Carbon cycle facts for kids
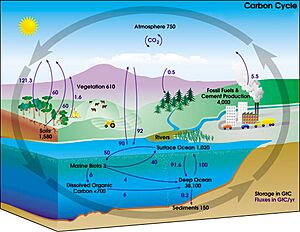
The carbon cycle is like Earth's big recycling system for carbon. Carbon is a super important element found in everything, from the air we breathe to the food we eat, and even in rocks! This cycle shows how carbon moves around our planet. Some parts of this journey take millions of years, while others happen every single day.
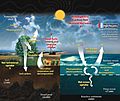
One way carbon gets into the air is from volcanoes. Another big way is when people burn fossil fuels like coal and gas. For most of Earth's history, volcanoes added the most carbon to the air. But in the last 100 years, humans burning fossil fuels have added about 100 times more carbon dioxide (CO2) than volcanoes!
The main way carbon is taken out of the air is through photosynthesis. This is how plants and other living things use sunlight to turn CO2 into food. When these organisms die and break down, some carbon goes back into the air. But some also gets buried deep down in the ground as sediment. Over a very long time, this sediment can turn into rock, like limestone, which stores the carbon. Carbon from plants can also become part of the soil, staying there for a long time.
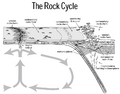
Another process that removes CO2 from the air is weathering. When it rains, CO2 in the air mixes with water to form a weak acid called carbonic acid. This acid helps break down rocks. The carbon from these broken-down rocks also ends up as sediment.
The ocean also plays a huge role. It can dissolve a lot of CO2 from the air. Right now, our oceans are taking in more CO2 than they release each year. However, this extra CO2 is making the oceans more acidic, which can be harmful to ocean life.
A huge amount of carbon is stored in sedimentary rocks, much more than in the atmosphere. Eventually, through plate tectonics, these rocks can be pushed deep into the Earth. At the edges of these moving plates, volcanoes form and release CO2 back into the air. This completes the long carbon cycle.
How Carbon Moves Around
The carbon cycle is a process where carbon is recycled through Earth's ecosystem. Living things, like us, have a lot of carbon in them (about 18%). This is much more than the amount of carbon found in the Earth itself (about 0.19%). So, living things need to get carbon from their nonliving surroundings. For life to keep going, this carbon must be recycled constantly.
Let's look at an example of how carbon moves in this cycle. Carbon dioxide from the atmosphere is taken in by plants. Plants use this CO2 in photosynthesis to make sugars, which give them energy. When the plant dies, it decomposes. Over millions of years, the carbon stored in the plant can turn into coal, a type of fossil fuel. When this coal is burnt, it releases carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere, starting the cycle again.
Today, the carbon cycle and how human activities affect it are big topics in the news. Fossil fuels are a non-renewable resource. This means they can't be easily replaced once we use them up. Since 1900, our use of fossil fuels has almost doubled every 20 years. When we burn these fuels, we release a lot of carbon dioxide. This extra CO2 contributes to the greenhouse effect, which can warm the planet, and also to acid rain.
The carbon cycle was first understood by scientists named Joseph Priestley and Antoine Lavoisier. Later, Humphry Davy helped make it more widely known.
More to Explore
Images for kids
-
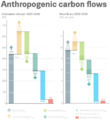
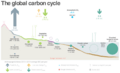
Fast carbon cycle showing the movement of carbon between land, atmosphere, and oceans in billions of tons (gigatons) per year. Yellow numbers are natural fluxes, red are human contributions, white are stored carbon. The effects of the slow carbon cycle, such as volcanic and tectonic activity are not included.
-
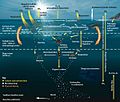
The slow carbon cycle operates through rocks The fast carbon cycle operates through the biosphere, see diagram at start of article ↑ -
Climate–carbon cycle feedbacks and state variables as represented in a stylised model Carbon stored on land in vegetation and soils is aggregated into a single stock ct. Ocean mixed layer carbon, cm, is the only explicitly modelled ocean stock of carbon; though to estimate carbon cycle feedbacks the total ocean carbon is also calculated.
See also
 In Spanish: Ciclo del carbono para niños
In Spanish: Ciclo del carbono para niños