California live oak facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Coast live oak |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Coast live oak foliage with new spring growth | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Genus: |
Quercus
|
| Species: |
agrifolia
|
 |
|
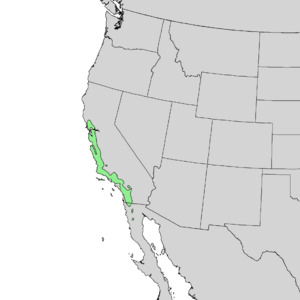
| Natural range | |
| Synonyms | |
|
List
Quercus acroglandis Kellogg
Quercus acutiglandis Sarg. Quercus agrifolia var. frutescens Engelm. Quercus agrifolia var. oxyadenia (Torr.) J.T.Howell Quercus oxyadenia Torr. Quercus pricei Sudw. |
|
The Coast Live Oak (Quercus agrifolia) is a special type of evergreen oak tree. It is also known as the California live oak or holm oak. This tree is native to the California Floristic Province, which means it naturally grows in California and parts of Mexico. You can find it mostly west of the Sierra Nevada mountains, from Mendocino County in California down to northern Baja California in Mexico.
Sometimes, it can be tricky to tell the Coast Live Oak apart from other oaks, like the canyon live oak. This is because their spiny leaves look quite similar.
Contents
About the Coast Live Oak Tree
Coast Live Oaks usually have many branches and can grow to be about 10 to 25 meters (33 to 82 feet) tall. Some of these trees can live for a very long time, even over 1000 years! Famous old examples include the Grand Oak and the Pechanga Great Oak.
Older trees often have thick, twisted, and gnarled trunks. When they are younger (around 20 to 70 years old), their tops are very round and full of leaves. As they get older, their trunks and branches become more visible, and the leaves are less dense. The oldest trees can have trunks more than 6 meters (20 feet) around and be over 30 meters (100 feet) tall!
What Do the Leaves Look Like?
The leaves of the Coast Live Oak are dark green and shaped like an oval. They are often slightly curved, like a bowl. Each leaf is about 2 to 7 centimeters (0.8 to 2.8 inches) long and 1 to 4 centimeters (0.4 to 1.6 inches) wide. The edges of the leaves are spiny, with sharp, thistle-like fibers coming from the veins.
The leaves on the outside of the tree are designed to soak up as much sunlight as possible. They have two or three layers of cells that help the tree make food from sunlight. These outer leaves are small, which helps them release heat from the sun. Leaves in the shade are usually wider and thinner, with only one layer of food-making cells. Their curved shape might help them catch scattered light from the leaves above.
Flowers and Acorns
The Coast Live Oak produces its flowers in the early to middle part of spring. The male flowers hang down in long clusters called catkins, which are about 5 to 10 centimeters (2 to 4 inches) long. The female flowers are tiny, less than 0.5 centimeters (0.2 inches) long, and grow in small groups of 1 to 3.
The fruit of the tree is a slender, reddish-brown acorn. These acorns are about 2 to 3.5 centimeters (0.8 to 1.4 inches) long and 1 to 1.5 centimeters (0.4 to 0.6 inches) wide. The bottom quarter of the acorn is covered by a small cup. What's interesting is that these acorns ripen quite quickly for a red oak, taking only about 7 to 8 months after the flowers are pollinated. Most other red oak acorns take much longer, about 18 months.
Different Types of Coast Live Oak
There are two main types, or varieties, of Quercus agrifolia:
| Image | Scientific Name | What It Looks Like | Where It Grows |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Quercus agrifolia var. agrifolia | Its leaves are smooth or slightly hairy on the underside, especially near the leaf veins. This type can mix with other oaks like the California black oak and interior live oak. | Found throughout the main area where the Coast Live Oak grows. |
| Quercus agrifolia var. oxyadenia | Its leaves are very hairy on the underside, with thick, tangled hairs. This type prefers rocky soils. It can also mix with the California black oak. | Found in the very southwestern part of California (around San Diego) and in Baja California, Mexico. |
Mixing with Other Oaks
Coast Live Oaks can sometimes mix their genes with other red oak species. This creates what are called "hybrids." For example, hybrids with the interior live oak are found in many parts of northern California. They also hybridize with the Shreve oak. This mixing shows how closely related these different oak species are.
