San Fernando Valley facts for kids
Quick facts for kids San Fernando Valley |
|
|---|---|

The San Fernando Valley looking northeast; from the top of Topanga Overlook Park above Woodland Hills in foreground
|
|
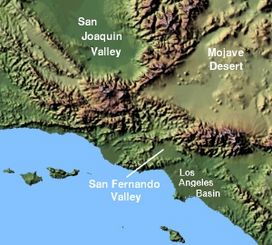
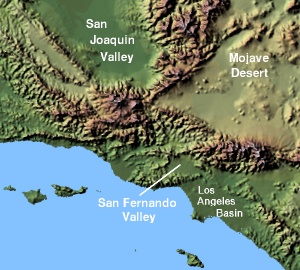
San Fernando Valley
|
|
| Area | 260 square miles (670 km2) |
| Naming | |
| Native name | Error {{native name}}: an IETF language tag as parameter {{{1}}} is required (help) |
| Geography | |
| Location | California |
| Population centers | Los Angeles, Burbank, Glendale, Calabasas, Hidden Hills, San Fernando |
| Borders on | Santa Susana Mountains (northwest), Simi Hills (west), Santa Monica Mountains and Chalk Hills (south), Verdugo Mountains (east), San Gabriel Mountains (northeast) |
The San Fernando Valley, often called the Valley, is a large urban area in Los Angeles County, California. It sits just north of the main Los Angeles Basin. A big part of the City of Los Angeles is located here. You'll also find other cities like Burbank, Calabasas, Glendale, Hidden Hills, and San Fernando. The Valley is famous for its movie studios, such as Warner Bros. Studio and Walt Disney Studios. It's also home to the Universal Studios Hollywood theme park.
Contents
- Exploring the Valley's Geography
- Understanding the Valley's Natural Habitat
- A Look at the Valley's History
- Parks and Fun Places in the Valley
- Cities and Neighborhoods of the Valley
- How the Valley is Connected: Transportation
- Valley Utilities and Services
- Culture and Arts in the Valley
- Valley Independence Efforts
- Who Lives in the San Fernando Valley: Demographics
- The Valley's Economy
- Learning in the Valley: Education
- Images for kids
- See also
Exploring the Valley's Geography
The San Fernando Valley covers about 260 square miles (670 km2). It's surrounded by mountains. To the northwest are the Santa Susana Mountains, and to the west are the Simi Hills. The Santa Monica Mountains and Chalk Hills are to the south. The Verdugo Mountains are to the east, and the San Gabriel Mountains are to the northeast. From higher spots in the Valley, you can even see the Downtown Los Angeles skyscrapers.
The Los Angeles River starts in the Valley. It begins where Calabasas Creek and Bell Creek meet in Canoga Park. These creeks get their water from the Santa Monica foothills and the Simi Hills. The river then flows east through the southern parts of the Valley. A special part of the river that isn't paved is found at the Sepulveda Basin. Another important waterway, the Tujunga Wash, flows from the San Gabriel Mountains. It joins the Los Angeles River in Studio City. The Valley floor ranges from about 600 ft (180 m) to 1,200 ft (370 m) above sea level.
Most of the San Fernando Valley is part of the city of Los Angeles. However, some other cities are also located here. Burbank and Glendale are in the southeast. Hidden Hills and Calabasas are in the southwest. San Fernando is completely surrounded by Los Angeles in the northeast. Universal City is a small area that isn't part of any city, and it's where Universal Studios is located. Mulholland Drive runs along the Santa Monica Mountains and marks the border between the Valley and areas like Hollywood.
Understanding the Valley's Natural Habitat
The San Fernando Valley used to be a natural home for many plants and animals. It had grasslands, oak forests, and chaparral shrub areas. Along the rivers and creeks, there were lots of lush plants. After the 1790s, European settlers started farming here. They grew grapes, figs, olives, and other garden crops.
A Look at the Valley's History
Early History Before California Statehood
For over 8,000 years, the Tongva people lived and thrived in the Valley. They had many villages and camps. The Tataviam people lived to the north, and the Chumash to the west. In 1769, the Spanish arrived and began to settle the Valley.
The first Spanish land grant in the Valley was called "Rancho Encino." This was in the northern part of the Valley, near what is now Mission Hills. Juan Francisco Reyes built a home there next to a Tongva village. However, the land was soon taken to build a mission. Mission San Fernando Rey de España was built in 1797. Juan Francisco Reyes was given other land, which became Rancho Los Encinos (now Los Encinos State Historic Park in Encino). Later, other Mexican land grants covered the Valley, including Rancho El Escorpión and Rancho Ex-Mission San Fernando.
