Farm facts for kids
A farm is a special piece of land where people grow crops (like fruits and vegetables) or raise animals (like cows, chickens, or pigs).
The people who do this important work are called farmers. Their job is called farming.
Land that is good for growing plants for food is called arable land. If someone's life is mostly about raising animals for food, it's called a pastoral life.
Some farms are very big, while others are small. There are many ways to farm. Some farmers grow food mainly for themselves and their families to eat. This is called subsistence farming. Other farms, especially big ones, sell their products to many people, often in urban areas (cities). This is called industrial farming. You'll find more subsistence farms in poorer countries and more industrial farms in richer countries.
Contents
History of Farming
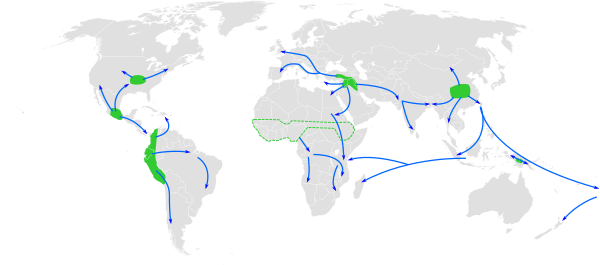
Farming didn't start in just one place. It was invented at different times and in different places around the world. A huge change happened about 12,000 years ago when people stopped being hunter-gatherers and started settling down to farm. This big shift is known as the Neolithic Revolution.
Later, there were other major changes in farming. The British Agricultural Revolution in the 1700s brought new tools and methods. Then, in the mid-1900s, the Green Revolution introduced new types of crops and farming techniques that helped grow even more food. Farming spread from the Middle East to Europe. By 4,000 BC, people in central Europe were using oxen to pull plows and wagons.
Different Kinds of Farms
Farms often have special names depending on what they produce:
- An orchard is a farm that grows fruits or nuts.
- A vineyard is a farm that grows grapes, usually for making wine.
- A stable is a farm where horses are raised and trained.
- A dairy farm produces milk and dairy products like cheese and yogurt.
- If animals are raised mainly for meat, it's often called a ranch.
- A plantation is a large farm that grows crops like tobacco, coffee, cotton, or sugarcane. These are often not essential foods.
Farms Around the World
Farming in the Americas
The land and buildings that make up a farm are sometimes called the "farmstead." In places like the United States, farms where animals like cattle are raised on open land are called ranches. If animals are kept in special areas and fed food grown elsewhere, these places are called feedlots.
The number of farms and family workers in the U.S. has changed a lot. In 1910, there were over 6 million farms. By 2000, that number had dropped to just over 2 million. More women are also becoming farm operators.
In 2007, farmers in the U.S. planned to plant a lot more corn. This was because there was a high demand for ethanol, which is a fuel made from corn. They expected to plant the largest corn crop since 1944.
Farming in Asia
Pakistan
In Pakistan, studies have shown that smaller farms often produce more food per area of land than very large farms. Small farmers also tend to earn more money from each piece of land they farm.
Nepal

Nepal is a country where farming is very important. About 80% of the people in Nepal work in farming. Rice is a main crop grown there, along with fruits like apples. Raising dairy animals and poultry (like chickens) is also becoming more common in Nepal.
Farming in Australia
Farming is a big part of Australia's economy. A farm in Australia is an area of land used for producing food or other goods, and it usually includes buildings.
Green agriculture is a way of farming that tries to be better for the environment. It often uses more local workers and natural fertilizers. This can create more jobs in rural areas.
Sometimes, people have a hobby farm. This is usually a smaller farm where the owners get most of their money from another job. They might use the farm for fun or to grow a little extra food, but it's usually not big enough to make a living from. Hobby farms can be around 2 hectares (about 5 acres) or even larger.
Very small farms that focus on one specific type of production might be called by their specialty, like a dairy (for milk) or a piggery (for pigs), instead of a "farm."
In remote parts of Australia, farms can be extremely large. These huge farms are often called stations.
Farming in Europe
In the United Kingdom, a farm usually means the area of land with pasture (grassland) and other fields, along with the farmhouse (where the farmer lives), farmyard, and other buildings. Very large farms or groups of farms owned by the same person might be called an estate. On the other hand, a very small farm around someone's home is called a smallholding. These are often focused on growing enough food for the family, with only a little extra to sell.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
A typical farm in Namibia.
See also
 In Spanish: Granja para niños
In Spanish: Granja para niños