List of the prehistoric life of Kansas facts for kids
Kansas is a state in the United States known for its wide-open spaces. But long, long ago, before humans walked the Earth, Kansas was home to many amazing prehistoric creatures! Scientists study fossils, which are the preserved remains or traces of ancient life, to learn about these incredible animals and plants. This article explores some of the fascinating prehistoric life that once lived in Kansas, from ancient sharks to giant mammoths.
Contents
Ancient Eras in Kansas
Scientists divide Earth's history into huge chunks of time called "eras." Each era had different types of plants and animals. Let's explore what Kansas was like in these ancient times.
Paleozoic Era: The Age of Ancient Life
The Paleozoic Era was a very long time ago, lasting from about 541 to 252 million years ago. During this era, Kansas was often covered by shallow seas, making it a perfect home for many marine creatures. Later, as the seas receded, land plants and early reptiles appeared.
Here are some of the cool creatures and plants from the Paleozoic Era found in Kansas:
- Ancient Fish and Sharks:
- †Acanthodes: This was a "spiny shark" that lived from the Early Devonian to the Permian period. It looked a bit like a modern shark but had spines.
-
- †Belantsea: A relative of modern-day Chimaeras (also called ghost sharks), this fish had a unique, flattened body.
-
- †Caseodus: Another ancient relative of chimaeras, Caseodus swam in the Carboniferous seas.
-
- †Ctenacanthus: This was a type of ancient shark. Fossils of its spines and teeth have been found.
-
- †Listracanthus: This cartilaginous fish, related to sharks, had strange, spine-like structures.
- Early Reptiles and Mammal Relatives:
- †Archaeovenator: This was one of the earliest known synapsids, which are animals that eventually led to mammals. It lived during the Carboniferous period.
-
- †Eocasea: Another very early synapsid, Eocasea was a small, lizard-like creature.
-
- †Ianthasaurus: This synapsid was a reptile-like animal that was an ancestor of mammals.
-
- †Ophiacodon: A larger synapsid that lived during the Carboniferous and Permian periods. It was a predator with a long snout.
-
- †Petrolacosaurus: This was one of the earliest known true reptiles, a small, lizard-like creature.
- †Spinoaequalis: An early reptile from the Carboniferous period.
- Invertebrates and Plants:
- †Aviculopecten: A type of ancient scallop, a shelled creature that lived in the sea.
- †Platyceras: This was a sea snail with a cone-shaped shell.
-
- †Calamites: A giant plant that looked like a huge horsetail, growing tall in ancient swamps.
- †Cordaites: An ancient tree with long, strap-like leaves, common in coal-forming forests.
- †Walchia: An early conifer tree, similar to modern pine trees.
Mesozoic Era: The Age of Dinosaurs
The Mesozoic Era, from about 252 to 66 million years ago, is famous for dinosaurs! While Kansas didn't have many land dinosaurs (it was mostly covered by a huge inland sea), it was home to incredible marine reptiles, flying reptiles, and ancient birds.
Here are some of the amazing creatures from the Mesozoic Era found in Kansas:
- Giant Marine Reptiles:
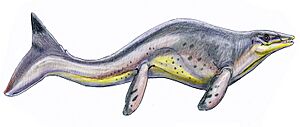
- †Brachauchenius: A massive plesiosaur, a type of marine reptile with a short neck and large head. It was a top predator in the ancient seas.
-
- †Dolichorhynchops: A fast-swimming plesiosaur with a long snout, perfect for catching fish.
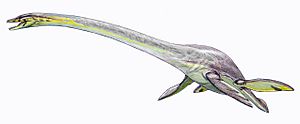
- †Elasmosaurus: This famous plesiosaur had an incredibly long neck, much longer than its body! It used its neck to ambush fish.
-
- †Megacephalosaurus: A large-headed plesiosaur, its skull alone could be over 6 feet long!
-
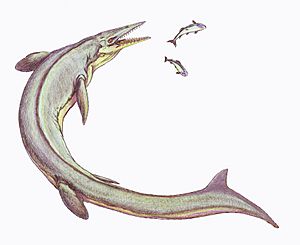
- †Platecarpus: A common mosasaur in the Kansas seas, known for its powerful tail and flippers.
-
- †Polycotylus: Another type of plesiosaur, known for its relatively short neck and powerful flippers.
-
- †Styxosaurus: A very large plesiosaur, similar to Elasmosaurus, with a long neck and small head.
-
- †Tylosaurus: One of the largest and most fearsome mosasaurs, Tylosaurus was a top predator, eating fish, sharks, and even other marine reptiles.
- Flying Reptiles and Toothed Birds:
- †Nyctosaurus: A type of pterosaur, or flying reptile, with a huge, antler-like crest on its head. It soared over the ancient seas.
-
- †Pteranodon: Another famous pterosaur, Pteranodon had a long, bony crest and a wingspan of up to 20 feet! It was a fish-eater.
-
- †Hesperornis: This was a large, flightless diving bird with teeth! It hunted fish in the ancient seas of Kansas.
-
- †Ichthyornis: A flying bird from the Late Cretaceous that also had teeth, showing how birds evolved from their reptile ancestors.
