Embraer facts for kids

Hangar with Embraer jets at the company headquarters, in São José dos Campos.
|
|
| Sociedade Anônima | |
| Traded as | B3: EMBR3 NYSE: ERJ Ibovespa Component |
| Industry | Aerospace, defense |
| Founded | August 19, 1969 |
| Founder | Ozires Silva |
| Headquarters |
,
Brazil
|
|
Area served
|
Worldwide |
|
Key people
|
Francisco Gomes Neto (President & CEO) Mauro Kern (Vice president) Jackson Schneider (Vice president) José Filippo (Vice president) |
| Products | Business, commercial, and military aircraft. Aircraft parts. Mission systems for air and ground operation |
| Brands | EMB, ERJ, Legacy, Lineage, LR, Phenom, Praetor |
| Revenue | |
|
Operating income
|
|
| Total assets | |
| Total equity | |
|
Number of employees
|
18,997 (2024) |
| Divisions | Embraer Defense & Security Embraer Commercial Aviation Embraer Executive Jets |
| Subsidiaries | Neiva, OGMA, Eve Air Mobility, Atech, Bradar, SAVIS |
Embraer S.A. is a big Brazilian company that builds airplanes. It's one of the largest aircraft makers in the world! Embraer designs and makes different types of planes, including those for passengers, business travel, and even military use. They also offer services like leasing planes and providing technical support.
Embraer is the third-largest producer of passenger planes globally, right after Boeing and Airbus. They also make military aircraft and are among the top 100 defense companies. Their main office is in São José dos Campos, Brazil, but they have offices and operations in many other countries like China, the Netherlands, Portugal, Singapore, and the United States.
The company started in 1969 with help from the Brazilian government. At first, they focused on making military planes for the Brazilian Air Force. But by the 1980s, they began making successful planes for regional flights that were sold all over the world. Embraer became a private company in 1994. Since 2000, its shares have been traded on stock exchanges in the United States and Brazil.
Embraer has different parts that focus on commercial planes, business jets, military aircraft, and even planes for farming. They are well-known for their ERJ and E-Jet planes, which are popular for short to medium-range flights. They also make popular business jets like the Phenom 300. As of May 2024, Embraer has delivered over 8,000 aircraft, including 1,800 E-Jet planes.
Contents
Embraer's Story: How It Started
The Brazilian government wanted to create its own aircraft industry. So, in 1969, they created Empresa Brasileira de Aeronáutica, which was shortened to Embraer. It was a government-owned company. The first president, Ozires Silva, was chosen by the government.
Embraer's first plane was a passenger aircraft called the Embraer EMB 110 Bandeirante. The company's headquarters were set up in São José dos Campos. This city was chosen because it already had a special school for aerospace technology since 1950.
Growing Big in the Early Years
The Brazilian government helped Embraer grow by ordering many planes. For the first few years, until 1975, Embraer only sold planes within Brazil.
In the 1970s and early 1980s, Embraer mostly made military planes like the Embraer AT-26 Xavante and the Embraer EMB 312 Tucano. But they also introduced passenger planes for regional flights. The Embraer EMB 110 Bandeirante first flew in 1968, and the Embraer EMB 120 Brasilia was launched in 1985. These planes were very successful and were sold to other countries.
Embraer also worked with an American company called Piper Aircraft starting in 1974. Embraer was allowed to build and sell Piper's small planes in Brazil and Latin America. At first, Piper sent parts for Embraer to put together. Later, Embraer started making most of the parts themselves. Between 1974 and 2000, Embraer built almost 2,500 Piper planes under this agreement.
Becoming a Private Company
Embraer was a government-run company, but in 1992, the Brazilian government decided to sell it to private investors. This process was part of a plan by the government at the time.
Embraer was sold to private owners on December 7, 1994. This helped the company avoid serious financial problems. Even though it became private, the Brazilian government kept a special share that allowed it to have some say in important decisions. Embraer continued to get contracts from the government in the years that followed.
Expanding Its Plane Types
In the mid-1990s, Embraer started focusing more on smaller commercial airplanes instead of mostly military ones. They soon began making larger regional planes that could carry 70 to 110 passengers, as well as smaller business jets.
By May 2019, Embraer was thinking about developing a new family of turboprop planes (planes with propellers) that could carry 50-70 passengers. These would be good for flights lasting 1.5 to 2 hours over distances of about 500-700 nautical miles (926-1,296 km). In August 2021, Embraer showed a new design for a 70-90 seat plane with quieter engines at the back. They aimed to launch this project in 2022 and have the planes flying by 2027 or 2028.
