Gough Island facts for kids

View of Gough Island
|
|
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | South Atlantic Ocean |
| Coordinates | 40°19′0″S 9°56′0″W / 40.31667°S 9.93333°W |
| Archipelago | Tristan da Cunha |
| Area | 91 km2 (35 sq mi) |
| Length | 13 km (8.1 mi) |
| Width | 7 km (4.3 mi) |
| Highest elevation | 910 m (2,990 ft) |
| Highest point | Edinburgh Peak |
| Administration | |
|
United Kingdom
|
|
| St Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha | |
| UNESCO World Heritage Site | |
| Criteria | Natural: (vii), (x) |
| Inscription | 1995 (19th Session) |
| Designated: | 20 November 2008 |
| Reference #: | 1868 |
Gough Island, also known as Gonçalo Álvares, is a wild volcanic island in the South Atlantic Ocean. It is a small part of the Tristan da Cunha group of islands. This group is a British overseas territory called Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha.
Gough Island is part of a special UNESCO World Heritage Site. This site also includes Inaccessible Island. The island is very far away from other land. It is about 400 km (250 mi) south-east of the main Tristan da Cunha islands. It is also 2,400 km (1,500 mi) from South Georgia Island and 2,700 km (1,700 mi) from Cape Town. The closest part of South America is over 3,200 km (2,000 mi) away.
No one lives on Gough Island permanently. Only a small team of about six people works at a weather station there. The South African National Antarctic Programme has managed this station since 1956. Gough Island is one of the most isolated places on Earth where people live all the time.
Contents
Island Names: Gough and Gonçalo Álvares
The island was first called Ilha de Gonçalo Álvares on old Portuguese maps. It was named after the Portuguese explorer Gonçalo Álvares. Later, it was named Gough Island after a British sailor, Captain Charles Gough. He saw the island in 1732.
For a long time, people sometimes mistakenly called it Diego Alvarez Island. This happened because the Portuguese name "Gonçalo" was sometimes confused with the Spanish name "Diego." It might also have been a simple mistake when reading old maps.
Gough Island's History
The island was most likely discovered in July 1505 by the Portuguese explorer Gonçalo Álvares. For the next 230 years, maps showed the island with his name.
In 1732, Captain Charles Gough of the British ship Richmond reported finding a "new" island. He thought it was about 400 miles east of the island Gonçalo Álvares had found. About 50 years later, mapmakers realized it was the same island! Even though the Portuguese found it first, the name "Gough's Island" became more common.
In the early 1800s, people who hunted seals lived on the island for short periods. The first known group was from the U.S. ship Rambler in 1804–1805. Seal hunting continued until 1910. During this time, 34 sealing ships visited the island.
Scientists started visiting the island in the early 1900s. The Scottish National Antarctic Expedition visited in 1904. The Shackleton–Rowett Expedition also stopped there in 1922.
In 1938, Britain officially claimed Gough Island. This happened during a visit by a Royal Navy ship called HMS Milford. In 1995, UNESCO declared the island a World Heritage Site. In 2004, nearby Inaccessible Island was added to the site, and it was renamed Gough and Inaccessible Islands.
Gough Island is a special place to see the solar eclipse of September 12, 2034. It's the only place outside South America where the full eclipse will be visible.
Geography and Geology
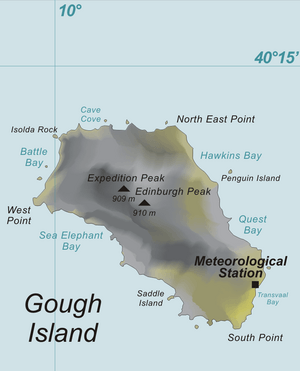
Gough Island is shaped like a rectangle. It is about 13 km (8.1 mi) long and 7 kilometres (4.3 mi) wide. The island covers an area of 91 km2 (35 sq mi). It has tall mountains, rising over 900 m (3,000 ft) above the sea. The highest point is called Edinburgh Peak. Other important places include Hags Tooth, Mount Rowett, Sea Elephant Bay, Quest Bay, and Hawkins Bay.
There are also smaller islands and rocks around Gough Island. These include Southwest Island, Saddle Island, Tristiana Rock, Isolda Rock, Round Island, Cone Island, Lot's Wife, Church Rock, Penguin Island, and The Admirals.
Island Climate
Gough Island has an oceanic climate. This means its weather is greatly affected by the ocean. Temperatures usually stay between 11 °C (52 °F) and 17 °C (63 °F) during the day all year round. This is because the island is so far out in the Atlantic Ocean.
