Climate of Florida facts for kids
The climate in the northern and central parts of the U.S. state of Florida is called humid subtropical. This means it's usually warm and humid, with plenty of rain. South Florida has a tropical climate, which is even warmer all year round.
Florida has a clear rainy season from May to October. During these months, the heat of the day often causes big thunderstorms. These storms bring heavy but quick bursts of rain.
From October to late April, Florida experiences its dry season. Sometimes, cold fronts from storms north of Florida can bring light, short rain showers to the northern and central areas. However, late winter can be very dry. In some years, the dry season is so severe that people have to limit their water use. While most of Florida doesn't get snow, northern Florida might see a little snow or sleet a few times every ten years.
The Gulf Stream is a warm ocean current that flows near Florida's coast. It helps keep temperatures mild near the coast all year, from Stuart on the east to Fort Myers on the west. This current also makes Florida's beaches have the warmest ocean water on the United States mainland. Florida's location also makes it sensitive to climate change, which can lead to stronger hurricanes and coastal flooding from sea level rise.
Contents
- What are the lowest and highest air pressures in Florida?
- How windy does it get in Florida?
- What are Florida winters like?
- What are Florida summers like?
- Does Florida get fog?
- How much does it rain in Florida?
- Why does Florida have so many thunderstorms?
- How do tropical cyclones affect Florida?
- How do climate cycles affect Florida's weather?
- What are the climates of some Florida cities?
- Images for kids
What are the lowest and highest air pressures in Florida?
Air pressure is how much the air around us pushes down. The lowest air pressure ever recorded from a big winter storm was 28.84 inches (976.7 hPa) during the Storm of the Century (1993). For a tropical storm, the lowest pressure was 26.35 inches (892 hPa) in the Florida Keys during the Labor Day Hurricane of 1935. The highest air pressure recorded in Florida was 30.74 inches (1041.1 hPa) in Tallahassee on February 5, 1996, and January 4, 1979.
How windy does it get in Florida?
In winter, winds usually blow from the north in northern Florida, down to places like Orlando. In other parts of the state, winds can come from different directions. During summer, winds generally blow from the east and southeast across the Florida peninsula. The strongest wind gust recorded between 1930 and 1997 was 115 miles per hour at Miami International Airport during Hurricane Andrew.
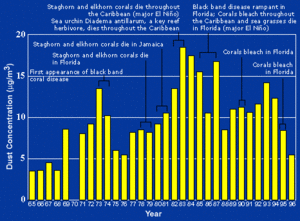
What is African dust and how does it affect Florida?
Sometimes in July, strong winds can carry dust from the Sahara Desert in Africa all the way across the ocean to Florida. When this happens, the sky might look white instead of blue, and sunsets can appear very red. This dust can also make the air quality worse in the Southeastern United States by adding tiny particles to the air. Over half of the African dust that reaches the U.S. affects Florida. Since the 1970s, these dust events have become more common due to droughts in Africa. Scientists think these dust events might be harming coral reefs in the Caribbean and Florida.
What are Florida winters like?

Florida generally has the mildest winters in the continental United States. Average low temperatures range from 65°F (18°C) in Key West to about 41°F (5°C) in Tallahassee. Daytime highs are usually between 62°F (17°C) in Tallahassee and 77°F (25°C) in Miami.
Warm winds from the tropics keep central and southern Florida warm during winter. Occasionally, strong cold fronts move south, bringing freezing or near-freezing temperatures to inland areas of central Florida. Miami might see a winter night below 45°F (7°C) a few times every ten years. Winters during an El Niño weather pattern tend to be cooler because there are more clouds, but they also have fewer freezes.
Florida has experienced 12 major freezes. Four of these were so severe that they killed many citrus trees, causing big economic problems for farmers. These "impact" freezes made farmers move their groves further south. Some of the most notable freezes happened in 1894-1895, 1962, 1983, and 1989.
The cold winter weather was a major factor in the Space Shuttle Challenger disaster on January 28, 1986. Temperatures near the Kennedy Space Center dropped below freezing, which caused parts of the shuttle to fail during launch.
What are Florida summers like?

During summer, average high temperatures are around 95°F (35°C) in northern Florida and 90°F (32°C) in the Keys. The highest temperatures can reach into the upper 90s°F (30s°C) across the state. The "heat index," which is how hot it feels with humidity, can easily reach 103°F–110°F (39°C–43°C).
People find relief from the summer heat in a few ways:
- Afternoon and evening thunderstorms cool things down.
