Orders of magnitude (area) facts for kids
Have you ever wondered how big things really are? From tiny cells to huge planets, everything has an area. Area tells us how much flat space something covers. This page will help you understand different sizes of areas, from super small to incredibly huge, using a special system called "orders of magnitude." It's like counting in powers of 10!
Contents
Tiny Areas: Smaller than a Millimetre
Let's start with areas that are too small to see without a microscope. These are measured in units like square nanometres (nm²) and square micrometres (µm²).
| Size (in square metres) | Example |
|---|---|
| 10−18 m² (1 square nanometre) | This is about the size of a single molecule! |
| 10−16 m² (100 nm²) | The surface of a typical protein, which is a tiny building block inside living things. |
| 10−12 m² (1 square micrometre) | The surface area of a tiny E. coli bacterium. |
| 10−10 m² (100 µm²) | The surface area of a red blood cell, which carries oxygen in your body. |
| 10−9 m² (1,000 µm²) | The size of a single pixel on an LCD screen. |
Small Areas: From Millimetres to Decimetres
Now, let's look at things you can see and touch, like a coin or a piece of paper.
| Size (in square metres) | Example |
|---|---|
| 10−6 m² (1 square millimetre) | The area of the head of a pin. |
| 10−5 m² (10 mm²) | The area of a small hole made by a hole punch. |
| 10−4 m² (1 square centimetre) | The area of one side of a U.S. penny. |
| 10−3 m² (10 cm²) | The area of a human retina (the back of your eye that sees light). |
| 10−2 m² (1 square decimetre) | The size of a small index card (3 × 5 inches). |
| 10−1 m² (10 dm²) | The size of a basketball's surface. |
Medium Areas: From Square Metres to Square Kilometres
These are sizes we deal with every day, like rooms, fields, and small towns.
| Size (in square metres) | Example |
|---|---|
| 100 m² (1 square metre) | The size of a large piece of paper (A0 size). This is also about the area of the top of an office desk. |
| 101 m² (10 square metres) | The size of a typical parking space. |
| 102 m² (100 square metres) | This is called one are. It's about the size of a volleyball court. |
| 103 m² (1,000 square metres) | The size of an Olympic-size swimming pool's water surface. |
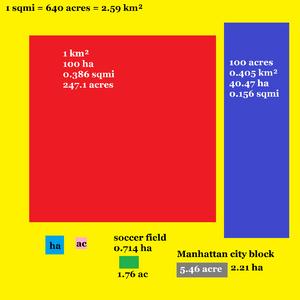
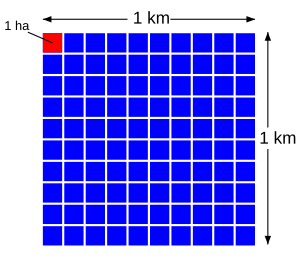
| 104 m² (10,000 square metres) | This is called one hectare (ha). It's about the size of a Manhattan city block. |
| 105 m² (100,000 square metres) | The size of Vatican City, the smallest country in the world. |
| 106 m² (1 square kilometre) | The size of Monaco, another very small country. It's also about 1 square mile. |
Large Areas: Cities, Countries, and Continents
Now we're talking about really big areas, like cities, countries, and even whole continents!
| Size (in square metres) | Example |
|---|---|
| 108 m² (100 square kilometres) | The land area of Paris, France (the inner city). |
| 109 m² (1,000 square kilometres) | The size of Hong Kong. |
| 1010 m² (10,000 square kilometres) | The size of Jamaica, an island country. |
| 1011 m² (100,000 square kilometres) | The size of South Korea. |
| 1012 m² (1 million square kilometres) | This is 1 square megametre. It's about the size of Egypt. |
| 1013 m² (10 million square kilometres) | The size of Canada, one of the largest countries in the world. It's also the size of Antarctica. |
| 1014 m² (100 million square kilometres) | The total land area of Earth! |
Huge Areas: Planets and Beyond
These are truly enormous areas, like the surfaces of planets, or even the vast spaces that planets travel through as they orbit the Sun.
| Size (in square metres) | Example |
|---|---|
| 1015 m² (1 billion square kilometres) | The surface area of Neptune, one of the largest planets in our solar system. |
| 1016 m² (10 billion square kilometres) | The surface area of Jupiter, the biggest planet in our solar system. |
| 1018 m² (1,000 billion square kilometres) | This is 1 square gigametre. It's the surface area of our Sun! |
| 1022 m² (10,000,000 billion square kilometres) | The area that Earth sweeps out as it orbits the Sun. |
| 1024 m² (1,000,000,000 billion square kilometres) | This is 1 square terametre. It's the surface area of a red supergiant star like Betelgeuse, which is much bigger than our Sun. |
| 1025 m² (10,000,000,000 billion square kilometres) | The surface area of a hypergiant star like VY Canis Majoris, one of the largest known stars! |
| 1041 m² | Roughly the area of the Milky Way galaxy's disk, where our solar system lives. |
| 1054 m² | The surface area of the entire observable universe! That's everything we can see from Earth. |
See also
 In Spanish: Anexo:Órdenes de magnitud (superficie) para niños
In Spanish: Anexo:Órdenes de magnitud (superficie) para niños
- Orders of magnitude
- List of political and geographic subdivisions by total area

