Gallia Narbonensis facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Province of Gallia Narbonensis
Provincia Gallia Narbonensis
|
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Province of the Roman Empire | |||||||
| 121 BC–5th century | |||||||
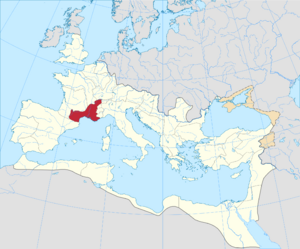 The province of Gallia Narbonensis within the Roman Empire in 125 AD |
|||||||
| Capital | Narbo Martius | ||||||
| Historical era | Antiquity | ||||||
|
• Established
|
121 BC | ||||||
|
• Visigothic conquest
|
5th century | ||||||
|
|||||||
| Today part of | France Italy Monaco |
||||||
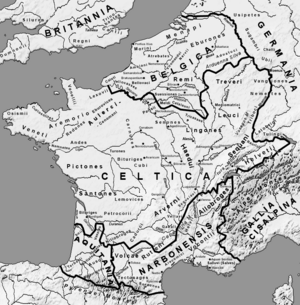
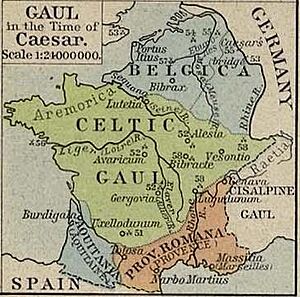
Gallia Narbonensis was an important Roman province in what is now Southern France. Its name means "Gaul of Narbonne" because Narbonne was its main city. People also called it Provincia Nostra ("Our Province") because it was the first Roman province north of the Alps mountains. Another name was Gallia Transalpina ("Transalpine Gaul"), which helped tell it apart from Cisalpine Gaul in Northern Italy.
This area became a Roman province in the late 2nd century BC. Gallia Narbonensis was surrounded by mountains: the Pyrenees to the west, the Cévennes to the north, and the Alps to the east. To the south was the Gulf of Lion (part of the Mediterranean Sea). The province was very valuable to the Roman Empire. It had a long-standing Greek city called Massalia (modern Marseille). Its location between the Roman provinces in Spain and the city of Rome was also very important.
What's in a Name?
The province was first called Gallia Transalpina, meaning "Gaul beyond the Alps." This helped people tell it apart from Cisalpine Gaul, which was "Gaul on this side of the Alps" (closer to Rome).
Later, the province was renamed Gallia Narbonensis. This new name came from its capital city, Colonia Narbo Martius, which is now the city of Narbonne. This Roman city was founded on the coast in 118 BC. The name Gallia Narbonensis likely became common during the time of Emperor Augustus.
The Romans often called it Provincia Nostra ("our province") or just Provincia ("the province"). This simple name stuck around! Today, the eastern part of this area is still called Provence in France.
How it Started
By the mid-2nd century BC, Rome was doing a lot of trade with Massalia. Massalia was a very old and rich Greek city, founded by settlers from Phocaea. Rome and Massalia became allies. Rome promised to protect Massalia from local Gauls, nearby Aquitani, and even Carthaginian ships. In return, Rome wanted a small strip of land. They needed this land to build a road to Hispania (modern Spain) to move their soldiers more easily. The people of Massalia cared more about their trade than about keeping all their land.
During this time, powerful Gallic tribes from the north threatened the cities along the Mediterranean coast. Two strong tribes were the Arverni and the Allobroges. In the First Transalpine War (125–121 BCE), a Roman general named Quintus Fabius Maximus Allobrogicus fought in the area. He defeated the Allobroges and the Arverni. This victory made Gallia Narbonensis much safer. The area officially became a Roman province in 121 BCE.
In this new Roman territory, the Romans founded the city of Narbonne in 118 BC. They also built the Via Domitia, which was the first Roman road in Gaul. This road connected Gaul to Hispania. They also built the Via Aquitania, which went towards the Atlantic Ocean. These roads made Narbonne a very important trading center. From Narbonne, the Romans managed the province, which was first called Transalpine Gaul and later Gallia Narbonensis.
During the Sertorian War (80–72 BCE), Gallia Narbonensis was a key place for Roman military actions. This war helped the Romans organize the province even more.
Later Years
Having control of Gallia Narbonensis gave Rome many benefits. It was a direct land route between Italy and Spain. It also acted as a protective barrier against attacks from other Gallic tribes on Italy. Plus, Rome controlled the profitable trade routes along the Rhône river, connecting Gaul to the markets of Massalia.
It was from Narbonne that Julius Caesar started his famous Gallic Wars. Caesar later rebuilt Narbonne and also founded new cities like Forum Julium and Arles. He also gave many communities in Gallia Narbonensis Roman citizenship. In 49 BC, during the civil war, Massalia sided with Caesar's enemies. After the war, Massalia lost its independence and became fully controlled by Rome.
In 40 BC, during a time when Rome was ruled by three powerful leaders (the Second Triumvirate), Lepidus was put in charge of Gallia Narbonensis. Later, when Augustus became the first Roman Emperor, he made Gallia Narbonensis a senatorial province. This meant it was governed by a proconsul, a high-ranking Roman official.
Around 314 AD, Emperor Diocletian changed how the Empire was organized. He combined Gallia Narbonensis and another province, Gallia Aquitania, into a new larger area called Dioecesis Viennensis. Its capital was in Vienne, further north. This new area was later renamed Dioecesis Septem Provinciarum (Diocese of the Seven Provinces).
Gallia Narbonensis and the areas around it became part of the Visigothic Kingdom between 462 and 477 AD. This marked the end of Roman control over the region. After the Goths took over, the western part of the area became known as Septimania, while the eastern part (east of the lower Rhone river) became known as Provence.
|