Cell theory facts for kids
In biology, cell theory is a major scientific idea. It states that all living organisms are made of cells. Cells are the basic building blocks of life. The theory also explains that all new cells are created by existing cells dividing.
For a long time, people did not know cells existed because they are too small to see with the naked eye. The invention of the microscope allowed scientists to discover this hidden world. Today, cell theory is one of the most important principles in the study of life.
Contents
History of Microscopes
The discovery of the cell was only possible after the invention of the microscope.
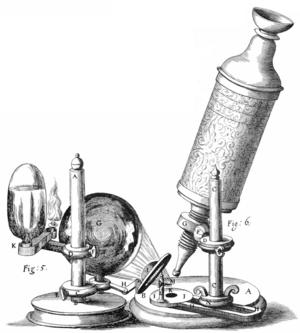
In the 1600s, scientists in Europe began making better lenses. Robert Hooke built a compound microscope, which uses more than one lens to magnify objects. In 1665, he used this tool to look at small insects and plants. He drew what he saw in a famous book called Micrographia.
Around the same time, Anton van Leeuwenhoek made his own microscopes in the Netherlands. He learned how to grind glass lenses very carefully. His microscopes were small and used only one lens, but they were very powerful. He could magnify objects up to 270 times their actual size. This allowed him to see things no one had ever seen before.
Discovery of Cells
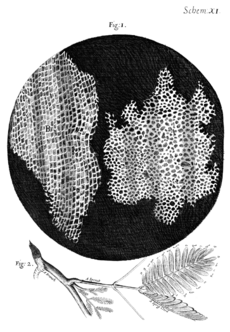
Robert Hooke was the first person to discover the cell. In 1665, he looked at a thin slice of bottle cork under his microscope. He saw that the cork was made of many tiny, empty spaces with walls around them.
Hooke thought these spaces looked like the small rooms, or "cells," that monks lived in. He gave them the name cells. At the time, Hooke did not know that these were the remains of living plant cells. He thought they were just channels for fluids in the plant.
Later, Anton van Leeuwenhoek used his powerful lenses to look at drops of pond water. He was amazed to see tiny creatures swimming around. He called these moving things "animalcules." Today, we know he was looking at microorganisms like bacteria and protozoa.
Leeuwenhoek was the first person to see single-celled organisms. He also looked at blood cells and other biological samples. His letters to the Royal Society in London helped prove that life existed even at a microscopic level.
Developing the Cell Theory


For almost two hundred years after Hooke and Leeuwenhoek, scientists did not fully understand that all life was made of cells.
In the 1830s, two German scientists made a breakthrough. Matthias Jakob Schleiden was a botanist who studied plants. He realized that every part of a plant was made of cells.
Theodor Schwann was a physiologist who studied animals. In 1839, he spoke with Schleiden and realized that animal tissues were also made of cells. This was a big discovery because animal cells are harder to see than plant cells.
Together, they proposed that cells are the basic unit of structure for all living things.
However, they argued about how new cells were made. Schleiden thought they formed like crystals. In the 1850s, another scientist named Rudolf Virchow corrected this. He stated that cells only come from other living cells. He used the famous Latin phrase Omnis cellula e cellula, which means "All cells come from cells."
The Three Main Rules
The classical cell theory has three major parts:
- All living things are made of cells. Some organisms, like bacteria, have only one cell. Others, like humans and trees, have trillions of cells.
- The cell is the basic unit of life. It is the smallest part of an organism that is considered alive.
- All cells come from pre-existing cells. Cells do not appear out of nowhere. They are created when a parent cell divides.
Modern Understanding
Today, scientists have learned even more about how cells work. The modern cell theory includes a few new ideas:
- Energy flow: Chemical reactions that create energy happen inside cells.
- Genetic information: Cells contain DNA, which holds the instructions for life. This information is passed from cell to cell during division.
- Chemical composition: All cells are made of the same basic chemical types, such as proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids.
See also
 In Spanish: Teoría celular para niños
In Spanish: Teoría celular para niños