Conservatoire national des arts et métiers facts for kids
|
Conservatoire National des Arts et Métiers
|
|
 |
|
| Motto |
Docet omnes ubique (Latin)
|
|---|---|
|
Motto in English
|
Teaching to everyone everywhere |
| Type | Public, Grand établissement, Grande école |
| Established | 1794 |
| Accreditation | Grande école, Commission des Titres d'Ingénieur, AMBA, EduQua |
| Budget | 174 M€ in 2020 |
| Chancellor | Olivier Faron (since 2013) |
| President | Gérard Mestrallet |
| Vice-Chancellor | Bernard Racimora |
|
Academic staff
|
1,670: 568 Professors-Researchers | 1,102 academic staff |
| Students | 70,000 (57.7% employees, 24% job seekers, 12% students, 6.3% self-employed) | 10% of foreign students |
| Postgraduates | 1,592 (Grande Ecole engineers enrollment) |
| 91 (enrolled at the EiCNAM Grande Ecole engineering School) | 340 in total | |
| Location |
Headquartered in Paris
,
France; campuses in Paris (36% of students), in 160 other French cities, in overseas France (3% of students), campuses in whole francophone Africa and in other countries (11% of students)
|
| Campus | Urban |
| Language | French, English |
| Affiliations | Paris-Saclay University, AMBA, CGE, Grand Etablissement, Consortium Couperin, Commission des Titres d'Ingénieur, EduQua, Elles Bougent, Hautes Écoles Sorbonne Arts et Métiers University, Répertoire national des certifications professionnelles |
The Conservatoire National des Arts et Métiers (CNAM) is a famous French university. Its name means "National Conservatory of Arts and Crafts." It's known as a grande école and grand établissement, which are special types of top universities in France. CNAM is part of a group of leading French schools, similar to the Ivy League in the United States.
CNAM was founded in 1794, right after the French Revolution. It was one of the first "Grande Écoles" created, along with other important schools like École polytechnique.
The main campus is in Paris, France. But CNAM also has campuses in many other French cities, in French territories overseas, and in several countries around the world, especially in Africa.
The main goal of CNAM is to offer education and do research. It focuses on helping people learn about science and industry. It's one of the largest universities in Europe for online learning and continued education, with about 70,000 students.
CNAM offers many different types of degrees, from Bachelor's to PhDs. These include degrees in science, engineering, law, business, and more. It's unique because it offers some science and engineering degrees completely online, even with lab classes.
The university also has a cool museum called the Musée des Arts et Métiers. This museum is dedicated to scientific and industrial inventions. It's located on the Paris campus and attracts many visitors each year.
Contents
What is CNAM's Story?
CNAM was started on October 10, 1794, during the French Revolution. A French bishop named Henri Grégoire suggested it. He wanted it to be a place to keep "machines, models, tools, drawings, and books" about arts and trades.
The old Saint-Martin-des-Champs Priory in Paris was chosen as the location. The collection officially opened in 1802.

At first, CNAM was mainly a place to collect inventions. But over time, it became a major educational institution. Today, it's known as a top university for:
- Adults who want to get higher education, like engineering, master's, or bachelor's degrees. Many of these classes are offered in the evenings or online.
- Young students who are learning a trade through apprenticeships.
- International students who want to study bachelor's and master's degrees taught in English.
The original collection of inventions is now part of the Musée des Arts et Métiers. The famous Foucault pendulum, which shows the Earth's rotation, was once displayed there. It was moved to the Panthéon for a while but is now back at the museum.

In 1819, CNAM started offering higher education courses. These included classes in applied mechanical engineering, applied chemistry, and industrial economics.
What are CNAM's Goals?
CNAM believes in the ideas of the Age of Enlightenment. This was a time in the 1700s when people thought that knowledge and education could help everyone. CNAM's values include fairness, helping others, and excellent academics.
As a public university in France, CNAM has three main goals:
- To provide education for people throughout their lives (lifelong learning).
- To do research and create new technologies.
- To share scientific and technical knowledge with everyone.
These goals are summed up in CNAM's motto: "Omnes docet ubique". This means "Teaching to everyone everywhere."
Where are CNAM Campuses?
Parisian Campus
About 36% of CNAM's 70,000 students study at the main campus in Paris. This campus is in a historic part of Paris called Le Marais. It's located in an old Benedictine monastery called Saint-Martin-des-Champs Priory. The church and buildings there were inspired by the Basilica of Saint-Denis.
The monastery was founded around 1059. Its beautiful Gothic dining hall from the 13th century is still there today. It was turned into the university's library in the 1800s.
-
The Parisian underground station of Arts & Métiers. Its Line 11 platforms were redesigned in a steampunk style.
-
Statue of Denis Papin, inventor of the Steam Engine, on the Parisian campus.
-
Statue of Nicolas Leblanc, who invented artificial soda ash.
-
View of the CNAM Parisian campus from Rue Réaumur.
-
The Avion III of Clément Ader at the Musée des Arts et Métiers.
Campuses in France
CNAM has campuses in 160 other cities across France. These regional centers work closely with the main campus in Paris. They are partly funded by local governments. Students usually apply to the CNAM center closest to where they live. Many courses are taught online, so students can attend from anywhere.

