Guayana Esequiba facts for kids
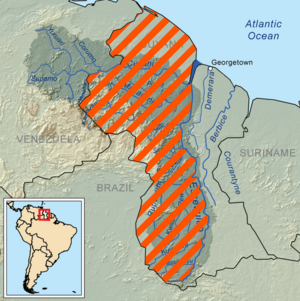
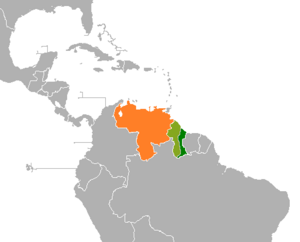
Guayana Esequiba, also known as Esequibo, is a large area of land in South America. It covers about 159,500 square kilometers (about 61,583 square miles). This territory is located west of the Essequibo River.
Currently, Guyana manages and controls this land. However, Venezuela also claims it as its own. This disagreement over the border started a long time ago, when both countries were colonies. Venezuela was a colony of Spain, while Guyana was a colony of the Netherlands and later the United Kingdom. The dispute became more complex when Guyana became independent from the United Kingdom in 1966.
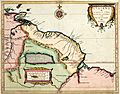
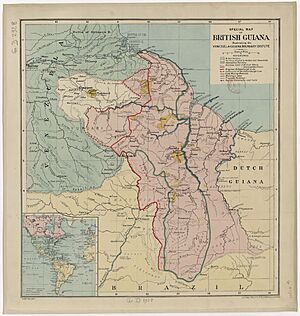
In 1840, the British government asked an explorer named Robert Hermann Schomburgk to map the borders of British Guiana. His map created what became known as the "Schomburgk Line." This line extended far beyond where the British actually lived, giving British Guiana control of the area near the mouth of the Orinoco River. Venezuela did not agree with these borders.
Tensions grew worse after gold was found in the region in 1876. This led Venezuela to end its diplomatic relationship with the United Kingdom in 1887. To solve the problem, the United Kingdom and Venezuela agreed to let a group of experts decide the border. The United States helped with this process. In 1899, the group made a decision called the Paris Arbitral Award. This decision mostly favored Britain.
Later, in 1949, a document written by Severo Mallet-Prevost was published after he had passed away. He was a secretary for the US-Venezuela team during the 1899 decision. His document said that the decision was influenced by the president of the group, Friedrich Martens, and a political deal between Russia and Britain. Because of this document, Venezuela complained to the United Nations in 1962. This led to the Geneva Agreement, signed with the United Kingdom in 1966.
The Geneva Agreement was signed by the United Kingdom, Venezuela, and British Guiana on February 17, 1966. This agreement states that all sides must find a peaceful and fair solution to the dispute. If they cannot agree, the decision on how to solve it will go to an "appropriate international organ" or, if they still can't agree, to the Secretary-General of the United Nations. The Secretary-General sent the entire issue to the International Court of Justice (ICJ). On December 18, 2020, the ICJ agreed to hear the case submitted by Guyana to settle the dispute.
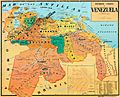
Today, Venezuela claims all the land west of the Essequibo River. They call this area Zona en Reclamación, which means "Zone in Reclamation." Historically, this claim did not include the areas near the Amazon River or the Pirara area. These parts were given to British Guiana in 1904 after a decision involving Brazil. The northwestern border of Guayana Esequiba follows the 1905 border set by the British-Venezuelan Mixed Boundary Commission, based on the 1899 decision. Venezuela now wants to change these legal borders and only accepts the Essequibo River as the boundary.
Guyana divides the territory into six administrative regions: Barima-Waini, Cuyuni-Mazaruni, Pomeroon-Supenaam, Potaro-Siparuni, Upper Takutu-Upper Essequibo, and Essequibo Islands-West Demerara. On maps, Venezuela often shows this area with stripes to mark it as disputed.
Population of the Claimed Regions
| Region of Guyana | Population (2012) |
|---|---|
| Barima-Waini | 26,941 |
| Cuyuni-Mazaruni | 20,280 |
| Pomeroon-Supenaam | 46,810 |
| Potaro-Siparuni | 10,190 |
| Upper Takutu-Upper Essequibo | 24,212 |
| Essequibo Islands-West Demerara | 107,416 |
| Total population of claimed regions | 235,849 |
Venezuelan Referendum
On October 31, 2023, the government of Guyana asked the ICJ for help. They wanted the court to stop a proposed vote in Venezuela. This vote was approved by Venezuela's National Electoral Council on October 23, 2023. The vote was about making Guayana Esequiba the 24th state of Venezuela. Guyana argued that this vote was a way for Venezuela to stop talking about a peaceful solution.
Many international groups spoke out against the proposed vote. The Commonwealth of Nations and the Caribbean Community (CARICOM) both supported Guyana. They also supported the ICJ process for solving the dispute. Because of the rising tensions, the Brazilian military increased its defenses along its northern border on November 29, 2023. On December 1, 2023, the ICJ ordered Venezuela not to try and change the territory currently controlled by Guyana until the court makes a final decision.
On December 3, Venezuelans reportedly voted to support their government's position in the dispute. The National Electoral Council first reported that 95% of voters approved of each question.
Images for kids
-
A 1625 map by Hessel Gerritsz, showing Dutch territory (in yellow) from the Orinoco River to the Amazon River.
-
A Punch cartoon after the border decision.
See also
 In Spanish: Guayana Esequiba para niños
In Spanish: Guayana Esequiba para niños
- Belizean–Guatemalan territorial dispute
- Borders of Venezuela
- Essequibo (colony)
- Gran Colombia
- Guayana Region
- Guyana–Venezuela relations
- South American territorial disputes
 | Stephanie Wilson |
 | Charles Bolden |
 | Ronald McNair |
 | Frederick D. Gregory |