Relative density facts for kids
Relative density, also called specific gravity, is a way to compare how "heavy" one material is compared to another. It's a ratio of their densities. Think of it as asking: "How much denser is this object than water (or air)?"
For solids and liquids, we almost always compare them to water. We use water at its densest point, which is around 4 °C or 39.2 °F (about 39°F). For gases, we usually compare them to air at room temperature (20 °C or 68 °F or 68°F).
If a substance has a relative density less than one, it means it's lighter than the reference material. For example, an ice cube has a relative density of about 0.91. Since this is less than 1 (the relative density of water), ice floats! If the relative density is greater than 1, the substance is denser and will sink. If it's exactly 1, then both materials have the same density. This means equal amounts of both substances would have the same weight.
Scientists and engineers need to be careful about temperature and pressure when measuring relative density. These conditions can change how dense a substance is. Pressure is usually measured at 1 atm (about 101.325 kPa), which is normal air pressure at sea level. Relative density is often used in industries to check the strength of solutions, like how much sugar is in syrup or how much salt is in brine.
How We Measure Relative Density
Measuring relative density means finding the density of a substance and then dividing it by the density of a reference material (like water). Density itself is simply the mass (how much "stuff" is in it) divided by its volume (how much space it takes up).
It's easy to measure mass, but finding the volume of an oddly shaped object can be tricky! One common way is to use a graduated cylinder filled with water. When you put the object in, the water level rises. The amount the water level goes up tells you the object's volume. Another way is to fill a container to the very top, put the object in, and collect the water that overflows. The volume of the overflowed water is the object's volume.
For any substance, its density, ρ, can be found using this idea: 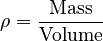 When we compare the densities to find relative density, many of the complex parts of the measurement cancel out, making it simpler to calculate.
When we compare the densities to find relative density, many of the complex parts of the measurement cancel out, making it simpler to calculate.
Examples of Relative Density
Here are some examples of relative density for different materials, compared to water:
| Material | Specific gravity |
|---|---|
| Balsa wood | 0.2 |
| Oak wood | 0.75 |
| Ethanol | 0.78 |
| Olive oil | 0.91 |
| Water | 1 |
| Ironwood | 1.5 |
| Graphite | 1.9–2.3 |
| Table salt | 2.17 |
| Aluminium | 2.7 |
| Cement | 3.15 |
| Iron | 7.87 |
| Copper | 8.96 |
| Lead | 11.35 |
| Mercury | 13.56 |
| Depleted uranium | 19.1 |
| Gold | 19.3 |
| Osmium | 22.59 |
(Keep in mind that these numbers are approximate and can vary slightly.)
- Did you know that Blood normally has a specific gravity of about 1.060? This means it's slightly denser than water.
Images for kids
-
A United States Navy Aviation boatswain's mate tests the specific gravity of JP-5 fuel.
See also
 In Spanish: Densidad relativa para niños
In Spanish: Densidad relativa para niños




