Edible-nest swiftlet facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Edible-nest swiftlet |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Edible-nest swiftlet in a museum | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Apodiformes |
| Family: | Apodidae |
| Genus: | Aerodramus |
| Species: |
A. fuciphagus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Aerodramus fuciphagus (Thunberg, 1812)
|
|
 |
|
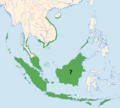
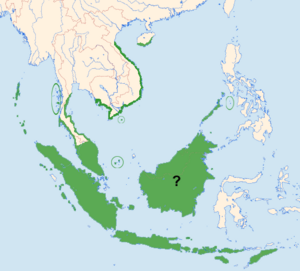
| Distribution | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Collocalia fuciphaga |
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The edible-nest swiftlet (Aerodramus fuciphagus), also called the white-nest swiftlet, is a small bird. It belongs to the swift family. You can find these birds in Southeast Asia.
This swiftlet is famous for its unique nest. The nest is white and see-through. It is made only from the bird's hardened saliva. This special nest is the main ingredient for bird's nest soup. This soup is a very expensive and popular dish in Chinese cooking.
Contents
What Does the Edible-Nest Swiftlet Look Like?
The edible-nest swiftlet is a medium-sized bird. It is about 14 centimeters (5.5 inches) long. Its body is slender and its upper parts are blackish-brown. The underside can be white or blackish-brown.
Its tail is short with a small notch. The bird has a black bill and black feet. Its legs are very short. The lower part of its legs, called the tarsi, usually has no feathers or just a few.
These swiftlets weigh about 15 to 18 grams. Their wings are long and narrow. When they fly, their swept-back wings look like a crescent moon.
Some types of edible-nest swiftlets have slight differences. For example, A. f. micans is lighter and grayer. A. f. vestitus is darker. Its rump (the lower back) is not as pale as other types.
Where Do Edible-Nest Swiftlets Live?
You can find the edible-nest swiftlet in several places. These include the Andamans, the coasts of South-East Asia, and the Indonesian Archipelago. Their home range is quite large, but it is spread out in many separate areas.
Different Types of Edible-Nest Swiftlets
There are six known subspecies of the edible-nest swiftlet:
- Aerodramus fuciphagus fuciphagus: This type lives in Java, Bali, and the western Lesser Sunda Islands.
- Aerodramus fuciphagus inexpectatus: Found in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Sometimes it visits Burma.
- Aerodramus fuciphagus dammermani: Only one of these has ever been found, on Flores.
- Aerodramus fuciphagus micans: Lives in the eastern Lesser Sundas, including Sumba, Savu, and Timor.
- Aerodramus fuciphagus vestitus: Found in Sumatra and Borneo. Some scientists think this might be a separate species called the brown-rumped swiftlet.
- Aerodramus fuciphagus perplexus: Lives in the Maratua Archipelago near eastern Borneo.
Another bird, Germain's swiftlet (Aerodramus germani), used to be considered the same species. Now, it is often seen as its own species. It lives in the Malay Peninsula, central Thailand, coastal Vietnam and Cambodia, Hainan, northern Borneo, and parts of the Philippines.
How Do Edible-Nest Swiftlets Behave?
Edible-nest swiftlets fly and feed in many different places. They can be found from coastal areas to mountains. On Sumatra and Borneo, they fly as high as 2,800 meters (about 9,200 feet). These birds usually fly above forests or at the forest edge. They also fly over open areas.
These swiftlets spend most of their lives flying. They eat flying insects, catching them while in the air. They also drink water while flying. Often, they feed in large groups with other types of swiftlets and swallows.
Nesting and Communication
Edible-nest swiftlets build their nests in colonies. They prefer coastal areas. They build nests in limestone caves, rock cracks, or sometimes on buildings. The nest is shaped like a bracket and is attached to a vertical surface. Their long legs help them cling to these surfaces. These swiftlets never land on the ground by choice.
The nest is white and clear. It is made of layers of hardened saliva. A typical nest is about 6 cm (2.4 inches) across. It is about 1.5 cm (0.6 inches) deep and weighs around 14 grams (0.5 ounces). The female swiftlet lays two white, oval eggs that are not shiny.
When they are in their nesting colonies, these birds make loud, bubbling calls. They also make a rattling sound. This sound is used for echolocation. Echolocation helps them find their way in the dark caves where they nest.
Why Are Edible-Nest Swiftlets Important?

The nests of edible-nest swiftlets are very valuable. They are used to make bird's nest soup. This soup is made by soaking and steaming the nests in water. People believe the soup has health benefits.
Because the nests are so valuable, many swiftlet colonies are harvested. This means people collect the nests to sell them. In some places, like the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, too many nests have been collected. This has made these swiftlet populations critically threatened.
To help protect the birds, people are now building special "bird houses." These are structures or old empty buildings designed to attract swiftlets. They even play recordings of bird calls on the roof to bring the swiftlets in. This helps "farm" the nests without harming wild populations as much. However, in cities, the loud bird calls and bird droppings from these houses can bother neighbors.
Images for kids
-
The nest before use in bird's nest soup
 | Victor J. Glover |
 | Yvonne Cagle |
 | Jeanette Epps |
 | Bernard A. Harris Jr. |