Southeast Asia facts for kids
| Area | 4,545,792 km2 (1,755,140 sq mi) |
|---|---|
| Population | 655,298,044 (3rd) |
| Population density | 135.6/km2 (351/sq mi) |
| GDP (nominal) | $2.557 trillion (exchange rate) |
| GDP (PPP) | $7.6 trillion |
| GDP per capita | $4,018 (exchange rate) |
| HDI | 0.684 |
| Ethnic groups | Austroasiatic, Austronesian, Melanesian, Negrito, Papuan, Sino-Tibetan and Tai peoples |
| Religions | Animism, Buddhism, Christianity, Confucianism, Hinduism, Islam, Tai folk, Taoism and Vietnamese folk |
| Demonym | Southeast Asian |
| Countries | |
| Languages |
Official languages
Other languages
Afro-Asiatic:
Arabic Austroasiatic:
Austronesian:
Creoles:
Dravidian: Indo-European: Tai–Kadai: Sino-Tibetan: Languages of Asia — All of the languages of Asia |
| Time zones | |
| Internet TLD | .bn, .id, .kh, .la, .mm, .my, .ph, .sg, .th, .tl, .vn |
| Calling code | Zone 6 & 8 |
| Largest cities |
Capital cities
Largest cities
|
| UN M49 code | 035 – South-eastern Asia142 – Asia001 – World |
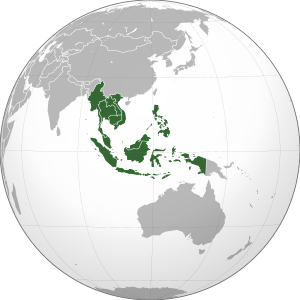
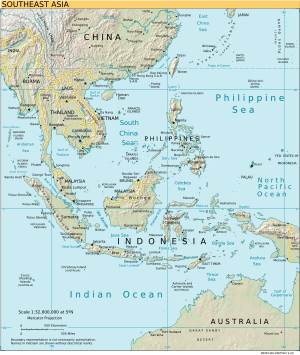
Southeast Asia is a large area in Asia. It is located south of China, east of India, and northwest of Australia. This region is bordered by East Asia to the north and the Pacific Ocean to the east. To the west, it meets South Asia and the Bay of Bengal. To the south, it touches Australia and the Indian Ocean.
Southeast Asia is special because it is the only part of Asia that lies partly in the Southern Hemisphere. Most of it is in the Northern Hemisphere. This region is made up of two main parts:
- Mainland Southeast Asia: This includes countries like Myanmar, Thailand, Peninsular Malaysia, Laos, Cambodia, and Vietnam. It was once known as Indochina.
- Maritime Southeast Asia: This part includes islands and peninsulas. It has countries like Indonesia, East Malaysia, Brunei, Singapore, the Philippines, and East Timor. It also includes the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India, Christmas Island, and the Cocos (Keeling) Islands. This area was historically called the Malay Archipelago.
The region sits where several Earth's plates meet. This causes a lot of earthquakes and volcanic activity. The Sunda Plate covers most of Southeast Asia. However, parts of Myanmar, northern Thailand, Laos, Vietnam, and the northern Philippines are on other plates. The mountains in Myanmar, Thailand, and Malaysia are part of a large mountain chain called the Alpide belt. The islands of the Philippines are part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, a zone with many volcanoes and earthquakes. Because these two active zones meet in Indonesia, the region often experiences earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
Southeast Asia covers about 4.5 million square kilometers (1.7 million square miles). This is about 10.5% of Asia's land or 3% of all land on Earth. More than 670 million people live here, which is about 8.5% of the world's population. It is the third most populated region after South Asia and East Asia. The region has many different cultures and ethnic groups, speaking hundreds of languages. Ten countries in Southeast Asia are members of ASEAN. This group works together on economic, political, and cultural matters.
Contents
Exploring Southeast Asia's Geography
Indonesia is the largest country in Southeast Asia. It also has the most islands in the world. Geologically, Indonesia is one of the most active places for volcanoes. The movement of Earth's plates has also created amazing mountains here. Puncak Jaya in Papua, Indonesia, is 5,030 meters (16,500 feet) tall. It is the only place in Southeast Asia where you can find ice glaciers. The highest mountain in all of Southeast Asia is Hkakabo Razi in northern Myanmar, standing at 5,967 meters (19,577 feet). It is part of the same mountain range as Mount Everest.
The South China Sea is a very important body of water in Southeast Asia. Many rivers from countries like the Philippines, Vietnam, Malaysia, Brunei, Indonesia, and Singapore flow into it.
Mayon Volcano in the Philippines is known for its perfect cone shape. Even though it is very active, its beautiful shape comes from its many past eruptions.
Where Southeast Asia Begins and Ends
Southeast Asia shares a border with the Australian continent to the southeast, which runs through Indonesia. There is also a cultural connection between Papua New Guinea and the Indonesian regions of Papua and West Papua. These areas share the large island of New Guinea.
Southeast Asia's Climate
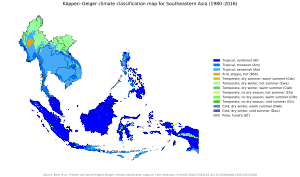
The climate in most of Southeast Asia is tropical. This means it is hot and humid all year, with lots of rain. Northern Vietnam and the Myanmar Himalayas are different. They have a subtropical climate with a cold winter and sometimes snow. Most of Southeast Asia has a wet season and a dry season. These seasons are caused by changes in winds, known as monsoons. The tropical rain belt brings even more rain during the monsoon season. The rainforests here are the second largest on Earth, after the Amazon. In the northern mountain areas, the high altitudes lead to cooler temperatures and drier landscapes.