The Treaty of Cahuenga was signed in 1847. This treaty ended the fighting of the Mexican–American War in California. It was signed by Californians and Americans at Campo de Cahuenga in the southeast Valley. The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848 officially ended the entire war.
California Statehood and Beyond
In 1874, dry wheat farming became popular in the Valley. J. B. Lankershim and Isaac Van Nuys made it very successful. In 1876, they sent the first wheat shipment from the United States to Europe.
The 20th Century: Growth and Change
The Aqueduct's Impact
In the late 1800s, Los Angeles gained rights to the water under the Valley. Farmers in the San Fernando Valley wanted to buy this extra water. However, a law said Los Angeles couldn't sell water outside its city limits. This led many independent towns around Los Angeles to join the city. By doing so, they could get access to the city's water system. These rural areas became part of Los Angeles in 1915.
A group of developers, including Harry Chandler and Henry E. Huntington, helped this growth. They extended the Pacific Electric Railway (Red Cars) through the Valley. They also planned new roads and towns like Lankershim (now North Hollywood) and Van Nuys. More areas like La Tuna Canyon and Tujunga also joined Los Angeles. These additions more than doubled the size of the city.
The new water from the aqueduct changed farming. Farmers switched from dry crops like wheat to irrigated crops like corn, beans, and cotton. They also grew many apricots, persimmons, and walnuts, as well as citrus fruits like oranges and lemons. Over time, as the Valley grew, most of these farms were replaced by new neighborhoods.
Valley Development and Growth
Three new industries helped the Valley grow a lot in the early 1900s: movies, cars, and airplanes. After World War II, the population grew even faster. Between 1945 and 1960, the Valley's population became five times larger! Los Angeles continued to add more areas of the Valley. For example, Porter Ranch joined Los Angeles in 1965.
Six cities in the Valley became independent from Los Angeles: Glendale (1906), Burbank and San Fernando (1911), Hidden Hills (1961), and Calabasas (1991). Universal City is a special area that is not part of any city, and it's home to the Universal Studios theme park.
The Northridge Earthquake
On January 17, 1994, a strong earthquake hit the Valley. It was called the Northridge earthquake and measured 6.7 on the Moment magnitude scale. Even though it was named "Northridge," the earthquake's center was actually in Reseda. This earthquake caused a lot of damage. Fifty-seven people died, and over 1,500 were seriously hurt. Many homes and businesses lost power, gas, or water. About 12,500 buildings were badly damaged, leaving thousands of people without homes. Major freeways were also damaged, causing traffic problems.
This was the second strong earthquake to affect the Valley in 23 years. In 1971, another earthquake caused 58 deaths and about 2,000 injuries.
The Valley Today
By the late 1990s, the San Fernando Valley became more urban and diverse. In 2002, some people in the Valley wanted to separate from Los Angeles and become their own city. They felt they weren't getting enough services from Los Angeles. Even though this attempt didn't succeed, the Valley has seen many improvements. A new city building was built in Van Nuys in 2003. The Metro Orange Line (now G Line) opened in 2005, and many new public schools have opened. Today, the Valley is very diverse, with a large Hispanic population.
Parks and Fun Places in the Valley

The San Fernando Valley has many city parks, recreation areas, and large natural preserves. These places are great for outdoor activities. Many are managed by the National Park Service, California State Parks, and local park groups.
