Glenn L. Martin Company facts for kids
 |
|
| Industry | Aerospace |
|---|---|
| Fate | Merged with American-Marietta Corporation later merged into Lockheed-Martin Corporation |
| Successor | Martin Marietta |
| Founded | 1917 |
| Founder | Glenn L. Martin |
| Defunct | 1961 |
| Headquarters |
,
United States
|
| Products | Aircraft |
The Glenn L. Martin Company, also known as The Martin Company, was an American company that built aircraft and later focused on aerospace. It was started by a aviation pioneer named Glenn L. Martin in 1917.
The Martin Company created many important airplanes for the defense of the United States and its allies. This was especially true during World War II and the Cold War. In the 1950s and 1960s, the company shifted from making airplanes to working on guided missiles, space exploration, and using outer space.
In 1961, the Martin Company joined with another big company, American-Marietta Corporation. Together, they formed the Martin Marietta corporation. Later, in 1995, Martin Marietta merged with a huge aerospace company called Lockheed Corporation. This created the Lockheed Martin corporation, which is one of the largest defense companies in the world today.
Contents
History of the Martin Company
How It Started
Glenn Luther Martin, a pioneer in aviation, first started a company on August 16, 1912. He began by building military training planes in Santa Ana, California. In 1916, his company merged with the Wright Company to form Wright-Martin Aircraft Company.
However, this merger did not work out well. So, Glenn Martin left to create a second Glenn L. Martin Company. This new company began on September 10, 1917, and was based in Cleveland, Ohio.
Early Air Combat in Mexico
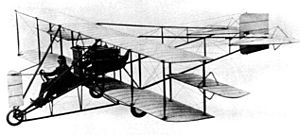
In 1913, rebels in Mexico bought a single-seat Martin Pusher biplane in Los Angeles. They planned to use it against government ships attacking the port of Guaymas. The plane was shipped in parts to Mexico.
The rebels named the aircraft Sonora. They put it back together and added a second seat for someone to drop bombs. The Sonora, armed with simple pipe bombs, made history. It performed the first known air-to-naval bombing attacks ever.
Martin's Role in World War I
During World War I, Martin had its first big success with the Martin MB-1 bomber. This was a large biplane designed for the United States Army. The MB-1 started service after the war ended.
A later design, the MB-2, was also very successful. The U.S. Army Air Service ordered many of these planes. The MB-2 was the main bomber used by the Air Service until 1930. It served in squadrons in Virginia, Hawaii, and the Philippines.
Between the World Wars
In 1924, the Martin Company won a contract to build a scout bomber designed by another company, Curtiss. Martin ended up producing 404 of these planes. In 1929, Martin moved its main factory. It sold the Cleveland plant and built a new, larger one in Middle River, Maryland, near Baltimore.
In the 1930s, Martin built large flying boats for the U.S. Navy. They also created the advanced Martin B-10 bomber for the Army. The company also produced the famous China Clipper flying boats. These planes were used by Pan American Airways for flights across the Pacific Ocean, from San Francisco to the Philippines.
Contribution to World War II
During World War II, Martin designed some very successful aircraft. These included the Martin B-26 Marauder and A-22 Maryland bombers. They also made the Martin PBM Mariner and Martin JRM Mars flying boats. These flying boats were widely used for air-sea rescue, fighting submarines, and transport.
The Martin Company was a major producer during the war. It built 1,585 B-26 Marauders. It also built 531 Boeing B-29 Superfortresses at its new factory in Nebraska. Among the B-29s made there were the Enola Gay and Bockscar. These planes dropped the two atomic bombs that ended the war on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, Japan.
After the War: Into Space
On April 22, 1957, the company changed its name to simply the Martin Company.
After the war, Martin continued to work on aircraft. They made the Martin AM Mauler attack plane and the successful B-57 Canberra bombers. They also produced the Martin P5M Marlin and Martin P6M SeaMaster seaplanes, and the Martin 4-0-4 passenger airliner.

The Martin Company then moved into the aerospace manufacturing business. It built the Vanguard rocket, which was one of America's first satellite booster rockets. The Vanguard was special because it was the first American space rocket designed from scratch. It was not a modified military missile.
Martin also designed and built the huge and powerful Titan I and LGM-25C Titan II intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs). The Martin Company in Florida was also the main contractor for the U.S. Army's Pershing missile.
The Martin Company was one of two final companies considered for building the command and service modules for the Apollo Program. However, National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) chose another company for these contracts.