- Sea breezes from the cooler ocean arrive in the late morning and afternoon.
- Sometimes, a tropical storm or hurricane can bring cooler air.
The highest temperature ever recorded in Florida was 109°F (43°C) in Monticello in 1931.
Does Florida get fog?
Florida gets a lot of dense fog in winter, especially in the morning. This fog can be dangerous for drivers. For example, on January 9, 2008, thick fog combined with smoke from a fire on Interstate 4. Visibility dropped to almost zero, leading to a huge 70-car pileup where five people died.
How much does it rain in Florida?
Florida gets the most rain during the summer months. In northern Florida, there's also a smaller peak in rainfall during winter. The driest months across the state are in the spring. During El Niño years, Florida usually gets more rain between November and March.
Because of the dry season from winter through spring, brush fires happen every year as temperatures rise in late spring. These fires usually stop by early June when the rainy season begins.
What are the rainfall records in Florida?
The most rain ever recorded in Florida in 24 hours was 38.70 inches (983 mm). This happened in Yankeetown during Hurricane Easy (1950). This was also the highest rainfall from any tropical storm in Florida's history.
The wettest month ever recorded at a Florida weather station was May 1891, when Gainesville, Florida received 30.90 inches (785 mm) of rain. The wettest year on record was 1879, when Pensacola, Florida got 127.24 inches (3232 mm) of rain. The driest year for a weather station was 1974, when Key West only received 19.99 inches (508 mm).
One of the worst years for wildfires was 1998, when 480 wildfires burned over 500,000 acres (2,000 km²) across the state. A statewide drought began in November 2005 and lasted until 2009.
Does it snow in Florida?
Snowfall is very rare in Florida. The earliest time snow or sleet was recorded was in 1774 in northern Florida. The latest it has fallen was on January 16, 2022, when snow flurries were seen in Crestview and other northern parts of the state.
The state record for snowfall is 5 inches (13 cm), set in northern Florida in January 1800, though some people question if this record is completely accurate. Snow flurries have even been reported as far south as Homestead in 1977, though they didn't stick to the ground.
Why does Florida have so many thunderstorms?
Florida has more thunderstorms than any other U.S. state. Some areas experience over 90 thunderstorm days each year, making Florida one of the most thundery places outside of the tropics. Florida also gets the most lightning strikes in the United States. Sadly, lightning causes several deaths each year, making it one of the deadliest weather events in the state. However, since 1992, lightning deaths have been slowly decreasing, likely because of lightning safety programs.
Severe thunderstorms can sometimes bring hail, very strong straight-line winds, and tornadoes. Very heavy rain from thunderstorms can also cause flash flooding. Thunderstorms happen most often in the summer but can occur at any time of year.
Are there tornadoes in Florida?
Florida actually has more tornadoes per square mile than any other state! However, these tornadoes are usually weaker and don't last as long as those in the Midwest or Deep South. Strong tornadoes do form occasionally in Florida, often when a cold front passes through in winter or spring. In February 1998, 42 people died in a very deadly tornado outbreak in Central Florida, which happened at night.
Even though Florida's tornadoes are often weaker, more people tend to die from them here. This is because Florida has a higher population density and many manufactured homes, which are more vulnerable to strong winds.
How do tropical cyclones affect Florida?

A tropical cyclone is a rotating storm system that forms over warm ocean waters, like a tropical depression, tropical storm, or hurricane. The earliest in the year a tropical cyclone has hit Florida was the Groundhog Day Tropical Storm in 1952. The latest was a hurricane that hit near Tampa on December 1, 1925. The strongest hurricane to ever hit Florida was the Labor Day Hurricane of 1935.
In 2004, Florida was hit by a record four hurricanes in one season! Hurricanes often create tornadoes in their northeast part. Tropical cyclones have affected Florida in every month except March. Almost one-third of these storms hit in September, and nearly three-fourths hit between August and October. This is the busiest time of the hurricane season. Monroe County has been hit by 26 hurricanes since 1926, which is the most for any county in the United States.
How do climate cycles affect Florida's weather?
Large climate patterns like El Niño and La Niña can have a big impact on Florida's weather.
- El Niño usually brings more rain than average in the spring. This can be followed by a higher risk of wildfires when the rain stops. Northern Florida is more likely to experience severe weather. Temperatures are often below normal, and there are more low-pressure systems in the Gulf of Mexico during winter. El Niño almost always reduces the number of tropical storms and hurricanes.
