Photosynthesis facts for kids
Photosynthesis is a super important process that plants and some tiny living things (microorganisms) use to make their own food, like sugars. The word "photosynthesis" comes from two old Greek words: "photo," which means light, and "synthesis," which means putting things together. So, it literally means "putting together with light"!
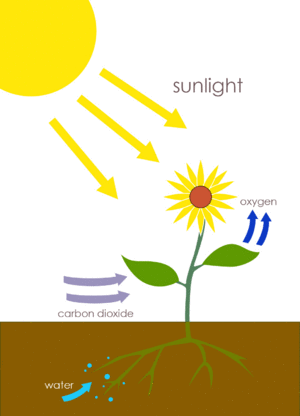
This process uses sunlight to change carbon dioxide and water into sugars. These sugars are like fuel for the plant's cells, giving them energy to grow and build other important parts. Photosynthesis is vital for almost all life on Earth. Green plants, algae, some protists, and certain bacteria all use it. Without it, we wouldn't have the food we eat or the air we breathe!
Here's the basic recipe for photosynthesis:
- 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 + 6 O2
- This means: carbon dioxide + water + light energy → glucose (a type of sugar) + oxygen
Carbon dioxide enters the plant's leaves through tiny holes called stomata. Water is soaked up from the soil by the plant's roots, which have special "hairs" to absorb more water.
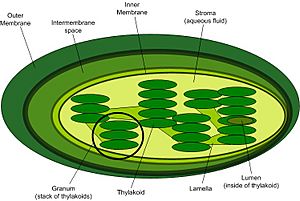
Photosynthesis happens inside tiny green parts in plant cells called chloroplasts. These chloroplasts are full of a green stuff called chlorophyll. Chlorophyll is amazing because it's what captures the light energy from the sun. In leaves, special cells called palisade cells have lots of chloroplasts to catch as much light as possible.
A cool thing about photosynthesis is that oxygen is made as a leftover product. This oxygen then leaves the plant and goes into the air. Almost all the oxygen in our atmosphere comes from plants and other photosynthetic organisms!
The glucose (sugar) that plants make is used for energy. Plants can also store this sugar as starch for later, especially when it's dark and they can't do photosynthesis. Glucose can also be changed into other things the plant needs to grow and reproduce, like cellulose (for strong cell walls), nectar, and fats.
Contents
How Photosynthesis Works
Photosynthesis happens in two main steps or "reactions." One step needs light to work, and the other doesn't directly need light, but it uses the energy made in the first step.
Light-Dependent Reactions
These reactions need light energy from the sun. When sunlight hits the chlorophyll in the chloroplasts, it helps to split water molecules. This process is called photolysis. When water splits, it creates oxygen, hydrogen, and tiny particles called electrons.
The hydrogen and energized electrons are then used to create special energy-carrying molecules called NADPH and ATP. Think of NADPH and ATP as tiny batteries that store energy. The oxygen gas that's made simply floats out of the plant as a waste product. All this happens in parts of the chloroplasts called grana.
Light-Independent Reactions (Dark Reaction)
This step doesn't need light directly, but it uses the energy stored in the ATP and NADPH molecules made during the light-dependent reactions. In this step, the plant takes carbon dioxide from the air. Using the ATP, NADPH, and other chemicals inside the chloroplasts, the plant builds glucose (sugar). This whole process is often called the Calvin cycle.
Once the glucose is made, it's moved all around the plant to wherever it's needed for energy or growth. So, even though this step doesn't need light, it can't happen without the energy from the light-dependent reactions!
What Affects Photosynthesis?
Just like baking a cake, you need the right ingredients and conditions for photosynthesis to work well. Three main things can affect how fast and how well plants make their food:
- Light intensity (how bright the light is)
- Carbon dioxide concentration (how much CO2 is in the air)
- Temperature
Light Intensity
If a plant doesn't get enough light, the light-dependent reactions will slow down. This means less ATP and NADPH (the energy batteries) will be made. With fewer energy batteries, the light-independent reactions won't be able to make much glucose. So, more light usually means faster photosynthesis, up to a certain point.
You can see this easily with a water plant like pondweed. If you put it under different light levels, you can count the oxygen bubbles it produces. More bubbles mean more photosynthesis!
Carbon Dioxide Levels
Carbon dioxide is a key ingredient for making glucose in the light-independent reactions. If there isn't enough carbon dioxide in the air around the plant, the plant won't be able to make much sugar, even if it has plenty of light and water. This will slow down the whole process.
Temperature
Photosynthesis relies on many special helpers called enzymes. Enzymes are like tiny workers that speed up chemical reactions. Just like us, enzymes work best at a certain temperature, called their "optimum temperature."
If it's too cold, the enzymes work very slowly, and photosynthesis slows down. If it gets too hot, the enzymes can get damaged (we say they "denature"), and then photosynthesis stops working almost completely. That's why greenhouses often control the temperature to help plants grow their best!
Early Life and Photosynthesis
The very first living things that could do photosynthesis probably appeared a very long time ago. They might have used different chemicals instead of water to get their electrons. Later, tiny organisms called Cyanobacteria evolved. They were special because they used water for photosynthesis, and this produced a lot of oxygen. This huge amount of oxygen changed Earth's atmosphere forever, making it possible for more complex life forms, like animals, to evolve!
Today, photosynthesis captures a massive amount of energy from the sun – way more than all the energy humans use! It also turns billions of tons of carbon into plant material every year, which is amazing.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
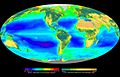
This picture shows where photosynthesis happens most around the world, both in the ocean (tiny phytoplankton) and on land (plants). Dark red and blue-green areas show lots of activity.
-
Jan Baptist van Helmont was an early scientist who did experiments related to plant growth.
-
Melvin Calvin was a scientist who helped discover the Calvin Cycle, the main part of the light-independent reactions.
-
The leaf is the main place where photosynthesis happens in plants.
See also
 In Spanish: Fotosíntesis para niños
In Spanish: Fotosíntesis para niños