Small Gardens and Historic Missions
- The Japanese Garden
- The gardens at Adobes
- The Orcutt Ranch Horticulture Center
- The Leonis Adobe
- The Andrés Pico adobe
- Los Encinos State Historic Park
- Mission San Fernando
Recreation Areas for Fun Activities
- Griffith Park, located at the southeastern end of the Valley
- Sepulveda Dam recreation area
- Hansen Dam recreation area
- Los Angeles River, with parks along its path in the Valley
Mountain Open-Space Parks for Exploring
- Backbone Trail System
- Bell Canyon Park
- Brand Park
- Chatsworth Park South
- Deukmejian Wilderness Park
- El Escorpión Park
- Juan Bautista de Anza National Historic Trail
- La Tuna Park
- Laurel Canyon Park
- Marvin Braude Mulholland Gateway Park
- O'Melveny Park above Granada Hills
- Rocky Peak Park
- Sage Ranch Park
- Santa Susana Pass State Historic Park
- Topanga State Park
- Upper Las Virgenes Canyon Open Space Preserve
- Verdugo Mountains Open Space Preserve
- Wilacre Park
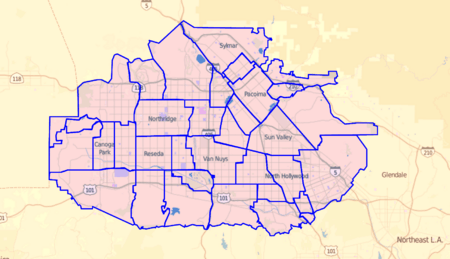
Cities and Neighborhoods of the Valley
Independent Cities in the Valley
Unincorporated Communities (Not Part of a City)
- Bell Canyon
- Calabasas Highlands
- Kagel Canyon
- Universal City
- West Chatsworth
Los Angeles Neighborhoods in the San Fernando Valley
- Arleta
- Cahuenga Pass
- Canoga Park
- Chatsworth
- Encino
- Granada Hills
- La Tuna Canyon
- Lake Balboa
- Lake View Terrace
- Mission Hills
- NoHo Arts District
- North Hills
- North Hollywood
- Northridge
- Pacoima
- Panorama City
- Porter Ranch
- Reseda
- Shadow Hills+
- Sherman Oaks
- Studio City
- Sun Valley
- Sunland-Tujunga+
- Sylmar
- Tarzana
- Toluca Lake
- Valley Glen
- Valley Village
- Van Nuys
- Warner Center
- West Hills
- Winnetka
- Woodland Hills
+ These communities are also included in the Crescenta Valley.
How the Valley is Connected: Transportation
Major Roads and Freeways
Many important freeways cross the Valley. These include Interstate 405, U.S. Route 101, and State Route 118. Other notable streets are Sepulveda Boulevard, Ventura Boulevard, and Victory Boulevard.
Public Transportation Options
The Valley has subways, special bus lanes, and many bus routes. These are run by different agencies. Some old railway paths have been turned into busways and train lines.
The Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority operates two Metro B Line subway stations in the Valley. These are in Universal City and North Hollywood. They connect the Valley directly to Hollywood and Downtown Los Angeles. The B Line also connects to the larger Metro train network. These stations also provide access to Bob Hope Airport and Amtrak trains.
The G Line busway runs across the Valley from east to west. It connects the North Hollywood B Line Station to the Warner Center Transit Hub in Woodland Hills. It then goes north through Canoga Park to the Chatsworth Metrolink train station.
More Metro Busway lines are planned for the Valley. One will go to Pasadena, and another will offer more east-west services. Metro is also looking into new ways to travel through the Sepulveda Pass, possibly with a heavy rail or monorail.
Trains and Airports
Metrolink commuter rail has two lines in the Valley: the Antelope Valley Line and Ventura County Line. These lines connect the Valley to downtown Los Angeles. There are two Metrolink stations near Burbank Airport.
Amtrak's Pacific Surfliner train stops at Burbank Airport, Van Nuys, and Chatsworth Station. From there, it goes to places like Santa Barbara or Union Station in Los Angeles.
The California High-Speed Rail Authority plans to have one station in the Valley, located in Burbank.
The Valley's two main airports are Hollywood Burbank Airport and the Van Nuys Airport. The Van Nuys Airport also has a shuttle service to LAX.
Valley Utilities and Services
Electricity, Gas, and Water
Most utilities in the Valley are provided by public city governments, mainly Los Angeles and Burbank. Some private companies also provide gas and electricity.
Electricity
- Los Angeles Department of Water and Power (serves most of the Los Angeles parts of the Valley)
- Burbank Water and Power
- Southern California Edison (serves San Fernando, Calabasas, and Hidden Hills)
Natural Gas
- Southern California Gas Company
Water
- Los Angeles Department of Water and Power (serves most of the Los Angeles parts of the Valley)
- Burbank Water and Power
- City of San Fernando
- Metropolitan Water District
Internet, Cable, and Phone Service
Large private companies provide internet, cable television, and cell phone service in the Valley. These include AT&T, Frontier Communications, Charter Communications (Spectrum), T-Mobile, Cricket Wireless, and Verizon Wireless.
Sanitation
Sanitation services are handled by the City of Los Angeles, the City of San Fernando, and the City of Burbank.
Healthcare Services
The San Fernando Valley has several hospitals. There are two Kaiser Permanente hospitals in Panorama City and Woodland Hills. Providence hospitals are in Burbank and Mission Hills. Other non-profit hospitals include Valley Presbyterian Hospital in Van Nuys and Northridge Hospital Medical Center in Northridge.