- Ancient Fish and Sharks:
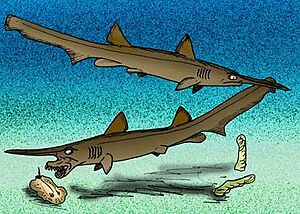
- †Cretoxyrhina: Also known as the "Ginsu shark," this was a large, powerful shark, similar to a great white shark.
-
- †Gillicus: A bony fish that was a common prey for larger marine predators.
-
- †Scapanorhynchus: A shark with a very long, pointed snout, similar to a modern goblin shark.
-
- †Squalicorax: Known as the "crow shark," this shark was a scavenger and predator, with serrated teeth.
- †Xiphactinus: A huge, predatory bony fish, sometimes called the "bulldog fish" because of its powerful jaws. It could grow up to 17 feet long!
- Other Marine Life:
- †Baculites: A type of ammonite, which were shelled creatures related to modern squids and octopuses. Baculites had a straight, uncoiled shell.
-
- †Inoceramus: A very large marine bivalve (like a clam) that could grow to enormous sizes.
-
- †Protostega: A giant sea turtle that swam in the Cretaceous seas.
- Land Animals:
- †Silvisaurus: This was a nodosaur, a type of armored dinosaur. It was one of the few land dinosaurs found in Kansas.
Cenozoic Era: The Age of Mammals
The Cenozoic Era, which began about 66 million years ago and continues today, is often called the "Age of Mammals." After the dinosaurs disappeared, mammals grew larger and became the dominant land animals. Kansas saw many different mammals, from giant sloths to saber-toothed cats.
Here are some of the fascinating creatures from the Cenozoic Era found in Kansas:
- Giant Mammals:
- †Amebelodon: An ancient elephant relative with unique, shovel-like lower tusks.
-
- †Bison latifrons: This was a giant bison, much larger than today's bison, with huge horns.
-
- †Camelops: An extinct type of camel that lived in North America.
-
- †Gomphotherium: Another elephant relative with four tusks (two upper and two lower).
-
- †Holmesina: A giant armadillo relative, much larger than modern armadillos.
-
- †Mammut americanum: The American mastodon, a large elephant-like animal with shaggy fur.
- †Mammuthus columbi: The Columbian mammoth, a huge elephant that roamed Kansas during the Ice Age.
-
- †Megalonyx: A giant ground sloth, as big as a bear, that walked on its knuckles.
- †Nothrotheriops: Another type of ground sloth, known for its shaggy fur and large claws.
-
- †Paramylodon: A large ground sloth that lived during the Pliocene and Pleistocene.

-
- †Platybelodon: An elephant relative with a very distinctive, flattened, shovel-like lower jaw.
-
- †Stegomastodon: Another elephant relative, common in North America during the Pliocene and Pleistocene.
-
- †Teleoceras: A short-legged, barrel-bodied rhinoceros that lived in Kansas. It was semi-aquatic, like a hippo.
- Ancient Horses and Dogs:
- †Aelurodon: A powerful, bone-crushing dog that lived during the Miocene.
-
- †Borophagus: Another type of bone-crushing dog, known for its very strong jaws.
- †Dinohippus: An ancient horse that was very similar to modern horses.
-
- †Equus simplicidens: Also known as the Hagerman horse, this was one of the earliest true horses in North America.

-
- †Hypohippus: A three-toed horse that lived in forests.
-
- †Leptocyon: One of the earliest ancestors of modern dogs and foxes.
-
- †Protohippus: An ancient horse with three toes, but the side toes were much smaller than the middle one.
- Saber-Toothed Cats:
- †Smilodon: The famous saber-toothed cat, known for its incredibly long, dagger-like canine teeth. It was a powerful predator during the Ice Age.
-
- †Homotherium: Another type of saber-toothed cat, sometimes called the "scimitar-toothed cat" because its teeth were shorter and more curved.
- Other Interesting Mammals:
- †Ceratogaulus: This was a unique "horned gopher," the only known rodent with horns!
-
- †Mylohyus: An extinct peccary, a pig-like animal, that lived in North America.
-
- †Ramoceros: An ancient pronghorn, a type of antelope-like animal unique to North America.
- Reptiles and Amphibians:
- †Chelydra serpentina: The common snapping turtle, which has been around for a very long time!
-
- †Lampropeltis getula: The eastern kingsnake, a non-venomous snake that eats other snakes.
-
- †Trachemys scripta: The pond slider, a common freshwater turtle.
- Modern Animals with Ancient Roots:
Many animals that live in Kansas today also have fossil records from the Cenozoic Era, showing that their ancestors lived here for millions of years. These include animals like:
-
- Bison (modern bison)
- Canis latrans (coyotes)
- Castor canadensis (beavers)
- Cynomys ludovicianus (prairie dogs)
- Lontra canadensis (river otters)
- Mephitis mephitis (striped skunks)
- Puma concolor (mountain lions)
- Taxidea taxus (badgers)
- Vulpes velox (swift foxes)
Kansas has a rich fossil history, showing how life on Earth has changed dramatically over millions of years!
 | Kyle Baker |
 | Joseph Yoakum |
 | Laura Wheeler Waring |
 | Henry Ossawa Tanner |