Dysnomia (moon) facts for kids
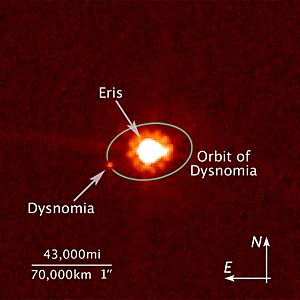
Dysnomia, to the left, and Eris, center
(Hubble Space Telescope). Eris was over-exposed so that Dysnomia would be visible. |
|
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Brown et al. |
| Discovery date | 10 September 2005 |
| Designations | |
| MPC designation | Eris I |
|
Named after
|
Δυσνομία Dysnomia |
| S/2005 (2003 UB313) 1 Dy (nickname) Gabrielle (nickname) |
|
| Adjectives | Dysnomian |
| Orbital characteristics | |
| Epoch 31 August 2006 (JD 2453979.0) | |
| 37273±64 km | |
| Eccentricity | 0.0062±0.0010 |
| 15.785899±0.000050 d | |
|
Average orbital speed
|
0.172 km/s |
| Inclination | ≈ 0° (to Eris's equator; assumed) 78.29°±0.65° (to Eris's orbit) 45.49°±0.15° (to celestial equator) 61.59°±0.16° (to ecliptic) |
| 126.17°±0.26° | |
| 180.83° | |
| Satellite of | Eris |
| Physical characteristics | |
|
Mean diameter
|
615+60 −50 km |
| Mass | (8.2±5.7)×1019 kg |
|
Mean density
|
0.7±0.5 g/cm3 |
| synchronous | |
| ≈ 0° to orbit (assumed) | |
| Albedo | 0.05±0.01 |
| 25.4 | |
| 5.6 | |
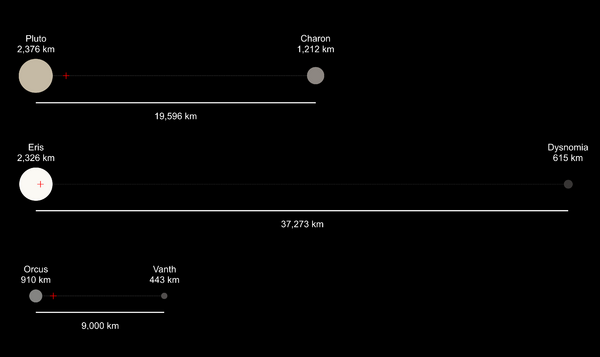
Dysnomia is the only known moon of the dwarf planet Eris. It is the second-largest known moon of a dwarf planet, after Charon, which orbits Pluto.
Scientists Mike Brown and his team discovered Dysnomia in September 2005. They used the W. M. Keck Observatory in Hawaii. Dysnomia was first given the temporary name S/2005 (2003 UB313) 1. It was officially named Dysnomia in September 2006. The name comes from the Ancient Greek word for "lawlessness." In Greek myths, Dysnomia is the daughter of the goddess Eris.
Dysnomia is about 615 kilometers (382 miles) wide. This means it is about 24% to 29% the size of Eris. It is much lighter than Eris. Scientists think it is mostly made of ice. Eris has a very bright, icy surface. But Dysnomia has a very dark surface. It reflects only 5% of the sunlight that hits it. This is like many other objects found far out in space beyond Neptune. These features suggest Dysnomia probably formed from a huge impact on Eris. This is similar to how Earth's Moon formed.
Contents
Discovering Dysnomia
In 2005, a team of scientists used the Keck telescopes in Hawaii. They were studying the four brightest objects in the Kuiper belt. These objects are Pluto, Makemake, Haumea, and Eris.
On September 10, 2005, they found a moon orbiting Eris. They gave it the temporary name S/2005 (2003 UB313) 1. Eris was already nicknamed "Xena" by the discoverers. So, they nicknamed its moon "Gabrielle" after Xena's friend.