Community Services
The main administrative center for the Valley is The Civic Center Van Nuys, located in Van Nuys. This area has a police station, courts, and city and county offices.
Libraries are provided by the Los Angeles Public Library and independent city libraries. Police services are handled by the Los Angeles Police Department, Los Angeles County Sheriff's Department, and local city police departments. Fire services are provided by the Los Angeles Fire Department and Los Angeles County Fire Department.
Culture and Arts in the Valley
The San Fernando Valley is home to many interesting cultural places:
- The Alex Theatre – Built in 1925, it's a center for arts and culture in Glendale.
- The Great Wall of Los Angeles – A very long mural (2,754 feet!) that shows the history of California. It's painted on the sides of the Tujunga Wash.
- The Museum of Neon Art (MONA) – A museum in Glendale dedicated to art made with neon lights.
- The Nethercutt Collection – A museum in Sylmar famous for its collection of classic cars. It also has old musical instruments and antique furniture.
- The Starlight Bowl – An outdoor amphitheater in Burbank that can hold 5,000 people. It was built in 1950.
- The Valley Performing Arts Center – Located at the CSUN campus, it has a 1,700-seat concert hall.
Valley Independence Efforts
Movements to Become a Separate City
In the 1970s, there was an attempt for the Valley to become its own city. Later, in 1997, a new law made it easier for the Valley to try again. Many residents felt they weren't getting fair services from Los Angeles.
The 2002 Vote
In 2002, the San Fernando Valley seriously campaigned again to separate from Los Angeles. They wanted to become a new, independent city. Many Valley residents felt they were paying too much in taxes compared to the services they received.
Before the vote, a group studied if a new Valley city would be financially stable. They found it would be, but it would need to make up for money Los Angeles would lose. This showed supporters that the Valley contributed more money than it got back. This led to a petition to put the idea on the ballot. Voters also got to choose a new name for the proposed city. Some names were San Fernando Valley, Rancho San Fernando, Mission Valley, Valley City, and Camelot. "Valley City" was chosen as the favorite name.
Some politicians were against the idea. Supporters argued that the Valley faced its own challenges, similar to other parts of the city.
The vote, called Measure F, did not pass. Even though a small majority in the Valley voted for it, the rest of Los Angeles voted against it. This was partly due to a campaign led by the then-mayor of Los Angeles. If the measure had passed, the new City of San Fernando Valley would have been one of the largest cities in the United States.
Neighborhood Name Changes
The NoHo Arts District was created in North Hollywood. Its name is a play on New York City's SoHo District. This change helped turn a regular suburb into a lively area for art and artists.
From 2002 to 2007, there was a discussion about officially recognizing Lake Balboa as a community. In 2007, the City Council approved renaming a larger part of Van Nuys to Lake Balboa.
Who Lives in the San Fernando Valley: Demographics
As of 2012, about 1.77 million people lived in the San Fernando Valley. About 41.8 percent were Hispanic or Latino, and 41.0 percent were non-Hispanic white. About 12.7 percent were Asian, and 4.6 percent were African American.
The largest city fully within the Valley is Burbank, with over 107,000 residents. Some of the most populated neighborhoods in Los Angeles within the Valley are Van Nuys and Pacoima. These areas have many apartment buildings and are quite dense.
The Valley has a diverse economy. While some areas are very well-off, others face economic challenges. Community efforts are continuously working to improve conditions across all neighborhoods.
The Valley's Economy
The Valley is home to many companies, especially those in movies, music, and television. Famous studios like CBS Studio Center, NBCUniversal, The Walt Disney Company, and Warner Bros. are located here.
In the past, the Valley was known for its advances in aerospace technology and nuclear research. Companies like Lockheed and Rocketdyne had important facilities here.
Learning in the Valley: Education
Public schools in the San Fernando Valley are managed by three school districts: the Los Angeles Unified School District, the Glendale Unified School District, and the Burbank Unified School District.
There are four community colleges in the Valley: Los Angeles Valley College in Valley Glen, Los Angeles Mission College in Sylmar, and Los Angeles Pierce College in Woodland Hills. The only state university in the Valley is California State University Northridge in Northridge.
In 1994, about 180,000 students attended public schools in the Valley. Around 45,000 students also attended over 200 private schools.
Images for kids
-
San Fernando vs Livermore valleys water comparison map by William Mulholland, 1912
-
Californio ranchero Eulogio F. de Celis once owned most of the San Fernando Valley.
See also
 In Spanish: Valle de San Fernando para niños
In Spanish: Valle de San Fernando para niños