Peace of Westphalia facts for kids
| Treaties of Osnabrück and Münster | |
|---|---|

The Ratification of the Treaty of Münster, 15 May 1648 (1648) by Gerard ter Borch
|
|
| Type | Peace treaty |
| Drafted | 1646–1648 |
| Signed | 15 May – 24 October 1648 |
| Location | Osnabrück and Münster, Westphalia, Holy Roman Empire |
| Parties | 109 |
The Peace of Westphalia refers to two important treaties. These were the Treaty of Osnabrück and the Treaty of Münster. They were signed on May 15 and October 24 in 1648. These treaties officially ended two major conflicts: the Thirty Years' War and the Eighty Years' War.
Many powerful groups were involved in these treaties. These included the Holy Roman Emperor, Ferdinand III from the House of Habsburg, and other German princes. Also involved were Spain, France, Sweden, and representatives from the Dutch Republic. Another treaty, the Treaty of the Pyrenees, was signed in 1659. It ended the war between France and Spain and is often seen as part of this larger peace agreement.
Contents
Where the Peace Talks Happened
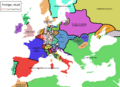
The discussions for peace took place in two cities: Münster and Osnabrück. These cities are about 50 kilometers (31 miles) apart. Today, they are in the German states of North Rhine-Westphalia and Lower Saxony.
Sweden preferred Osnabrück because it had a Protestant background. France chose Münster because it was a Catholic city. Two locations were needed because Protestant and Catholic leaders did not want to meet in the same place. The Catholics used Münster, while the Protestants used Osnabrück for their meetings.
What Changed After the Treaties
The Peace of Westphalia brought many important changes to Europe.
New Independence for the Dutch
One big result was that Spain finally accepted the independence of the Dutch Republic. This meant the Dutch were now their own country, ending the Eighty Years' War.
Power Changes in the Holy Roman Empire
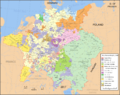
Before the treaties, Ferdinand III, the Holy Roman Emperor, had gained a lot of power. The Peace of Westphalia took some of this power away from him. This meant that the rulers of the different German states within the Holy Roman Empire could once again decide the religion for their own lands.
- Everyone agreed to recognize the Peace of Augsburg from 1555. This agreement said that each prince could choose the official religion for his state. The choices were Catholicism, Lutheranism, and now, for the first time, Calvinism.
- Christians who lived in an area where their religion was not the official one were given important rights. They were allowed to practice their faith in public during certain hours and in private whenever they wished.
Land Changes
There were also some changes to who controlled certain areas of land across Europe.
Related Pages
Images for kids
-
The reverse of this medal: Christina of Sweden as Minerva holding an olive branch in her left arm and grasping the tree of knowledge with her right hand.
See also
 In Spanish: Paz de Westfalia para niños
In Spanish: Paz de Westfalia para niños
 | Anna J. Cooper |
 | Mary McLeod Bethune |
 | Lillie Mae Bradford |