Metallurgy facts for kids
Metallurgy is the exciting study of metals. It also looks at alloys, which are special mixtures of different metals. People who learn about or work with metals are called metallurgists. They figure out how to get metals from rocks, make them into useful shapes, and understand how they behave.
Contents
Getting Metals from Rocks
Metals are often found inside rocks called ores. These ores usually contain a metal combined with oxygen, forming something called an oxide. Imagine a metal stuck to oxygen!
What is Smelting?
The first big step in metallurgy is called smelting. This is how we separate the pure metal from the oxygen and other stuff in the ore. Smelting often uses chemistry or electricity. It usually needs very, very high temperatures to work.
How Iron is Made
Iron is a very common metal. It is smelted from iron ore in huge structures called blast furnaces. A blast furnace is a tall, upright oven. Inside, it gets fed with iron ore, coke (a type of coal), and limestone.
Hot air is blown into the furnace. The coke burns and helps remove the oxygen from the iron ore. This creates pure iron and carbon dioxide gas. The limestone helps collect any leftover rock material, forming a waste product called slag. The iron melts and flows out as a liquid at the bottom. This liquid iron is then often turned into steel. Slag can be used to make things like bricks or concrete.
How Aluminum is Made
Aluminum is another important metal. It is smelted in special electric ovens called electric arc furnaces. Aluminum ore is placed at the bottom of the furnace. A strong electric current passes through the ore. This makes the temperature rise so high that the oxygen separates. What's left is shiny, metallic aluminum.
How Copper is Made
Copper can be made in a few ways. Sometimes, raw copper ore is heated over a flame. This burns off sulfur and other unwanted parts, leaving behind rough copper.
Another way to get very pure copper is through electrolysis. This method uses electricity. Large pools are filled with a water solution called an electrolyte. An electric current is sent through the pool. All the copper in the solution then gathers on a special metal plate called a cathode.
Making Metal Parts
Another big part of metallurgy is making useful items from metals. These items, or "parts," must be made carefully. They need to be strong enough not to break when they are used. Metallurgists work hard to make sure the metal is perfect for its job.
Sometimes a metal part needs to be super strong. Other times, it needs to be tough, meaning it won't break easily. Choosing the right metal is important. For example, steel is cheap, but it can rust. Metallurgists follow specific plans to pick the best metal for each part.
Shaping Metal Parts
Metal often starts as a solid block called an ingot. Metallurgists know many ways to turn an ingot into a useful part.
- Forging: One way is by hitting the metal with a very big hammer. This process is called forging.
- Rolling: To make thin sheets of metal, the ingot is passed between two large rollers. This is called rolling.
Making metal hot makes it softer and easier to shape. That's why many metal parts are made using hot metal. This is known as hot work.
Joining Metal Parts
Two metal parts can also be joined together using a lot of heat. This process is called welding. Iron is a metal that is quite easy to weld.
Testing Metals
Metallurgists use many tools to understand metals better. This helps them decide how to work with the metal.
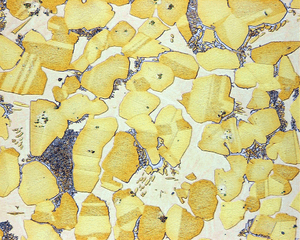
Using a Microscope
The microscope is one of the most helpful tools. It lets metallurgists see the tiny structures inside the metal. This gives them clues about how the metal will behave.
The Tension Test
Sometimes, metals are pulled until they break. This is called the tension test. This test provides important information about how strong and flexible the metal is.
Images for kids
-
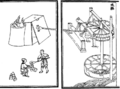
Furnace bellows operated by waterwheels, Yuan Dynasty, China.
See also
 In Spanish: Metalurgia para niños
In Spanish: Metalurgia para niños
 | Dorothy Vaughan |
 | Charles Henry Turner |
 | Hildrus Poindexter |
 | Henry Cecil McBay |