Business Jets for Travel
At an airshow in 2000, Embraer introduced the Legacy 600, which was a business jet version of their regional jet. It started flying in 2002. In 2005, Embraer created a special part of the company just for executive jets. That same year, they planned the Phenom 100, a small jet for air taxi services. It started flying in 2008 and led to the larger Phenom 300.
Embraer also developed the mid-size Legacy 450 and Legacy 500 from scratch. The Lineage 1000 is a luxury version of the E190 passenger jet. By 2016, Embraer had delivered its 1,000th executive jet. In October 2018, Embraer announced two new business jets: the Praetor 500 and the Praetor 600.
Military Transport Planes
On April 19, 2007, Embraer announced they were thinking about making a new military transport plane with two jet engines. Work on this began in May 2009 with money from the Brazilian Air Force. This new plane, called the C-390, uses a lot of the technology from the Embraer 190 passenger jet. It can carry up to 23 tons of cargo and is designed to replace older cargo planes.
Several countries, including Argentina, showed interest in buying the KC-390 transport plane.
Partnership with Boeing (Canceled)
In 2018, Embraer and Boeing announced a plan to work together. Boeing would own 80% of Embraer's commercial aviation business. This was seen as a response to Airbus buying a large part of a competing company. Under this plan, Embraer would keep its business jet and defense parts. The new company would be called Boeing Brasil—Commercial.
In November 2019, Boeing and Embraer announced another partnership. This one was for promoting and developing new markets for the C-390 Millennium military transport plane. This new company would be called Boeing Embraer – Defense.
However, in April 2020, Boeing canceled its plan to buy Embraer's commercial operations. This happened because Boeing was facing big financial challenges due to the COVID-19 pandemic and issues with its 737 MAX planes. In November 2020, Embraer announced that it had lost money in the third quarter of that year because of the pandemic and travel restrictions.
STOUT Military Transport Aircraft
In December 2019, Embraer and the Brazilian Air Force started working on a new light military transport aircraft. This plane, called the Short Take Off Utility Transport (STOUT), is meant to replace older planes like the EMB-110 Bandeirante and EMB-120 Brasilia.
How Embraer Works
Embraer is divided into four main parts:
- Commercial Aviation: This part handles designing, building, selling, and leasing passenger jets, and also provides support services for them.
- Defense & Security: This part focuses on researching, developing, building, and supporting military aircraft and related products.
- Executive Aviation: This part deals with designing, building, and selling executive jets (business jets) and providing support services for them.
- Other: This part includes making aircraft parts, mechanical and hydraulic systems, planes for spraying crops, and training customers.
Company Information
Here's a quick look at Embraer's business over the years:
| Year | Revenue (US$ b) |
Net income (US$ m) |
Employees | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | 6.2 | 342 | 21,648 | |
| 2014 | 6.2 | 334 | 22,301 | |
| 2015 | 5.9 | 69.2 | 23,050 | |
| 2016 | 6.2 | 178 | 20,348 | |
| 2017 | 2.5 | 264 | 20,320 | |
| 2018 | 5.0 | –178 | 20,530 | |
| 2019 | 5.4 | –322 | 21,271 | |
| 2020 | 3.7 | –731 | 18,125 | |
| 2021 | 4.1 | –44.7 | 18,320 | |
| 2022 | 4.5 | –185 | 19,475 | |
| 2023 | 5.3 | 164 |
Where Embraer Builds Planes
Embraer's main office and biggest factory are in São José dos Campos, Brazil. They also have other factories in Brazil in places like Botucatu, Eugênio de Melo, and Gavião Peixoto. The company has offices in cities around the world, including Beijing, Fort Lauderdale, Amsterdam, Singapore, and Washington, D.C..
Factories Outside Brazil
- They build Phenom 100EV, 300E, Praetor 500, and 600 planes at Melbourne Orlando International Airport in Florida, USA.
Other Companies Embraer Owns or Works With
- EAMS – Embraer Aircraft Maintenance Services Inc. (in Nashville, USA) – This company provides maintenance services for planes.
- OGMA – Indústria Aeronáutica de Portugal (in Alverca do Ribatejo, Portugal) – This company maintains, repairs, and makes aircraft parts.
- Embraer Aircraft Holding, Inc. – Their main office in the U.S. is in Fort Lauderdale, Florida.
- Embraer Aero Seating Technologies – Started in September 2016 in Titusville, Florida, this company makes seats for aircraft.
- Mesa Unit (in Mesa, Arizona, USA) – Started in 2008, this unit repairs and maintains Phenom and Legacy business jets.
- Windsor Locks Unit (in Windsor Locks, Connecticut, USA) – Also started in 2008, this unit also repairs and maintains Embraer's business jets.
