Florida softshell turtle facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Florida softshell turtle |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Testudines |
| Suborder: | Cryptodira |
| Family: | Trionychidae |
| Genus: | Apalone |
| Species: |
A. ferox
|
| Binomial name | |
| Apalone ferox (Schneider, 1783)
|
|
 |
|
| Florida softshell turtle range | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The Florida softshell turtle (Apalone ferox) is a type of softshell turtle. It lives in the southeastern parts of the United States. These turtles are known for their unique, soft shells.
Contents
Where Florida Softshell Turtles Live
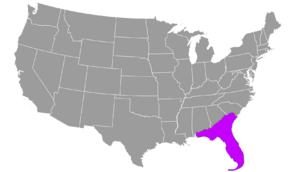
The Florida softshell turtle mostly lives in the state of Florida. You can also find them in southern parts of South Carolina, Georgia, and Alabama. It is the only softshell turtle species that lives all over the Florida peninsula.
Their Homes and Habitats
Florida softshell turtles are found in many different freshwater places. They can even live in some slightly salty water. However, they prefer water that moves slowly or is still. You can find them in swamps, lakes, marshes, wet prairies, small rivers, creeks, and even ponds. They sometimes live in ponds formed in man-made ditches or sinkholes.
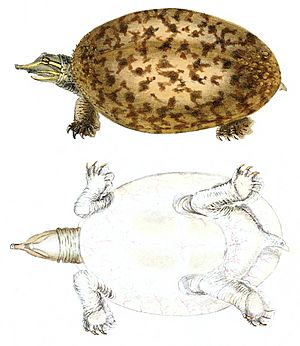
What Florida Softshell Turtles Look Like
The Florida softshell turtle is a large turtle. It has a flat, pancake-shaped body and a long neck. Its head is long with a snorkel-like nose. It also has large webbed feet, each with three claws.
Unlike most turtles with hard shells, the Florida softshell has a soft, leathery shell. This shell is made of cartilage instead of hard bone. Their color ranges from olive green to dark brown. They are the darkest softshell turtles in Florida. Other softshell turtles in Florida include Apalone mutica calvata and Apalone spinifera aspera.
Their underside is white or cream-colored. This color pattern is called countershading. It helps them hide from predators. They are the largest softshell turtles in Florida and all of North America. They can grow from 15 to 76 centimeters (about 6 to 30 inches) long.
Size Differences Between Males and Females
Female Florida softshell turtles are much larger than males. Adult females are often 3 to 5 times bigger. Males usually weigh about 2.68 kilograms (5.9 pounds). Their shell length is about 35 centimeters (14 inches).
Nesting adult females weigh about 6.65 kilograms (14.7 pounds). Their shell length is about 40.1 centimeters (15.8 inches). The heaviest female ever recorded weighed 43.6 kilograms (96.1 pounds)! Males tend to have longer tails than females of the same size.
Baby Turtles
Hatchlings (baby turtles) have lighter shells. They have yellow and orange markings and a colored rim around their shell. They also have stripes of the same color on their face and neck. Their plastron (bottom shell) is usually dark. As the turtles get older, these bright colors fade away. Adults become the dark-brown color you usually see.
Behavior and Diet
The Florida softshell turtle spends almost all its time in the water. It only comes out to bask in the sun or to lay eggs. In the water, it likes to bury itself in the sandy or muddy bottom. Like all softshell turtles, it can move very fast both in water and on land.
These turtles are omnivores, meaning they eat both plants and animals. However, their diet is mostly meat. They eat fish, insects, crustaceans (like crabs or shrimp), frogs, and mollusks (like snails). They may also scavenge for food, meaning they eat dead animals.
Life Cycle and Reproduction
Male Reproduction
Male Florida softshell turtles have a specific reproductive cycle. They mate in the spring. Then, they produce sperm in the fall. This sperm is stored through the winter. They use this stored sperm for copulation (mating) the next spring. Males produce sperm every year.
Males become ready to reproduce when they are small. They can start reproducing quickly, sometimes as young as two years old.
Female Reproduction
Females become ready to reproduce at a larger and more varied size than males. Some may be ready when their bottom shell is 24 centimeters (9.4 inches) long. Others might not be ready until they are closer to 30 centimeters (12 inches) long. Females usually start reproducing between 5 and 8 years old.
The female nesting season is from early April to early August. The eggs hatch in about 60 to 90 days. Not all females reproduce every year. About 10% of females in one study showed signs of not being able to reproduce in a breeding season.
Florida softshell females can lay an average of 4 to 5 batches of eggs in one season. They might lay a new batch every three weeks. These turtles have one of the highest egg production rates of any reptile each year. Studies show they lay over 20 eggs per batch on average. The largest batch found had 38 eggs!
Their Role in Nature
Adult Florida softshell turtles are important predators in their water homes. They mostly eat meat. They are high up on the food chain, usually eating other animals.
However, even these large turtles have predators. Alligators are known to eat adult Florida softshell turtles. Raptors (like eagles or hawks) might catch young turtles. Animals that eat turtle eggs include fish crows, foxes, raccoons, skunks, and river otters.
Using Alligator Nests
Scientists have seen female Florida softshell turtles lay their eggs in American alligator (Alligator mississippiensis) nests. This happens in lakes across Florida, like Lake Okeechobee and Lake Apopka. Other turtle species also do this.
Turtles often use empty alligator nests. But they have also been known to lay eggs in nests that alligators are still using! They do this more often when there are not many good places to lay eggs. This also happens during years with a lot of rain, when high water levels reduce nesting spots.
Even though they use alligator nests, more Florida softshell turtles are found in lakes with few or no alligators. They also thrive in lakes with lots of plant life. This suggests that both predators and food availability affect softshell turtle populations.
Threats from Humans
The Florida softshell turtle is common in Florida and other areas where it lives. But human activities can threaten them. Some of these threats include:
- Being caught for their meat.
- Being caught for the pet trade.
- Being hit by cars on roads.
See also
 In Spanish: Tortuga de caparazón blando de Florida para niños
In Spanish: Tortuga de caparazón blando de Florida para niños