What Dysnomia is Like
In 2015, scientists used the Atacama Large Millimeter Array (ALMA) to study Eris and Dysnomia. They looked at the heat coming from the system. This showed that Dysnomia was large and very dark. Early estimates said it was about 700 kilometers (435 miles) wide.
More observations in 2018 helped scientists get a better idea of its size. Dysnomia is about 615 kilometers (382 miles) wide. This is 24% to 29% of Eris's size. Its surface reflects only about 5% of light. This means it is darker than coal. This is a common feature for objects of its size in the outer Solar System.
Dysnomia is the second-largest moon of a dwarf planet. Only Charon, Pluto's moon, is bigger. Eris's surface is very bright, reflecting 96% of light. This is a big difference from Dysnomia's dark surface.
Eris and Dysnomia are tidally locked to each other. This means they always show the same side to each other. Scientists have studied how Dysnomia affects Eris's movement. They found that Dysnomia's mass must be very small. This suggests Dysnomia is mostly made of ice. Its shape is not known, but its low density means it is likely not perfectly round.
Dysnomia appears much fainter than Eris. It is 500 times fainter in visible light. But in near-infrared light, it is only about 60 times fainter. This shows that Dysnomia has a very different color and surface from Eris.
How Dysnomia Orbits
Scientists used observations from the Keck and Hubble telescopes. They used Dysnomia's orbit to figure out Eris's mass. They used Kepler's third law of planetary motion. This law helps calculate the mass of a larger object by observing a smaller object orbiting it.
Dysnomia orbits Eris at an average distance of about 37,300 kilometers (23,177 miles). It takes about 15.786 days to complete one orbit. This is about half a month. These measurements showed that Eris is 1.27 times more massive than Pluto.
Dysnomia's orbit around Eris is almost a perfect circle. It has a very low orbital eccentricity of about 0.0062. This means its distance from Eris changes by only about 462 kilometers (287 miles) during its orbit.
Scientists believe Dysnomia's orbit should have become a perfect circle over millions of years. If its orbit is not perfectly circular, it might mean something else is affecting it. Perhaps there is another, smaller moon orbiting Eris. However, the small difference might also be due to measurement errors.
Dysnomia's orbit is tilted about 78 degrees compared to Eris's orbit around the Sun. Because this tilt is less than 90 degrees, Dysnomia orbits Eris in the same direction that Eris orbits the Sun. Around the year 2239, Eris and Dysnomia will have a special event. Their orbital plane will line up with the Sun. This will allow them to eclipse each other.
How Dysnomia Formed
Scientists now know that eight out of the ten largest objects beyond Neptune have moons. But only about 10% of the smaller objects have moons. This suggests that large objects in the Kuiper Belt often crashed into each other in the past.
When objects about 1,000 kilometers (620 miles) wide collide, they can throw off a lot of material. This material can then come together to form a moon. Scientists think this is how Earth's Moon formed. A huge object hit Earth very early in the Solar System's history.
Naming Dysnomia
Mike Brown, who discovered the moon, chose the name Dysnomia. In Greek myths, Dysnomia is the daughter of Eris. This fits the pattern of naming moons after figures connected to the main planet. For example, Jupiter's largest moons are named after Jupiter's lovers. Saturn's moons are named after his fellow Titans.
The English meaning of "Dysnomia" is "lawlessness." This also connects to Lucy Lawless, the actress who played Xena in Xena: Warrior Princess. Before their official names, Eris was nicknamed "Xena" and Dysnomia was "Gabrielle." Brown said this connection was just a coincidence.
One main reason for the name was its similarity to Brown's wife's name, Diane. This follows a tradition. Pluto's name starts with the initials of Percival Lowell. He founded the observatory where Pluto was discovered. James Christy, who found Charon, named it after his wife Charlene. He added the Greek ending -on to "Char." Similarly, "Dysnomia" starts with the same letter as Brown's wife, Diane.
See also
 In Spanish: Disnomia (satélite) para niños
In Spanish: Disnomia (satélite) para niños