Congolian rainforests facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Congolian rainforests |
|
|---|---|
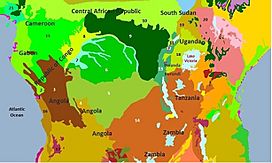
Congolian rainforest ecoregions: 2. Atlantic Equatorial coastal forests, 6. Central Congolian lowland forests 7. Eastern Congolian swamp forests, 8. Western Congolian swamp forests, 9. Northeastern Congolian forests, 15. Northwestern Congolian lowland forests
|
|
| Ecology | |
| Realm | Afrotropical |
| Biome | Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests |
| Geography | |
| Countries | |
The Congolian rainforests are huge forests in Central Africa. They cover the area around the Congo River and its smaller rivers. These forests are special because they are the only big rainforests that take in more carbon than they release. This helps our planet a lot.
Contents
About the Congolian Rainforests
The Congolian rainforest is the second-largest tropical forest in the world. Only the Amazon rainforest is bigger. It covers a huge area, more than 500 million acres (about 2 million square kilometers). This forest spreads across six different countries in Africa. It holds about a quarter of all the tropical forests left on Earth.
You can find parts of the Congolian forests in southeastern Cameroon and Gabon. They are also in the Republic of the Congo. A large part is in the northern and central Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Where the Forest Meets Other Areas
To the north, south, and southwest, the rainforest slowly changes. It becomes a drier area called a forest-savanna mosaic. This is a mix of drier forests, savannas (grassy plains), and grasslands.
To the west, the Congolian forests connect to the Lower Guinean forests. These stretch from southwestern Cameroon to southern Nigeria. Both forest areas are very similar. Sometimes, they are called the Lower Guinean-Congolian forests together.
To the east, the lowland Congolian forests rise into mountains. Here, you find the Albertine Rift montane forests. These forests grow on the mountains along the Albertine Rift. This rift is a part of the big Great Rift Valley system in East Africa.
Different Forest Areas
The World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) has divided the Congolian forests into six main areas. These are called ecoregions:
- Atlantic Equatorial coastal forests (found in Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Republic of the Congo, Angola, and Democratic Republic of the Congo)
- Northwestern Congolian lowland forests (found in Cameroon, Central African Republic, Gabon, and Republic of Congo)
- Western Congolian swamp forests (found in Republic of the Congo and Democratic Republic of the Congo)
- Eastern Congolian swamp forests (found only in the Democratic Republic of the Congo)
- Central Congolian lowland forests (found only in the Democratic Republic of the Congo)
- Northeastern Congolian lowland forests (found in Democratic Republic of the Congo and Central African Republic)
Plants and Animals of the Rainforest
The Congolian rainforests are home to over 10,000 types of plants. About 30% of these plants are endemic. This means they are found only in this forest and nowhere else in the world. While not as diverse as the Amazon, this forest still has amazing plant and animal life. It is much richer than most other places on Earth.
More than 400 kinds of mammals live here. These include amazing animals like African forest elephants and African bush elephants. You can also find chimpanzees, bonobos, mountain gorillas, and lowland gorillas. The okapi, a unique animal that looks like a mix of a zebra and a giraffe, lives only in the northeastern Congolian rainforests.
The rainforests are also home to 1,000 types of native birds. Plus, there are 700 different kinds of fish swimming in its rivers and streams.
Protecting the Rainforest
The Congolian rainforests face some dangers. People are cutting down trees for wood (logging). They are also clearing land to grow oil palm trees for oil. Mining also destroys parts of the forest.
Another big problem is the hunting of wild animals for food, known as the bushmeat trade. Poaching, which is illegal hunting, also reduces the number of animals.
Even with these threats, the Congolian rainforest has been losing trees at a slower rate than other big tropical forests. During the 2000s, only about 0.3% of the forest was lost each year. This is the lowest deforestation rate among major tropical forest areas.
See also
 In Spanish: Selva del Congo para niños
In Spanish: Selva del Congo para niños