- La Niña often brings dry conditions in late fall, winter, and early spring. This increases the risk of wildfires in the spring and summer. Temperatures tend to be slightly above normal, and the chance of hurricane activity increases a lot.
Scientists use these patterns to make long-term weather forecasts. However, other patterns like the Arctic oscillation and North Atlantic oscillation can change these predictions, especially in winter. These can cause temperatures to drop significantly from what's normally expected, but they can only be predicted about two weeks in advance.
What are the climates of some Florida cities?
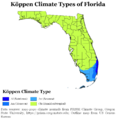
Most of Florida has a humid subtropical climate. However, the Miami Metropolitan Area, southwest Florida (from Fort Myers south), and all of the Florida Keys have a tropical wet-and-dry climate. This means they have distinct wet and dry seasons, like many tropical regions.
Cities like Orlando and Jacksonville get between 2,400 and 2,800 hours of sunshine each year. The rest of the state, including Miami, gets even more sunshine, between 2,800 and 3,200 hours annually.
| Weather chart for Pensacola, Florida | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
5.3
61
43
|
4.7
64
45
|
6.4
70
52
|
3.9
76
58
|
4.4
83
66
|
6.4
89
72
|
8
91
75
|
6.9
90
74
|
5.8
87
70
|
4.1
79
60
|
4.5
70
51
|
4
63
45
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| temperatures in °F precipitation totals in inches source: NOAA |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Metric conversion
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weather chart for Tallahassee, Florida | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
4.4
64
40
|
4.9
67
42
|
5.7
73
47
|
3.7
80
53
|
4.3
87
62
|
7.1
91
69
|
8.3
92
72
|
7.3
91
72
|
5.4
88
69
|
3.2
81
57
|
3.3
72
47
|
4.2
66
41
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| temperatures in °F precipitation totals in inches source: Florida Climate Center |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Metric conversion
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weather chart for Jacksonville, Florida | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
3
65
43
|
3.4
68
45
|
3.7
74
50
|
2.8
80
56
|
3.4
86
64
|
6
90
70
|
6.6
92
73
|
7.2
91
73
|
7.8
87
70
|
3.9
80
61
|
1.9
73
51
|
2.6
67
44
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| temperatures in °F precipitation totals in inches source: Florida Climate Center |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Metric conversion
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weather chart for Orlando, Florida | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2.4
71
49
|
2.4
74
52
|
3.8
78
56
|
2.6
83
60
|
3.5
88
66
|
7.6
91
72
|
7.3
92
74
|
7.1
92
74
|
6.1
90
73
|
3.3
85
66
|
2.2
78
59
|
2.6
73
52
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| temperatures in °F precipitation totals in inches source: NOAA |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Metric conversion
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weather chart for Daytona Beach, Florida | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2.7
68
47
|
2.8
71
50
|
4.2
75
54
|
2.2
79
59
|
3.1
85
65
|
5.8
88
71
|
5.8
90
73
|
6.4
90
73
|
7
87
72
|
4.2
82
66
|
2.7
76
58
|
2.6
71
51
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| temperatures in °F precipitation totals in inches source: Florida Climate Center |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Metric conversion
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weather chart for Tampa, Florida | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2.3
70
52
|
2.7
72
54
|
2.8
76
59
|
1.8
81
62
|
2.9
86
69
|
5.5
89
74
|
6.5
90
75
|
7.6
90
75
|
6.5
89
74
|
2.3
84
68
|
1.6
78
61
|
2.3
72
55
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| temperatures in °F precipitation totals in inches source: Florida Climate Center |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Metric conversion
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weather chart for Miami, Florida | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
1.8
76
60
|
2.1
77
61
|
2.5
80
64
|
3.2
83
68
|
5.9
86
72
|
9.3
88
75
|
6.2
90
77
|
8
90
77
|
9.1
88
76
|
7
85
72
|
2.9
81
68
|
2
77
62
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| temperatures in °F precipitation totals in inches source: Florida Climate Center |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Metric conversion
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weather chart for Key West, Florida | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2
75
65
|
1.6
76
66
|
1.7
79
69
|
1.8
82
72
|
3.1
85
76
|
4.6
88
78
|
3.7
89
80
|
5.3
90
79
|
6.6
88
78
|
5
85
76
|
2.5
80
71
|
2
76
67
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| temperatures in °F precipitation totals in inches source: Florida Climate Center |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Metric conversion
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Images for kids
-
Climate types in Florida.
 | Selma Burke |
 | Pauline Powell Burns |
 | Frederick J. Brown |
 | Robert Blackburn |