- Melbourne Unit (in Melbourne, Florida, USA) – Started in 2011, this is the first factory in the United States to do the final assembly of aircraft. It builds the Phenom 100 and Phenom 300 business jets.
- ECC Leasing – Embraer's own leasing company, based in Dublin, Ireland. It manages and re-markets Embraer planes that the company owns.
- Eve - Embraer is working with another company to potentially build a new factory and make a new electric air taxi called Eve.
Types of Aircraft Embraer Makes
By December 2018, Embraer was a leader in the market for jetliners with fewer than 150 seats. They had 100 operators using their ERJ and E-Jet planes.
Passenger Planes (Commercial)
Current Models
- Embraer E-Jet family
- Embraer 170 (66–78 passengers)
- Embraer 175 (76–88 passengers)
- Embraer 190 (96–114 passengers)
- Embraer 195 (100–124 passengers)
- Embraer E-Jet E2 family
- Embraer 175-E2 (80–90 passengers)
- Embraer 190-E2 (97–114 passengers)
- Embraer 195-E2 (120–146 passengers)
Older Models
- Embraer EMB 110 Bandeirante (18 passengers)
- Embraer EMB 120 Brasilia (30 passengers)
- Embraer ERJ family
- Embraer ERJ 135 (37 passengers)
- Embraer ERJ 140 (44 passengers)
- Embraer ERJ 145 (50 passengers)
- Embraer/FMA CBA 123 Vector (prototype – a test model)
-
Embraer ERJ family (ERJ 145)
-
Embraer E-Jet family (Embraer 190)
Military Aircraft
Current Models
- Embraer EMB 314 Super Tucano (light attack plane)
- Embraer C-390 Millennium (medium transport plane)
- Embraer R-99 (plane for early warning and control)
- JAS 39 Gripen E/F (multirole fighter jet)
Older Models
- Embraer EMB 111 Bandeirante (light transport plane)
- Embraer EMB 312 Tucano (trainer plane)
- AMX International AMX (attack jet)
- Embraer MFT-LF (trainer/light attack, prototype only)
- Embraer Xavante (a version of the Aermacchi MB-326)
Business Jets
Current Models
- Embraer Phenom 100 (very light jet)
- Embraer Phenom 300 (light jet)
- Embraer Praetor 500 (mid-size jet)
- Embraer Praetor 600 (super mid-size jet)
Older Models
- Embraer Legacy 450 (mid-size jet)
- Embraer Legacy 500 (super mid-size jet)
- Embraer Legacy 600/650 (large jet, based on the ERJ family)
- Embraer Lineage 1000 (very large jet, based on the E-Jet family)
Utility Aircraft
Current Models
- Embraer EMB 202 Ipanema (plane for spraying crops)
Older Models
- Embraer EMB 121 Xingu (general utility plane)
Piper Planes Built by Embraer
Current Models
- Embraer Seneca (based on Piper PA-34)
- Embraer Corisco/Tupi (based on Piper PA-28 Archer II)
Older Models
- Embraer Carioca/Minuano/Sertanejo (based on Piper PA-32)
- Embraer Navajo (based on Piper PA-31)
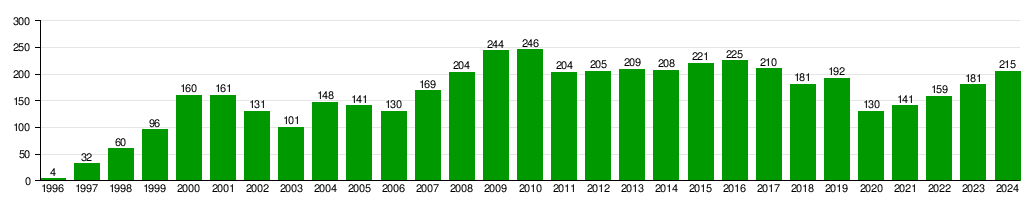
How Many Planes Embraer Has Delivered
This table shows how many commercial aircraft Embraer has delivered each year. This includes military versions of commercial planes.
| Year | 1996 | 1997 | 1998 | 1999 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deliveries | 4 | 32 | 60 | 96 | ||||||
| Year | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 |
| Deliveries | 160 | 161 | 131 | 101 | 148 | 141 | 130 | 169 | 204 | 244 |
| Year | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 |
| Deliveries | 246 | 204 | 205 | 209 | 208 | 221 | 225 | 210 | 181 | 192 |
| Year | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 | 2026 | 2027 | 2028 | 2029 |
| Deliveries | 130 | 141 | 159 | 181 | 206 | – | – | – | – | – |
 |
| As of 7 January 2025[update] |
See also
 In Spanish: Embraer para niños
In Spanish: Embraer para niños



















