Southern red muntjac facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Southern red muntjac |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Adult female and offspring (Muntiacus muntjak), in Malaysia, September 2012 | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Artiodactyla |
| Family: | Cervidae |
| Subfamily: | Cervinae |
| Genus: | Muntiacus |
| Species: |
M. muntjak
|
| Binomial name | |
| Muntiacus muntjak (Zimmermann, 1780)
|
|
 |
|
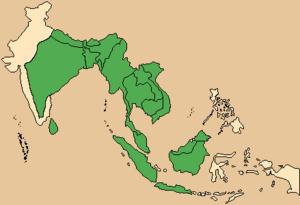
| Range of the northern red muntjac (M. vaginalis) and the southern red muntjac (M. muntjak) | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The southern red muntjac (Muntiacus muntjak) is a type of deer that lives in Southeast Asia. People used to call it the Indian muntjac or common muntjac. But scientists recently changed its name to focus on the muntjacs found in places like Sunda and Malaysia. Other similar deer are now called the Northern red muntjac.
Muntjacs are also known as barking deer because of the sounds they make. This deer is listed as Least Concern by the IUCN Red List. This means it is not currently in danger of disappearing.
This muntjac has soft, short fur that can be brownish or grayish. It sometimes has creamy marks. It is one of the smallest deer in the world. The southern red muntjac eats many different things, like grass, fruit, young plant shoots, and seeds. It also eats bird eggs and small animals. Sometimes, it even eats dead animals.
Male muntjacs have small antlers that usually branch only once. They also have long canine teeth and a special scent gland near their eyes. They use this gland to mark their areas.
Contents
What is a Southern Red Muntjac?
The southern red muntjac has a soft, thick coat of fur. This fur is even thicker in colder places. Its face is darker, and its legs are dark to reddish-brown. The color of its fur can change with the seasons, from dark brown to yellowish or grayish brown. Its belly is white.
Male muntjacs have short antlers, about 10 centimeters (4 inches) long. These antlers grow from long stalks covered in hair above their eyes. Female muntjacs do not have antlers. Instead, they have tufts of fur and small bony bumps.
Males also have long, slightly curved upper canine teeth. These teeth can be 2 to 4 centimeters (0.8 to 1.6 inches) long. They use these teeth when fighting other males.
A muntjac's body can be 89 to 135 centimeters (35 to 53 inches) long. Its tail is about 13 to 23 centimeters (5 to 9 inches) long. They stand 40 to 65 centimeters (16 to 26 inches) tall at the shoulder. Adult muntjacs weigh between 13 and 35 kilograms (29 and 77 pounds). Males are usually bigger than females.
Muntjacs are special because they have large, clear scent glands on their faces, just in front of their eyes. They use these glands to mark their territory or to attract females. Males have bigger glands than females.
Where Do They Live?
The southern red muntjac is found in many parts of Southeast Asia. This includes the Malay Peninsula, Sumatra, Java, Bali, and Borneo. People also believe they live in parts of Thailand and Myanmar. They used to live in Singapore but are now gone from there.
These deer live on land in forests. They are quite tough and can adapt to changes in their home.
Different Types of Southern Red Muntjac
Scientists have studied different types, or subspecies, of muntjacs. Some of these were once thought to be southern red muntjacs but are now considered different species. For example, the Malabar red muntjak and the northern red muntjac are now seen as their own species.
The southern red muntjac species now includes types found in places like Belitung, Bangka Island, Sumatra, Java, Bali, Lombok, Malaysia, Borneo, Bintan Island, and Lingga Islands.
Behavior and Daily Life
The southern red muntjac is often called "barking deer" because it makes a sound like a dog's bark when it senses danger.
Adult muntjacs usually live alone. The only times they are not alone are during mating season or when a mother is with her young fawns. Male muntjacs keep their distance from each other. They mark their areas by rubbing their scent glands on grass and bushes. This helps other muntjacs know who owns the territory.
Males also scrape their hooves on the ground and rub tree bark with their teeth to leave scent marks. These marks tell other muntjacs if an area is taken. Males often fight over these territories, good food, and the chance to mate with females. They use their short antlers and sharp canine teeth in these fights. If a male cannot get his own territory, he is more likely to be caught by a predator.
During mating season, the rules about territories are relaxed. Males wander around looking for females.
Who Hunts the Muntjac?
Many animals hunt these deer. These predators include tigers, leopards, clouded leopards, pythons, crocodiles, dholes (wild dogs), Asiatic black bears, fishing cats, Asian golden cats, and golden jackals. Younger muntjacs (fawns) can be hunted by foxes, raptors (like eagles), and wild boars.
Muntjacs are very alert. When they feel stressed or sense a predator, they start making their barking sound. This barking was once thought to be a way for them to talk to each other during mating season, as well as a warning signal.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
Southern red muntjacs are polygamous animals, meaning one male mates with several females. Females can start having babies when they are one to two years old. They can have babies throughout the year. Each cycle lasts about 14 to 21 days, and they are ready to mate for about 2 days during that time.
The mother carries her baby for 6 to 7 months. Usually, she has one baby at a time, but sometimes she has twins. Females often give birth in thick bushes or plants to hide their young from other deer and predators. The young muntjac stays with its mother for about 6 months. After that, it leaves to find its own territory.
Males often fight each other to control a group of females. Unlike some other deer, southern red muntjacs do not have a specific breeding season. They can reproduce any time of the year.
Evolution and Genetics
Scientists have found old bones that show southern red muntjacs have been around for at least 12,000 years. This was during the late Pleistocene epoch.
Scientists are very interested in studying muntjacs because different types of muntjacs have a very wide range in the number of chromosomes they have. The female southern red muntjac has the lowest number of chromosomes recorded for any mammal, with only 6 chromosomes. Males have 7 chromosomes. For comparison, the similar Reeves's muntjac has 46 chromosomes!
Muntjacs are the oldest known members of the deer family. The very first deer-like animals had horns, not antlers. But the muntjac is the earliest known species to actually have antlers that they shed.
Threats to Muntjacs
Southern red muntjacs are hunted by people for fun, for their meat, and for their skin. This often happens near farms because the deer can damage crops and rip bark from trees.

Images for kids
 | Emma Amos |
 | Edward Mitchell Bannister |
 | Larry D. Alexander |
 | Ernie Barnes |







