canton, 80,000 people died from the plague between January and June of 1894. Daily boat traffic quickly spread the plague to nearby Hong Kong, where over 2,400 people died in just two months during the 1894 Hong Kong plague.
This third pandemic spread the disease to port cities all over the world in the late 1800s and early 1900s through shipping routes. For example, the plague infected people in Chinatown in San Francisco from 1900 to 1904.
The last major outbreak in the United States happened in Los Angeles in 1924. However, the disease is still found in wild rodents today and can sometimes be passed to humans who come into contact with them. The World Health Organization considered this pandemic active until 1959, when worldwide cases dropped to 200 per year.
During the 1894 Hong Kong plague outbreak, a scientist named Alexandre Yersin discovered the bacteria that causes the plague. This bacteria is now named Yersinia pestis after him.
Plague in Culture and History
The huge number of deaths and the major changes to society caused by plague outbreaks have made it a very important topic in many stories and historical writings. The Black Death especially is mentioned in many old writings. Famous writers like Chaucer, Boccaccio, and Petrarch wrote about it.
For example, The Decameron by Boccaccio tells the story of people who leave Florence to escape the Black Death. Personal stories about living through plague times have also been popular. Samuel Pepys's diary, for instance, talks about his experiences during the Great Plague of London in 1665–66.
More recently, books like Albert Camus's novel The Plague and films like Ingmar Bergman's The Seventh Seal use the plague as a background. They explore ideas about how society, groups, and individuals deal with such a terrible disease. They also look at how people face death and what it means to be human during a crisis.
Plague and Warfare
Some of the earliest examples of using disease in warfare involved the plague. In the 14th century, armies were said to have thrown diseased bodies over city walls to spread the illness. This was done by Jani Beg when he attacked the city of Kaffa in 1343.
Later, during the Second Sino-Japanese War, the Imperial Japanese Army used plague as a weapon. They used fleas carrying the bubonic plague to attack cities. For example, in 1940, they bombed Ningbo with plague-infected fleas. These actions caused outbreaks of the plague.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Peste bubónica para niños
In Spanish: Peste bubónica para niños
- List of epidemics
- Plague (disease)
- Plague doctor