Where the Name Comes From
The name agrifolia comes from Latin words. When the species was named, it was compared to a plant that looked like a holly or a holly-leaved oak. The word "Agrifolia" is an old Latin form of "Aquifolium," which means holly. This is why the tree is sometimes called "holm oak," as "holm" is an old word for holly.
Home and Environment
The Coast Live Oak is special because it's the only native California oak that really thrives near the coast. It loves the mild winters and summers that come from being close to the ocean. It can even handle some sea salt carried by the wind. The coastal fog helps it stay cool during the dry California summers.
This tree is often the main type of plant in its forest home, called a "coast live oak woodland." It often grows alongside trees like California bay laurel and California buckeye. Smaller plants that grow with it include toyon, different types of manzanita, and western poison-oak.
Coast Live Oaks usually grow on well-drained soils on coastal hills and plains, often near streams that flow all year. You can find them in different natural areas, including coast live oak woodlands and mixed evergreen forests. While they usually grow within 100 kilometers (60 miles) of the Pacific Ocean at elevations below 700 meters (2,300 feet), in southern California, they can sometimes be found as high as 1,500 meters (4,900 feet).
The California oak moth caterpillar eats only the leaves of the Coast Live Oak. Every 8 to 10 years, there are so many caterpillars that they can eat almost all the leaves off healthy trees. But don't worry, the trees usually recover! Some scientists think the caterpillars might even help the oak trees by providing fertilizer. The Coast Live Oak is also the only known food source for the caterpillars of another moth, Chionodes vanduzeei.
Pollen and Allergies
The pollen from the Coast Live Oak can cause strong allergies in some people. The tree releases its pollen in the spring.
How People Have Used Coast Live Oaks
Past Uses

Many different Native American groups used the acorns from the Coast Live Oak as a very important food. They would grind the seeds into a meal, wash it, and then boil it into a mush or bake it into bread.
In the 1700s, when Spaniards came to the San Fernando Valley, they used the wood to make charcoal. This charcoal was used to heat kilns for making adobe bricks. Later, this type of charcoal was also used in baking, making gunpowder, and for early electric power industries.
In the 1700s and 1800s, shipbuilders liked the tree's unusual, angled branches. They used them to make special joints for ships. Early pioneers moving west would cut down small amounts of wood to make farm tools and wagon wheels. However, the biggest impact was when large areas of oak woodlands were cleared to build big cities like San Diego and San Francisco. Because of its irregular shape, the tree was often not cut down for building timber, which also led early settlers to think the Coast Live Oak had special, almost magical, qualities. Its grand appearance has made it a popular subject for landscape painters in California since the mid-1800s.
Modern Uses
Today, the Coast Live Oak is often planted in gardens and parks in the western USA. However, it is sensitive to changes in the ground and how water drains. It's very important not to add soil around the base of the tree when building or landscaping.
Also, if you water your garden, try to avoid regularly watering the soil directly under the oak's branches (its drip line) during the summer. Wet soil in the summer can increase the risk of diseases like sudden oak death, which are caused by tiny organisms in the soil.
Places Named After the Oak
The Coast Live Oak, especially using its Spanish names like encino or encina (meaning "oak"), encinitas ("little oaks"), and encinal ("oak grove"), gave its name to many places in California. These include Rancho Los Encinos, the Los Angeles community of Encino, Encinitas near San Diego, and Encinal del Temescal, which is now the city of Oakland.
Paso Robles, which originally meant "Pass of the Oaks," also refers to these trees in its name.
See also
 In Spanish: Encina de California para niños
In Spanish: Encina de California para niños