Southeast Asia is one of the areas most affected by climate change. Climate change will greatly impact farming in the region. For example, irrigation systems will change due to different rainfall patterns. This will affect water quality and supply. Climate change also poses a serious threat to the fishing industry in Southeast Asia.
The Environment and Wildlife of Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is mostly warm and humid, with a climate shaped by monsoons. It is home to many different animals. On the islands of Borneo and Sumatra, you can find orangutans, Asian elephants, Malayan tapirs, Sumatran rhinoceroses, and Bornean clouded leopards. Six types of binturong (also called bearcats) live here. The one found on Palawan island is now considered vulnerable.
Three types of tigers live in the region: the Sumatran tiger on Sumatra, the Malayan tiger in peninsular Malaysia, and the Indochinese tiger in Indochina. All of these tigers are endangered.
The Komodo dragon is the largest living lizard species. It lives on the islands of Komodo, Rinca, Flores, and Gili Motang in Indonesia.

The Philippine eagle is the national bird of the Philippines. Scientists consider it the largest eagle in the world. It lives only in the forests of the Philippines.
Wild Asian water buffalo and smaller related animals like the anoa used to be common across Southeast Asia. Today, the domestic Asian water buffalo is widespread, but its wild relatives are rare and endangered.
The mouse deer is a tiny deer, about the size of a toy dog or cat, with small tusks. It is mostly found on Sumatra, Borneo (Indonesia), and the Palawan Islands (Philippines). The gaur, a giant wild ox even larger than a wild water buffalo, is mainly found in Indochina. There is not much scientific information about amphibians in Southeast Asia.
Birds like the peafowl and drongo live in this region, extending as far east as Indonesia. The babirusa, a pig with four tusks, can also be found in Indonesia. The hornbill was valued for its beak and used in trade with China.
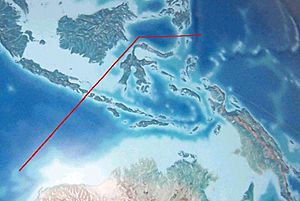
The Indonesian Archipelago is divided by the Wallace Line. This line follows a boundary between Earth's plates. It separates animal species that are typical of Asia from those found in Australia. The islands between Java/Borneo and Papua are a mixed zone called Wallacea, where both types of animals live. As development increases and populations grow in Southeast Asia, there is more concern about how human activities affect the environment. However, a large part of Southeast Asia remains untouched and is home to many wild animals. Most countries in the region now understand the need to protect their forests. This helps prevent soil erosion and saves many different plants and animals. Indonesia, for example, has created many national parks and preserves for this reason. Still, some species, like the Javan rhinoceros, are very close to extinction, with only a few left in western Java.
The shallow waters of the Southeast Asian coral reefs have the most diverse marine life in the world. They are full of coral, fish, and molluscs. Experts say that the marine life in Raja Ampat (Indonesia) is the most diverse ever recorded. This area is much richer in species than any other part of the Coral Triangle, which includes Indonesia, the Philippines, and Papua New Guinea. The Coral Triangle is the center of the world's coral reef diversity. The Verde Passage is called the "center of the center of marine shorefish biodiversity." The whale shark, the world's largest fish, and six types of sea turtles can also be found in the South China Sea and the Pacific Ocean areas of the Philippines.
The plants and trees in the region are mostly tropical. In some countries with very tall mountains, you can find plants that prefer cooler, temperate climates. These rainforest areas are currently being logged, especially in Borneo.
Even though Southeast Asia has rich plant and animal life, it is facing serious deforestation. This loss of forests means animals like the orangutan and the Sumatran tiger are losing their homes. Scientists predict that over 40% of animal and plant species in Southeast Asia could disappear in the 21st century. Also, haze is a common problem. The worst regional hazes happened in 1997 and 2006. During these times, many countries were covered in thick haze, mostly from "slash and burn" farming in Sumatra and Borneo. To fight this, several Southeast Asian countries signed the ASEAN Agreement on Transboundary Haze Pollution.
The 2013 Southeast Asian Haze caused air pollution levels to become very dangerous in some areas. For example, Muar had an extremely high API level of 746 on June 23, 2013.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
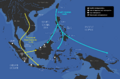
The Austroasiatic and Austronesian expansions into Maritime Southeast Asia.
-
Borobudur temple in Central Java, Indonesia
-
Angkor Wat in Siem Reap, Cambodia
-
Fort Cornwallis in George Town marks the spot where the British East India Company first landed in Penang in 1786, thus heralding the British colonisation of Malaya
-
The Mayon Volcano, Philippines
-
The Mother Temple of Besakih, one of Bali's most significant Balinese Hindu temples.
-
Thai Theravada Buddhists in Chiang Mai, Thailand.
-
Bái Đính Temple in Ninh Bình Province – the largest complex of Buddhist temples in Vietnam
-
The prayer hall of the Goddess of Mercy Temple, the oldest Taoist temple in Penang, Malaysia.
-
Sultan Omar Ali Saifuddin Mosque in Brunei, an Islamic country with Sharia rule.
-
Roman Catholic Cathedral-Basilica of the Immaculate Conception, the metropolitan see of the Archbishop of Manila, Philippines.
-
Paddy field in Vietnam
-
Thai manuscript from before the 19th-century writing system
-
Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
-
Bangkok, Thailand
-
Manila, Philippines
-
Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
-
Jakarta, Indonesia
See also
 In Spanish: Sudeste Asiático para niños
In Spanish: Sudeste Asiático para niños
 | Delilah Pierce |
 | Gordon Parks |
 | Augusta Savage |
 | Charles Ethan Porter |