Campuses Around the World
CNAM also has campuses in French territories overseas and in many other countries. These include:
- Overseas France: French Guiana, French Polynesia, Guadeloupe, Martinique, Mayotte, New Caledonia, Réunion.
- Africa: Algeria, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Djibouti, Gabon, Guinea, Ivory Coast, Lebanon, Madagascar, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, Republic of the Congo, Senegal, Chad, Togo, Tunisia.
- America: Haiti (with the State University of Haiti).
- Asia: China (in Dongguan and Wuhan).
- Europe: Germany (with Darmstadt University of Applied Sciences), Switzerland (in the Lemanic Basin region, near Geneva Lake).
What Can You Study at CNAM?
CNAM has different departments and schools that focus on specific areas of study. In 2016, CNAM created 16 "national teaching teams" (EPN) to organize its courses.
Main Study Areas (EPNs)
- Building and Energy
- Surveying and Topography
- Electronics, Electrotechnics, Automation
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Computer Science and Engineering
- Mathematics and Statistics
- Chemical, Pharmaceutical, and Food Industries
- Maritime Transport and Marine Biology
- Economics, Finance, Insurance, Banking
- Accounting, Finance, Audit
- Geography and Sociology
- Health and Social Care
- Labor Studies
- Law and Real Estate
- Strategies and Management
- Innovation
Special Schools and Institutes
CNAM also has many specialized schools and institutes, such as:
- Ecole Pasteur-Cnam: For public health.
- Ecole Vaucanson: For students from vocational backgrounds.
- EiCnam Ecole d'ingénieur.e: A top engineering school.
- ENASS: For insurance studies.
- Enjmin: For video games and interactive media.
- ICH: For real estate law.
In 2020, CNAM had 1,670 academic staff, including professors and researchers.
Research at CNAM
CNAM has a strong focus on research. It offers PhD programs, which can be done online or on campus. There are about 340 PhD students from 40 different countries.
PhD Programs
CNAM has two main PhD schools:
- One for Science and Engineering (SMI).
- One for Humanities and Arts (Abbé-Grégoire).
CNAM also partners with other French universities for PhD programs, including the Paris-Saclay University.

Research Centers
CNAM has many research centers and laboratories, covering topics like:
- Computer science and communication
- Labor and employment
- Fluid dynamics
- Genomics and chemistry
- History of technology
- Food research
- And many more!
What Degrees Does CNAM Offer?
CNAM offers a wide range of academic programs. In 2022, it had 4,366 different courses.
Types of Degrees
- Degrees recognized by the National Directory of Professional Certifications (RNCP):
* 626 Bachelor's, Master's, and PhD degrees. These follow the European Bologna Process, making them easy to transfer internationally. * 126 Engineering degrees. * 64 vocational certificates.
- Other Diplomas and Certificates:
* 241 CNAM Certificates. * 89 CNAM Diplomas.
- Courses:
* 2,201 courses that are part of a degree, with about 84% taught online. * 657 continuing education courses that lead to a certificate.
How "Grande Écoles" Work
CNAM is a "Grand Établissement" and a "Grande École." These are elite universities in France. They usually offer only Master's degrees, MBAs, and PhDs. Students are selected through very tough national exams. This system ensures that the best students get in.
"Grandes écoles" are separate from the main French university system, but they often work together. Graduating from a "grande école" like CNAM is seen as a key step for top jobs in France. These degrees are recognized by the French Ministry of National Education.
French higher education degrees are organized into three levels: Bachelor's, Master's, and Doctorate. These levels use a system called ECTS credits, which helps students move between different programs and countries. A Bachelor's degree usually requires 180 ECTS (3 years of study after high school), and a Master's requires an additional 120 ECTS (2 more years).
How to Get into a "Grande École"
One of the main ways to get into a "Grande École" is through tough national competitive exams. Many students prepare for these exams for two years after high school.
However, because CNAM offers remote and continuous education, you don't always need to go through these special preparatory classes. Instead, candidates for the "Grande École" program at CNAM need to pass required tests in subjects like Mathematics, Chemistry, Biology, and English. They also need some work experience (at least 6 months in a related field) and a certain level of previous education (like two years of higher education after high school). There's also an interview.
These competitive exams are very selective. Some "Grande Écoles" accept less than 10% of applicants. This means many students don't get in, not because they did poorly, but because others did even better.
Famous People from CNAM
Many notable people have studied or taught at CNAM.

