Eskimo Nebula facts for kids
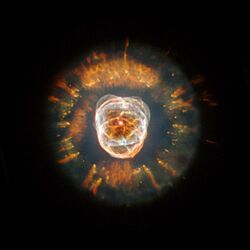
The Eskimo Nebula (also known as NGC 2392) is a beautiful cloud of gas and dust in space. It has other fun names like the Clown Face Nebula or the Lion Nebula. This amazing object is a type of planetary nebula.
It looks like a person's head wearing a warm parka hood. This nebula is made from the outer layers of a star similar to our Sun. These layers were gently pushed away into space.
The Eskimo Nebula is about 6,500 light-years away from Earth. You can see it with a small telescope in the Gemini constellation.
| Emission nebula | |
|---|---|
| Planetary nebula | |
|
|
| Observation data: J2000 epoch | |
| Right ascension | 07h 29m 10.7669s |
| Declination | +20° 54′ 42.488″ |
| Distance | 6520±560 ly |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 10.1 |
| Apparent dimensions (V) | 48; × 48; |
| Constellation | Gemini |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Radius | ≥0.34 ly ly |
| Absolute magnitude (V) | ≤0.4 |
| Notable features | – |
| Designations | NGC 2392, Caldwell 39, PN G197.8+17.3 Central Star: HIP 36369, HD 59088, TYC 1372-1287-1 |
Contents
Exploring the Eskimo Nebula
What is a Planetary Nebula?
A planetary nebula is not actually a planet. It is a cloud of gas and plasma. This cloud forms when a star like our Sun reaches the end of its life. The star sheds its outer layers into space. These layers then glow brightly.
The Eskimo Nebula is a special kind called a "double-shell" nebula. This means it has two main layers of gas. The inner part has bright, thin streams of gas. These streams are pushed out by a strong flow of particles from the star at its center.
The outer part of the nebula is a large disk. It contains long, unusual streams of gas. These streams can stretch for a light-year or more.
The Star at its Heart
Right in the middle of the Eskimo Nebula is a very hot, bright star. This star is known as HD 59088. It is an O-type star, which means it is much hotter and bigger than our Sun.
This central star is what makes the surrounding gas glow. It sends out powerful energy. This energy causes the gas to light up in vibrant colors.
A Look Back in Time: Discovery and Events
How it was Found
The Eskimo Nebula was first seen by the famous astronomer William Herschel. He discovered it on January 17, 1787. He was observing the sky from Slough, England.
Herschel described it as "A star 9th magnitude with a pretty bright middle, nebulosity equally dispersed all around. A very remarkable phenomenon." This means he saw a star surrounded by a glowing cloud. Today, NGC 2392 is part of the Herschel 400 observing program. This program helps amateur astronomers find interesting objects.
Moon's Shadow Play
On January 9, 1982, something special happened. The Moon passed in front of the Eskimo Nebula. This event is called an occultation. It happened during a Total Lunar Eclipse over parts of the world.
People in Greenland, the Arctic, and northern Europe could have seen this. Observers in England also witnessed the event. Another similar event is predicted to occur during the January 2066 lunar eclipse. This future event is expected over parts of Asia and the Northwest Pacific.
See also
- List of planetary nebulae
- New General Catalogue
 | Lonnie Johnson |
 | Granville Woods |
 | Lewis Howard Latimer |
 | James West |