Even though it's in the southern hemisphere, it rarely freezes. Summers are not very hot. It rains a lot throughout the year, and there isn't much sunshine. Snow can fall in the mountains, but it is rare near the sea.
| Climate data for Gough Island (1961–1990, extremes 1956–1990) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 26.4 (79.5) |
25.7 (78.3) |
25.9 (78.6) |
22.6 (72.7) |
20.5 (68.9) |
20.6 (69.1) |
19.3 (66.7) |
21.7 (71.1) |
19.3 (66.7) |
21.4 (70.5) |
23.9 (75.0) |
25.1 (77.2) |
26.4 (79.5) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 17.2 (63.0) |
17.4 (63.3) |
16.9 (62.4) |
15.4 (59.7) |
13.7 (56.7) |
12.4 (54.3) |
11.5 (52.7) |
11.2 (52.2) |
11.5 (52.7) |
12.9 (55.2) |
14.9 (58.8) |
16.2 (61.2) |
14.3 (57.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 13.9 (57.0) |
14.4 (57.9) |
13.9 (57.0) |
12.8 (55.0) |
11.3 (52.3) |
10.0 (50.0) |
9.1 (48.4) |
8.9 (48.0) |
8.9 (48.0) |
10.1 (50.2) |
11.9 (53.4) |
13.2 (55.8) |
11.5 (52.7) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 11.1 (52.0) |
11.6 (52.9) |
11.3 (52.3) |
10.4 (50.7) |
8.9 (48.0) |
7.6 (45.7) |
6.6 (43.9) |
6.5 (43.7) |
6.6 (43.9) |
7.8 (46.0) |
9.4 (48.9) |
10.3 (50.5) |
9.0 (48.2) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 5.3 (41.5) |
5.1 (41.2) |
4.8 (40.6) |
3.7 (38.7) |
1.4 (34.5) |
0.1 (32.2) |
−0.9 (30.4) |
−2.7 (27.1) |
0.2 (32.4) |
0.5 (32.9) |
2.4 (36.3) |
4.1 (39.4) |
−2.7 (27.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 210 (8.3) |
183 (7.2) |
254 (10.0) |
276 (10.9) |
286 (11.3) |
310 (12.2) |
273 (10.7) |
304 (12.0) |
270 (10.6) |
249 (9.8) |
213 (8.4) |
241 (9.5) |
3,069 (120.9) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 16 | 13 | 18 | 19 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 21 | 20 | 18 | 16 | 18 | 225 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 81 | 82 | 82 | 82 | 82 | 83 | 83 | 83 | 81 | 81 | 81 | 81 | 82 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 183.8 | 148.8 | 123.3 | 95.6 | 83.7 | 60.4 | 71.7 | 87.5 | 101.6 | 128.5 | 161.4 | 182.9 | 1,429.2 |
| Source 1: NOAA, Deutscher Wetterdienst (extremes) | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: climate-charts.com | |||||||||||||
The Weather Station
A weather station has been operating on Gough Island since 1956. It is run by the South African Weather Service. This station is very important for predicting winter weather in South Africa. This is because cold fronts often move towards South Africa from the south-west.
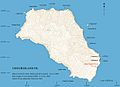
The station was first in a place called The Glen. But in 1963, it moved to the southern lowlands of the island, at 40°20′57.68″S 9°52′49.13″W / 40.3493556°S 9.8803139°W. The new location helped them collect better and more reliable weather data.
People on the Island
Every year, a new team arrives by ship from Cape Town to work at the weather station and do scientific research. Since 2012, the ship S. A. Agulhas II brings the teams. Each team is called "Gough" plus an expedition number. For example, the 1956 team was "Gough 01," and the 2013 team was "Gough 58." A new team always replaces the old one, so there are always people living on the island.
A team usually includes:
- A senior meteorologist (a weather scientist)
- Two junior meteorologists
- A radio technician
- A medic
- A diesel mechanic
- Several biologists (who study living things)
The team gets enough food to last the whole year. People and supplies arrive by helicopter from a special ship. Sometimes, they use a crane on a cliff near the station, which is called "Crane Point."
Maps
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Isla de Diego Álvarez para niños
In Spanish: Isla de Diego Álvarez para niños
 | Jessica Watkins |
 | Robert Henry Lawrence Jr. |
 | Mae Jemison |
 | Sian Proctor |
 | Guion Bluford |