Korea under Japanese rule facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Japanese Korea
|
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1910–1945 | |||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
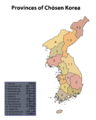
Korea (dark red) within the Empire of Japan (light red) at its furthest extent
|
|||||||||||
| Status | Colony of the Empire of Japan |
||||||||||
| Capital | |||||||||||
| Common languages | Japanese (official) Korean |
||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||
| Emperor | |||||||||||
|
• 1910–1912
|
Meiji | ||||||||||
|
• 1912–1926
|
Taishō | ||||||||||
|
• 1926–1945
|
Shōwa | ||||||||||
|
Governor-General
|
|||||||||||
|
• 1910–1916
|
Terauchi Masatake | ||||||||||
|
• 1916–1919
|
Hasegawa Yoshimichi | ||||||||||
|
• 1942–1944
|
Kuniaki Koiso | ||||||||||
|
• 1944–1945
|
Nobuyuki Abe | ||||||||||
| Historical era | Empire of Japan | ||||||||||
|
• Japanese protectorate
|
17 November 1905 | ||||||||||
|
• Annexation treaty signed
|
22 August 1910 | ||||||||||
|
• Annexation by Japan
|
29 August 1910 | ||||||||||
|
• March 1st Movement
|
1 March 1919 | ||||||||||
|
• Sōshi-kaimei order
|
1939 | ||||||||||
| 15 August 1945 | |||||||||||
| Currency | Korean yen | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| Today part of | North Korea South Korea |
||||||||||
From 1910 to 1945, the Empire of Japan took control of Korea. This time is known as Korea under Japanese rule or Japanese occupation. Before this, Joseon Korea was already influenced by Japan through a treaty signed in 1876.
Japanese leaders, military, and business people worked together to connect Korea's politics and economy with Japan. In 1905, the Korean Empire became a protectorate of Japan. This meant Japan ruled Korea indirectly. Then, in 1910, Japan officially took over Korea with the Japan–Korea Treaty of 1910. This happened without the agreement of the Korean Emperor Gojong or his son, Emperor Sunjong.
Japan made Korea a colony and set up a special government called the Governor-General of Chosen. This government, based in Keijō (now Seoul), had almost complete power over Korea.
Contents
Life Under Japanese Rule
During this period, Japan focused on making Korea more like Japan. They also continued to develop industries in Korea, which had started earlier.
Building New Infrastructure
The Japanese government built many public works projects. This included new railroads like the Gyeongbu Line and Gyeongui Line. They also improved major roads and ports. These changes helped the economy grow. Korea's economy grew by about 4.2% each year between 1912 and 1937.
Controlling Korean Culture
Japanese rule also tried to change Korean culture. They wanted to make Koreans adopt Japanese customs and language. This included efforts to make Koreans change their names to Japanese ones, known as Sōshi-kaimei.
Korean Independence Efforts
Many Koreans did not want to be ruled by Japan. They formed the Korean independence movement. One major event was the March 1st Movement in 1919. This was a large protest where Koreans demanded their freedom.
The End of Japanese Rule
Japanese rule over Korea ended on August 15, 1945. This happened when Japan surrendered at the end of World War II. After Japan's surrender, the armies of the United States and the Soviet Union moved into Korea.
Dividing Korea
The arrival of these two powers led to the division of Korea. The northern part of Korea was controlled by the Soviet Union, and the southern part was controlled by the United States. This created two different governments and economic systems.
Treaty on Basic Relations
In 1965, Japan and South Korea signed the Treaty on Basic Relations. This treaty stated that the earlier agreements between Japan and Korea, especially those from 1905 and 1910, were never truly valid.
Lasting Impact
Even today, the time of Japanese rule is a sensitive topic in both North Korea and South Korea. The effects of this period are still felt.
Some of the negative impacts include:
- Industrialization that mostly benefited Japan.
- The exploitation of Korean people, meaning they were used for Japan's benefit.
- Efforts to suppress Korean history and culture.
- The use of Korea's natural resources for Japan.
- The difficult situation of Koreans who cooperated with the Japanese, known as Chinilpa.
Images for kids
-
General power of attorney to Lee Wan-yong sealed and signed by the last emperor, Sunjong, on August 22, 1910.
-
A news article showing that Park Chung-hee submitted an oath of loyalty to Japan to join the Manchukuo Imperial Army in 1939.
-
Crown Prince Lieutenant General Yi Un, Prince Captain Yi Geon, and Captain Yi Wu in 1938.
-
Lieutenant Park Chung-hee, Manchukuo, 1944.
-
Korean volunteers in the Imperial Japanese Army, January 1943.
See also
 In Spanish: Ocupación japonesa de Corea para niños
In Spanish: Ocupación japonesa de Corea para niños
 | Bayard Rustin |
 | Jeannette Carter |
 | Jeremiah A. Brown |