- Louis de Broglie: A Nobel Prize winner in Physics.
- Louis Pasteur: A famous chemist and biologist, known as the "father of microbiology."
- Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot: A physicist who helped create modern Thermodynamics.
- Paul Doumer: A former President of France.
- Jean-Baptiste Say: A well-known economist.
- Mialy Rajoelina: The First Lady of Madagascar.
- Henri Grégoire: The founder of CNAM.
- Melchior Ndadaye: The first elected president of Burundi.
- Léon Bourgeois: A former Prime Minister of France and Nobel Peace Prize winner.
- Jean Prouvé: A famous French metal worker, architect, and designer.
- Valérie Petit: A French politician.
- Marc Seguin: A French engineer who invented the wire-cable suspension bridge.
- Gaston Planté: Invented the first reusable lead-acid battery.
- Robert Solow: A Nobel Prize winner in Economics.
- Henri Fayol: Developed important theories about business administration.
- Josef Rotblat: A physicist and Nobel Peace Prize winner.
- Yves F. Meyer: A mathematician who won the Abel Prize.
- Alexandre Millerand: A former Prime Minister and President of France.
- Claude Cohen-Tannoudji: A physicist who won the Nobel Prize for Physics.
- Nicolas-Jacques Conté: Inventor of the modern pencil.
- Bernard Kouchner: A French doctor and politician, co-founder of Médecins Sans Frontières.
- Francis Mer: A former French Minister of Economy.
- Claude Pouillet: A physicist who studied the greenhouse effect.
- Alain Bauer: A criminologist.
- Pierre Athanase Larousse: A famous French lexicographer and encyclopedist.
- Pierre-Louis Lions: A mathematician who won the Fields Medal.
- Thibault Damour: A theoretical physicist known for work on gravitational waves.
- Serge Haroche: A physicist who won the Nobel Prize for Physics.
- Stéphane Le Foll: A French politician and former Minister of Agriculture.
- Charles Dupin: A French mathematician and engineer.
- François Gernelle: Invented the first micro-computer using a micro-processor, the Micral N.
- Michel Colomban: An aeronautical engineer who designed the Colomban Cri-cri aircraft.
- Pierre Bézier: An engineer and mathematician who invented the Bézier curves used in computer graphics.
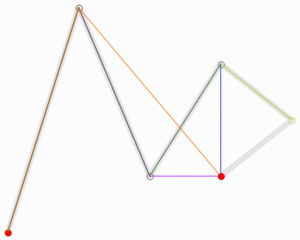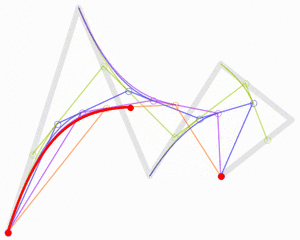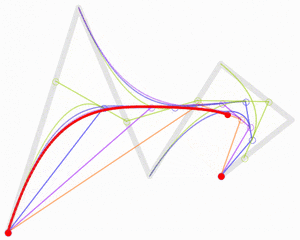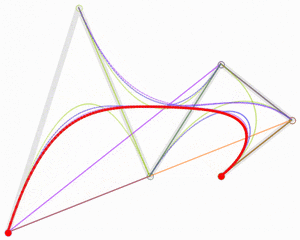
CNAM Traditions
- Vandermonde: This is a secret society at CNAM, said to be similar to the Skull & Bones society at Yale University.
- "Auditeurs": Students at CNAM are often called "auditeurs," which means "listeners" or "auditors," instead of just "students."
- Graduation Scarves: Graduates from the EiCNAM Engineering School receive special colored scarves at their graduation ceremony. The color depends on their major:
* Building, Energy, Nuclear Power Engineering * IT Engineering * Bioinformatics, Chemical, Bio-Engineering, Risk Management * Automation, Robotics, Electrical Engineering * Electronic Systems, Telecommunication Engineering * Aeronautics, Aerospace, Rail Operation Engineering * Material, Mechanical, Mechatronics Engineering
CNAM Foundation
In 1973, the Louis-de-Broglie Foundation was created at CNAM. It was started by Nobel Prize winners in Physics, Louis de Broglie and Louis Néel, and Fields Medal winner René Thom. This foundation focuses on research in physics. It is now located at the French Academy of Sciences in Paris.
-
Louis de Broglie (1892–1987) Nobel Prize Laureate in Physics.
-
Louis Néel (1904– 2000) Nobel Prize Laureate in Physics.
-
René Thom (1923–2002) Fields medallist.
CNAM Partnerships
CNAM is part of a larger group of universities and institutions called HeSAM. This group includes 11 members and 4 associated institutions, with a total of 110,000 students.
Some of the members of HeSAM are:
- École nationale supérieure des arts et métiers
- French National Conservatory of Arts and Crafts (CNAM)
- École Boulle
- École Duperré
- École Estienne
- Institut Français de la Mode
- Paris School of Business
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Conservatorio Nacional de Artes y Oficios para niños
In Spanish: Conservatorio Nacional de Artes y Oficios para niños
- Écoles de l'an III scientifiques























