Green Lake (Texas) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Green Lake |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
 |
|
| Location | Calhoun County, Texas |
| Coordinates | 28°31′43″N 96°50′23″W / 28.5287°N 96.8397°W |
| Basin countries | United States |
| Surface area | 10,000 acres (40 km2) |
Green Lake is a natural lake in Calhoun County, Texas. It's located in the area where the Guadalupe River sometimes floods. The lake is famous for its greenish water, which is how it got its name.
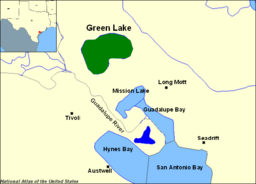
You can find Green Lake about 12 miles west of Port Lavaca and 22 miles south of Victoria. Even though it's less than 3 miles from the coast of San Antonio Bay, its water is fresh. Green Lake is the biggest natural freshwater lake completely inside Texas. It covers an area of about 10,000 acres (40 square kilometers).
About 2,200 years ago, the Guadalupe River delta separated the lake from San Antonio Bay. This created a wetland area perfect for many types of water birds. Old discoveries show that the Karankawa people used to live near the lake.
In the 1800s, a rich farming community called Green Lake grew near the lake. But after the American Civil War, it became very small. The lake was important during the war because it had fresh water and was close to the Gulf of Mexico. After a tough time during the Great Depression, the community grew a little in 1947 when oil was found nearby. A made-up lake with a similar name and story is in the 1998 book Holes.
Contents
About Green Lake's Water
Green Lake is about 13 miles around and 2 miles wide. The water is shallower near the edges. It gets deepest in the middle, a few hundred feet from the shore. The bottom of the lake is mostly flat and is about 4 feet deep on average.
The nearby Guadalupe River often floods the area. This flooding is the main way the lake gets new fresh water. The shoreline is naturally grassy and wet, with marshy areas between the lake and San Antonio Bay.
To help with drainage, a wall called a levee was built in 1969. This levee separated the lake from the Victoria Barge Canal. The canal runs along the north and east sides of the bay. It also cut off some small waterways from the lake. The canal starts north of Victoria and flows into San Antonio Bay near Seadrift. Hog Bayou flows along the west side of Green Lake. It goes through the Guadalupe Delta Wildlife Management Area to the south before joining Mission Lake.
Green Lake's History
How Green Lake Formed
Green Lake first started as an inlet, or small arm, of San Antonio Bay. Around 2,500 years ago, the Guadalupe River changed its path and moved westward. As it moved, it dropped off silt (fine dirt), creating a delta that grew into San Antonio Bay.
About 2,200 years ago, this delta grew so much that it completely crossed the bay. This cut off the northern part, which then became Green Lake. Pottery and burial sites found in the area suggest that Karankawa Indians lived there when the lake formed. Shells from brackish water clams called Rangia cuneata were found north of the lake. This shows that the water was once a mix of fresh and salt water.
Early Settlements Near the Lake
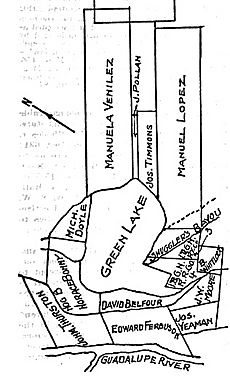
In the 1850s, rich cotton farmers from Kentucky moved to the fertile lands near Green Lake. They built plantations and started the town of Green Lake, Texas. People at the time described it as a place with "wealth and social standing of the residents."
After the American Civil War, many people who returned found that their slaves, farm animals, and equipment were gone. Most residents moved away. However, in the early 1900s, farmers came back. The town of Green Lake slowly grew to about 300 people by 1914. At that time, much of the land nearby was used for raising livestock.
The lake itself was used for transporting wood and for fishing. Between 1900 and 1915, about US$100,000 worth of fish were caught from the lake. Sometimes, the lake bed would dry out for long periods, and plants would grow in certain areas. Local people even started growing cotton in the dry lake bed.
In 1917, the state of Texas went to court to get the lake bed back. In a case called Welder v. State, the Texas Court of Civil Appeals in Austin said that Green Lake was a permanent lake and could be used for boats. This meant the lake bed belonged to the state. However, without permission from the Texas Attorney General, the Texas Land Commissioner sold the lake bed to a private buyer in 1918 for farming.
Later, in 1948, another court case, State v. Bryan, said that this sale was valid. But in 1967, a new law called the Texas Water Rights Adjudication Act said Green Lake was a public body of water. The Supreme Court of Texas agreed with this in 1988. They said it was a lake, not just a low area filled with rainwater.
During the Great Depression, the population of Green Lake dropped to just 25 people. It stayed low until oil was found nearby in 1947. Twenty oil wells were built at the Green Lake oilfield. By 2000, the population of Green Lake was 51, the same as in 1970 and 1990.
Green Lake During the Civil War
Green Lake played a part in the American Civil War. When Texas was thinking about leaving the United States, federal troops were stationed there. General David E. Twiggs, who led the federal troops, talked with Texas leaders about giving up federal property.
When the U.S. military found out about these talks, they decided to replace Twiggs. Texas saw this as a problem and began to take federal property by force. Twiggs agreed to surrender the property if his troops could leave Texas peacefully. They were allowed to leave, but only from the Texas coast.
Colonel Carlos Waite arrived and moved the troops near Green Lake. This was a good spot because they could wait for ships near a source of fresh water. While they were there, Fort Sumter was attacked, starting the war. Texas became worried about so many armed federal troops in the area. Since their nations were now at war, Texas decided the deal with Twiggs was off. They began capturing federal troops, forcing them to join the Confederacy or become prisoners of war. Some companies of troops elsewhere in the state tried to escape to Green Lake. Later in the war, several groups of soldiers camped by the lake and complained about mosquitos.
Plants and Animals of Green Lake
The area around Green Lake has forests with many types of trees. These include pecan, black willow, cedar, American elm, hackberry, and green ash.
To the south, the Guadalupe Delta Wildlife Management Area is a wetland. It's home to thousands of egrets and other birds. You can see birds like the brown pelican, reddish egret, white-faced ibis, wood stork, bald eagle, white-tailed hawk, peregrine falcon, and the whooping crane. American alligators also live in this area.
Redfish and trout used to be the main types of fish in the lake. But their numbers went down after a large wall was built. Now, a lot of silt (fine dirt) from the Guadalupe River settles in the lake. This happens because a freshwater channel was dug to supply farmers and a plant in Seadrift. This channel has harmed the delta ecosystem by reducing the nutrients the river brings to the area.