Atlantic Equatorial coastal forests facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Atlantic Equatorial coastal forests |
|
|---|---|

Jungle near Oyala in Equatorial Guinea
|
|
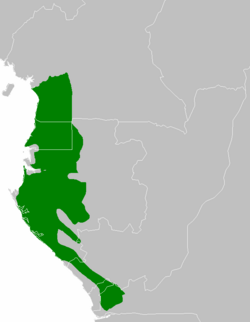
Geographic extent
|
|
| Ecology | |
| Realm | Afrotropical |
| Biome | Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests |
| Borders | Central African mangroves, Cross–Sanaga–Bioko coastal forests, Northwestern Congolian lowland forests and Western Congolian forest–savanna mosaic |
| Geography | |
| Area | 189,700 km2 (73,200 sq mi) |
| Countries | |
| Coordinates | 0°09′N 10°37′E / 0.15°N 10.62°E |
| Conservation | |
| Conservation status | relatively stable |
| Protected | 43,768 km² (23%) |
The Atlantic Equatorial coastal forests are also called the Congolian coastal forests. This amazing ecoregion is a type of tropical moist forest. It covers hills, plains, and mountains along the Atlantic coast of Central Africa. You can find these forests in countries like Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, the Republic of the Congo, Angola, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
These forests are full of life! They are home to many large mammals. These include western gorillas, chimpanzees, forest elephants, and African buffalo. You can also find many smaller mammals, birds, amphibians, reptiles, and insects here. Other cool primates living in these forests are black colobus monkeys and mandrills.
Contents
What are the Atlantic Equatorial Coastal Forests?
These forests cover a huge area of about 189,700 square kilometers (73,200 sq mi). They stretch along the Atlantic coast. In the north, they start in low hills. Further south and east, they reach into mountains.
The forests cover the southwest part of Cameroon. They also cover mainland Equatorial Guinea, known as Río Muni. A large part of Gabon's coastal plains is also covered. A thin strip of these forests goes southeast through the Republic of the Congo. It also reaches the eastern part of the Cabinda area in Angola. This strip ends just north of the Congo River in the Kongo Central province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Where are these forests located?
The Atlantic Equatorial coastal forests are the most southern part of the Lower Guinean forests. This is a group of moist coastal forests. They stretch north and west into southwestern Cameroon and southern Nigeria.
The Atlantic Ocean is to the west of these forests. You can find small areas of Central African mangroves along the coast. These mangroves grow where rivers meet the sea, in salty water. The region starts from the Sanaga River in Cameroon. It goes south to just north of the Congo River. Several other large rivers flow through this area.
To the east, these coastal forests change into the Northwestern Congolian lowland forests. This is part of the huge Congolian rainforests. These rainforests cover the large Congo Basin. To the southeast, the Western Congolian forest–savanna mosaic borders these coastal forests.
This ecoregion is a tropical area. It gets a lot of rain all year round.
Animals and Plants of the Forest
This area is very special for its plant life. Along with the nearby Cross–Sanaga–Bioko coastal forests, it has about half of all the unique plants found in tropical West Africa. Some important places for plants are the Monts de Cristal in Gabon. The Mayombe area is also important. It is located where the Republic of the Congo, Angola, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo meet.
What animals live here?
Many unique forest mammals live here. These include the sun-tailed monkey and the long-footed shrew. You can also find the lesser Angolan epauletted fruit bat and the African smoky mouse. Of course, there are also forest elephants and gorillas. Chimpanzees and other primates also call these forests home. The forests are also rich in many different kinds of birds.
Some special amphibians that live only here include:
- The Apouh night frog (Astylosternus schioetzi)
- Perret's snout-burrower
- The Gabon dwarf clawed frog (Hymenochirus feae)
- The Ogowe River frog (Phrynobatrachus ogoensis)
- Andre's clawed frog
Protecting the Forests

Many animals in these forests are in danger. This includes the primates. They are hunted for their meat or as trophies. Elephants are hunted for their meat and for their tusks. Logging, which is cutting down trees for wood, is also a big threat. This is happening in Cameroon, Gabon, the Republic of Congo, and especially in Equatorial Guinea.
However, large areas of forest still remain. The animal life is still very rich. This is especially true in southern Equatorial Guinea and in Gabon. Gabon has turned many large areas into national parks. One example is Loango National Park, which is in this ecoregion.
In 2017, experts looked at the area. They found that 43,768 square kilometers (16,900 sq mi) of the ecoregion are protected. This means about 23% of the forest is safe.
Protected areas in the forests
Some of the protected areas include:
- Douala Edéa Wildlife Reserve in Cameroon
- Campo Ma'an National Park in Cameroon
- Monte Alen National Park in Equatorial Guinea
- Monte Temelón Nature Reserve in Equatorial Guinea
- Crystal Mountains National Park in Gabon
- Loango National Park in Gabon
- Lope National Park in Gabon
- Moukalaba-Doudau National Park in Gabon
- Waka National Park in Gabon
- Wonga Wongue National Park in Gabon
Cities and Towns in the Region
This region does not have many people living in it. The South Region (Cameroon) is mostly covered by forest. It has the coastal town of Kribi, which is a resort. The Campo Ma'an National Park is also in this region.
All of mainland Equatorial Guinea (Río Muni) is in this region. This includes the port city of Bata. In Gabon, besides logging camps, small groups of farmers and fishers live in the forests. This includes traditional forest people like the Bakola and Bagyeli.
Gabonese towns found among the coastal forests include:
- Lambaréné: This town is home to the famous Albert Schweitzer Hospital.
- Ndjolé: This is a base for logging activities.
- Fougamou: This town is a good starting point for visiting the Waka National Park.
- Gamba: This is an oil center. It is also a base for visiting Loango National Park.
See also
 In Spanish: Selva costera ecuatorial atlántica para niños
In Spanish: Selva costera ecuatorial atlántica para niños