Martin went on to build even larger booster rockets for NASA and the U.S. Air Force. This was the Titan III series, with over 100 rockets produced. These rockets were vital for sending space probes like the two Voyager Project probes to the outer planets. They also launched the two Viking Project probes to Mars and the two Helios probes close to the Sun.
Finally, the U.S. Air Force needed a rocket that could launch even heavier satellites. The Martin Company responded with its extremely large Titan IV series of rockets. When the Titan IV began service, it could carry more weight into orbit than any other rocket being built.
One Titan IV, with a powerful upper stage, launched the heavy Cassini space probe to the planet Saturn in 1997. The Cassini probe orbited Saturn for many years, sending back tons of scientific data. Production of the Titan IV ended in 2004.
In 1961, the Martin Company merged with American-Marietta Corporation, a company that made chemicals and construction materials. This formed the Martin Marietta Corporation. In 1995, Martin Marietta merged with the Lockheed Corporation. This created the Lockheed Martin Corporation, which became the largest defense company in the world.
Many important people in the American aerospace industry worked at the Martin Company. These included founders of other major aviation companies like Donald Douglas (Douglas Aircraft) and Lawrence Dale Bell (Bell Aircraft). Glenn Martin also taught William Boeing how to fly and sold him his first airplane.
Products
Aircraft
| Model name | First flight | Number built | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Martin MB-1 | 1918 | 20 | Twin-engine biplane bomber |
| Martin NBS-1 | 1920 | 130 | Twin-engine biplane bomber |
| Martin MO | 1924 | 36 | Single-engine observation plane |
| Martin T3M | 1926 | 124 | Single-engine biplane torpedo bomber |
| Martin T4M | 1927 | 103 | Single-engine biplane torpedo bomber |
| Martin BM | 1929 | 33 | Single-engine biplane torpedo bomber |
| Martin PM | 1930 | 55 | Twin-engine flying boat patrol plane |
| Martin P3M | 1931 | 9 | Twin-engine flying boat patrol bomber |
| Martin B-10 | 1932 | 348 | Twin-engine bomber |
| Martin M-130 | 1934 | 3 | Four-engine flying boat airliner |
| Martin PBM Mariner | 1939 | 1,366 | Twin-engine flying boat patrol bomber |
| Martin 167 Maryland | 1939 | 450 | Twin-engine bomber |
| Martin B-26 Marauder | 1940 | 5,288 | Twin-engine bomber |
| Martin 187 Baltimore | 1941 | 1,575 | Twin-engine bomber |
| Martin JRM Mars | 1942 | 7 | Four-engine flying boat transport |
| Boeing B-29 Superfortress | 1944 | 536 | Four-engine bomber (built by Martin) |
| Martin AM Mauler | 1944 | 151 | Single-engine attack plane |
| Martin P4M Mercator | 1946 | 21 | Twin-engine patrol bomber |
| Martin 2-0-2 | 1946 | 47 | Twin-engine airliner |
| Martin XB-48 | 1947 | 2 | Prototype six-jet bomber |
| Martin P5M Marlin | 1948 | 285 | Twin-engine flying boat patrol bomber |
| Martin XB-51 | 1949 | 2 | Prototype three-jet bomber |
| Martin 4-0-4 | 1950 | 103 | Twin-engine airliner |
| Martin B-57 Canberra | 1953 | 403 | Twin-jet bomber |
| Martin P6M SeaMaster | 1955 | 12 | Four-jet flying boat patrol bomber |
Aircraft Engines
- Martin 333: A four-cylinder piston engine.
Missiles and Rockets
- AAM-N-4 Oriole
- ASM-N-5 Gorgon V
- MGM-1 Matador
- MGM-13 Mace
- MGM-18 Lacrosse
- Bold Orion
- Titan (rocket family)
- SM-68 Titan
- HGM-25A Titan I
- LGM-25C Titan II
- Viking (rocket)
Booster Rockets
- The four-stage Vanguard rocket
- Titan II GLV
- Titan III
- Titan IIIB
- Titan IIIC
- Titan IV
- After being removed from military use, about 50 Titan II missiles were used by the U.S. Air Force to launch satellites.
Automobile
- 1928 Martin 100 Aerodynamic
See Also
- Glenn L. Martin Maryland Aviation Museum
- Martin State Airport
 | Chris Smalls |
 | Fred Hampton |
 | Ralph Abernathy |






